

Vol. 41 (Issue 12) Year 2020. Page 2
BAYTAEVA , Gulnara R. 1; AYAZHANOVA , Madina K. 2; ABDILDINOVA , Meruert N. 3; SUBEBAEVA , Zhuldyz K. 4; DIGAY , Damir A. 5 & GUSSENOV , Barkhudar Sh. 6
Received: 23/12/2018 • Approved:27/03/2020 • Published 09/04/2020
ABSTRACT: The article discusses the features of the foreign economic potential of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Features of legal protection of subjects of foreign economic activity are designated. The structure of management of foreign economic activity is presented. The main methods of state-legal regulation and management of foreign economic activity are considered. The main directions of foreign economic activity of enterprises of the Republic of Kazakhstan are structured. The mechanism of state regulation of foreign economic activity is offered. |
RESUMEN: En el artículo se examinan las características de la capacidad económica externa de la República de Kazajstán. Se señalan las características de la protección jurídica de los sujetos de actividad económica externa. Se presenta la estructura de la gestión de la actividad económica externa. Se examinaron los principales métodos de reglamentación y gestión de la actividad económica externa. |
In connection with the diversification of foreign economic activity of the Republic of Kazakhstan has become relevant more complete coverage of the forms and methods of foreign operations, investment, loans, foreign exchange transactions, description of risks in foreign trade (foreign economic activity) and other issues of commercial operations abroad.
The statistical publications provide data on the relationship of Kazakhstan with the countries of near and far abroad, although these terms do not reflect the range of geographical boundaries, but rather the proximity of economic relations (Artemov, 2016).
Foreign economic activity of economic entities of the Republic of Kazakhstan is regulated by state bodies, ministries and departments, but the main subject of foreign economic relations is the enterprise itself (Bank, firm, company), which works directly with a foreign partner (Gussenov, 2018).
The implementation of certain types of commercial activities is carried out only on the basis of a license issued by the authorized state bodies. Commercial enterprises transfer of intellectual property is also carried out on the basis of a license agreement under which the rights of ownership and use of the property are transferred (Balabanov, 2015).
In addition to the reporting of enterprises of the Republic of Kazakhstan, it is necessary to study the reporting forms of foreign firms, from which you can get information about their activities, contacts and contractors, profitability, profitability, reliability, creditworthiness and other aspects (Bayanova, 2014).
In General, the National Bank of Kazakhstan prepares a balance of payments for the Republic of Kazakhstan, the indicators of which reflect the activities of all economic entities in the foreign economic market and disclose the international investment position of the country (Batizi, 2015).
Consideration of the role and importance of accounting in foreign economic activity gives an idea of the variety of forms of foreign commercial activity, in this connection, entrepreneurs need to consider these issues in accordance with existing international norms, rules and customs governing the activities of subjects of foreign economic relations and determine their goals (Fig.1) (Kurnickaya, 2018).
Figure 1
The structure of the objectives of state regulation of foreign economic activity in the Republic of Kazakhstan
(compiled by the authors on the basis of the studied material (Kurnickaya, Gussenov, 2018)
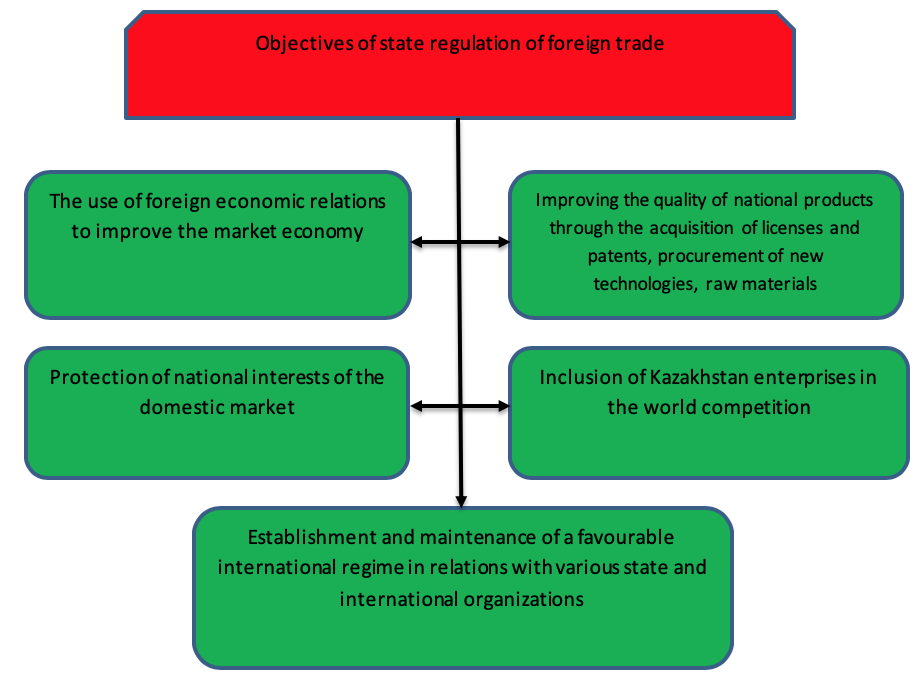
It is possible to allocate the main directions of foreign economic activity of the enterprises of the Republic of Kazakhstan:
● export-import operations (Kurnickaya, 2018);
● joint entrepreneurship in the fields of production, Finance, foreign trade, services;
● investment activity in the framework of attracting foreign investment in the economy;
● foreign currency transactions, etc.
Research into new markets should begin with a comprehensive study:
● potential capabilities of enterprises of a foreign state, their reporting and other indicators of activity in the domestic and foreign markets (Balabanov, 2015);
● problems arising as a result of insufficient preparation for commercial relations in foreign regions;
● full market research of goods, contractors, conditions, legislation, customs, habits of business circles of another country.
In his annual address to the people, President N. A. Nazarbayev noted: "the global system of the world economy is a well – established mechanism that works according to its own rules. According to these rules we have to work. We are not expected in the world markets, but we need to become popular and gain a foothold in them." To do this, it is necessary to create an innovative-oriented national economy, the level of openness of which should promote the attraction of new industrial and information technologies, the development of the country's export potential and the provision of personnel trained at the level of international standards, etc. This is facilitated by active and effective foreign economic activity (FEA) (Dyrka, Gussenov, 2018).
Each country has the right to choose and mutually beneficial cooperation with other States in all spheres of economy and politics. Foreign economic activity is implemented both at the state level and at the level of individual economic entities. In the first case, foreign economic activity is aimed at establishing interstate bases of cooperation, the creation of legal, trade and political mechanisms that stimulate the development and increase the efficiency of foreign economic relations. Rational foreign economic policy of the state can lead to an increase in the rate of growth of national income, accelerating scientific and technological progress, increasing the concentration of production and efficient use of capital investments, etc. For this purpose, it is necessary to take into account the following factors of development of foreign economic activity (Kushlin, 2016):
1. Uneven economic development of different countries of the world. Each country has its own structure of industries, different levels of development of industry, agriculture, transport, communications, services, its specialization in the economy.
Specialization of industrial or agricultural production gives a strong impetus to the development of foreign trade, which is very important for small territory and population in developed capitalist countries: the Netherlands, Norway, Belgium, Finland and others. These countries have a share of exports in the gross national product of about 50% and about the same share is imported (Dyrka, 2018).
2. The difference in human, raw materials, financial resources. Every year, 25 million people move around the world in search of work. There are countries with surplus labor resources: China, India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nigeria and others. And there are also regions: Western Europe, the United States, the middle East, South America, which need an influx of workers. Therefore, the movement of workers from country to country, regulated by the International labour organization, the process is objectively necessary, contributing to the development of foreign economic activity.
The establishment of foreign economic relations between States contributes to the ability of some countries of the world: Japan, Singapore, Hong Kong, Panama, Bahrain and others - to allocate funds for lending to firms, enterprises, banks located in different countries.
3. The nature of political relations. The presence of friendly political relations between the countries contributes to the strengthening of foreign economic activity. And, on the contrary, political confrontation sharply reduces foreign trade turnover, up to the rupture of economic ties (Gussenov, 2018).
4. Different level of scientific and technical development. The formation of foreign economic activity is facilitated by the exchange between the countries of students, trainees, researchers, teachers; joint research, experiments; participation in geological and archaeological expeditions; execution of contracts for design, research and design works.
5. Features of geographical location, natural and climatic conditions.
As a result of the state's influence on foreign economic activity, the following changes in the world economy will occur (Kushlin, 2016):
* further deepening of the international division of labour;
* economy of public work in countries actively engaged in foreign trade, joint entrepreneurship and participation in other forms of foreign economic relations;
* intense and efficient exchange of results of work;
* further strengthening of political, scientific, technical, cultural and other links;
* increasing the number of countries in the world creating a market economy;
* successful operation of transnational corporations and concerns;
* expanding the range of countries that have achieved full convertibility of their currencies.
Based on the above, we can determine the following main strategic objectives of foreign economic activity of Kazakhstan (Gussenov, 2015):
- continuation of the policy of liberalization of foreign economic activity in accordance with the interests of the country and ensuring its national security, improving the competitiveness and efficiency of foreign economic activity in terms of integration of the country into the world economy;
- development of export potential with emphasis on gradual diversification of the structure of exported goods, implementation of the policy of rational import substitution;
- support for the interests of domestic exporters in the availability of foreign markets for them.
The theoretical and methodological basis of the research consists of conceptual provisions, conclusions and recommendations presented and substantiated in fundamental and applied research of Kazakh, Tajik and other foreign scientists in the field of the theory of foreign economic activity development, as well as the works of leading Kazakh and foreign researchers in the field of the theory of strategic management. The methodological basis of the study is the economic system approaches to the study of the object of study using the methods of analysis, synthesis, induction, deduction, comparison, statistical groups, as well as regulations and Decrees of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The information base of the study was the statistical data of the Committee on statistics of the Ministry of national economy, the program of export development of the Republic for the period up to 2020, as well as reports of a number of enterprises participating in foreign economic activity. The materials placed on the sites of the global Internet network were also attracted.
In the process of the study were used General methods of research: methods of analysis of financial statements: horizontal, vertical, ratio, comparison, and other.
In modern conditions, all States, without exception, regulate their foreign economic policy through both the customs tariff and non-tariff restrictions.
United States of America. Regulation of foreign economic activity of the United States is carried out by the system of state bodies, the functions of which are listed in table 1.
Table 1
Functional characteristics of foreign trade management bodies in the United States
(compiled by the authors on the basis of the studied material (Gussenov, Dyrka 2018)
Authorized state body |
Functions in the field of foreign economic activity |
President of country |
sets tariffs, provides preferences, imposes embargoes on certain types of products |
Energy ministry |
Issuance of licenses for the import of petroleum products |
Ministry of the interior and Ministry of trade |
Licensing of duty-free importation of watches and clockworks from U.S. island territories |
Agriculture ministry |
Licensing of import of some agricultural goods |
Bureau of sport fishing and hunting of animals and birds of the Ministry of internal Affairs |
Permission to import dangerous species of wild animals and some species of animals and birds, the import of which is prohibited in the United States, |
Justice department |
Issuance of exceptional orders for the import of drugs |
Head of the Department of alcoholic beverages, tobacco and firearms of the Ministry of Finance. |
Authorization to import weapons, ammunition, explosives and weapons of war. |
Commerce department |
Evaluation of the fact that the product is offered in the us market at its market value |
In terms of absolute volumes of foreign trade turnover, the US is the largest trading power in the world. For example, in 2017, us exports amounted to 3287.4 billion. doll. During the same period, Russian exports amounted to 771.8 billion. doll. (WTO, international trade statistics, 2016-2017; CIA-world guide, 2017).
The main means of regulating U.S. imports is the imposition of customs duties on imports.
Great Britain. The government will give priority to the development of foreign trade and investment cooperation with foreign countries. The basis of the customs legislation of the UK is the Customs code of the European Union of 1992 (EU Directive No. 913/92 of 12 October 1992 establishing the Customs code of the European community). The UK foreign economic regulators and their functions are presented in table 2 (Gussenov, 2017).
Table 2
Functions of foreign economic management bodies in the United Kingdom
(compiled by the authors on the basis of the studied material (Gussenov, 2017, 2018)
Authorized state body |
Functions in the field of foreign economic activity |
Ministry of business, enterprise and state reform (DBERR) |
Authority to formulate and implement foreign economic policy in the UK, including administrative and organizational measures and regulatory functions to support domestic producers and exporters |
Royal service for taxes, duties and customs (HMRC). |
Collection of customs duties and protection of borders", including "protection of the British society from illegal import of medicines, alcoholic beverages, tobacco and tobacco products, "tax evasion"; application of tariff measures on behalf of and on behalf of authorized ministries; maintenance of HS; implementation of import and export control; collection of statistics on foreign trade. |
DBERR in the face of the Control import licensing (ImportLicensingBranch) - |
implementation of licensing policy in the UK. |
The Ministry for the environment, food and rural Affairs (Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs - DEFRA) |
responsible for the import of animal products, plants and plant products. |
Food standards Agency |
monitors the possible impact of food imports to the UK on the health of citizens. The Agency has special powers with regard to import policies for fishery, shellfish and non-animal food products. |
Royal service of taxes, duties and customs |
controls the movement of goods and vehicles across the UK-EU customs border and charges the appropriate fees; |
Ministry of environment, food and rural Affairs |
responsible for the export of animal and plant products as well as plants. |
British trade and investment service (UK Trade&Investment - UKTI). |
promotion of British goods and services to foreign markets; assistance to UK companies when they enter the foreign market; attraction of foreign investments. |
ECGD |
encouraging the promotion of British goods and investments in foreign markets through insurance against political and commercial risks of loans to domestic producers, as well as British foreign direct, portfolio and other types of investments provides financial guarantees for medium - and long-term loans, including the organization of financing of British exports on favorable terms. |
In the field of tariff regulation of imports, the basic document is the Integrated tariff of the United Kingdom (Integrated Tariff of the United Kingdom), which includes the Common customs tariff of the European Union, the system of statistical nomenclature, as well as the system of harmonized description and coding of goods developed within the framework of the customs cooperation Council. In the UK, the nomenclature of goods, customs duty rates and procedures similar to those adopted in the EU member States are applied. Goods from EU countries are imported duty-free, duties are applied when importing goods from outside the EU (Gussenov, 2018).
Japan. Let us consider some features of Japan's foreign economic activity. Active participation of the state in the organization and implementation of foreign economic activity (FEA) is a characteristic feature of Japan over the past four decades.
The effectiveness of the Japanese foreign economic complex largely depends on the strength of the institutional foundations of foreign economic activity. In the system of public administration in this area can be identified administration, coordination and Advisory.
Among the public administration occupies a special place the Ministry of foreign trade and industry (MFTI), MFTI provides the development of trade relations with foreign countries, addresses associated with external trade, foreign exchange issues, and promotes the production of export goods, establish quotas on import of licensed goods, issues permits for the import, specifies relevant trading rules (Nesterenko, 2013).
Consistency and coherence in the implementation of trade and economic policy is largely ensured through close inter-Agency coordination of government bodies. Among the interdepartmental coordination structures are the Trade Council, the Meeting of Ministers of economic Affairs, the Joint headquarters of the government and the ruling party for structural reforms. A feature of the Japanese system of public administration of foreign trade is the presence of a large number (more than 200) of Advisory bodies operating at different levels, up to the government and the Prime Minister.
The world's largest system of state trade and investment insurance contributes to the development of foreign economic activity. It includes General trade insurance, insurance of currency risks, export bills, export bonds, advance payments for imports, foreign investments, loans to foreign enterprises.
The Japanese system of foreign trade regulation differs in the form of interaction between the state and business. It is based on the adoption by the private sector of the most important strategic directions of public policy, a kind of “public mentality” of this sector. This model of regulation, which uses not only rigidly administrative measures and methods, but also complements their “soft" forms, can significantly improve the efficiency of public policy, organically combining it with the laws of the market.
China. The principles of China's foreign economic activity and their main content are in table 3.
Table 3
Principles of Chinese foreign trade
(compiled by the authors on the basis of the studied material (Sorkin, 2016; Dyrka, 2018)
Principle |
Content of the principle |
State control of foreign trade. |
The government and the Ministry of foreign trade manage the operations of sorting, licensing of imports and exports, inspection of foreign trade enterprises, control of foreign currency, restriction of export prices, protection of customs taxes, control and prohibition of smuggling |
Principle of equality and mutual benefit |
It is defined by the policy of peaceful coexistence, which means respect for the sovereignty and integrity of the territory, non-aggression, non-interference in internal politics, equal and mutually beneficial cooperation and coexistence. These principles are enshrined in the first Chinese Constitution. |
Self-orientation |
Creation of the integral economic system. At the same time, it is considered wrong to rely only on international assistance, as the other extreme - the policy of closed doors-is unacceptable. It assumes a balanced policy in the development of the economy with a focus on their own forces, along with the mandatory expansion of exports and imports. |
Basis of development of foreign trade activity-own production |
For foreign trade is important to own production to guarantee the supply of exports |
Unified planning and regulation of domestic and foreign trade. |
In the context of the weak development of production with a large population, it was decided to plan and regulate the supply to the domestic market and for export in order to ensure the priority of meeting the basic needs of its population and to guarantee priority supplies for foreign trade obligations. |
One of the main areas of China's foreign trade regulation after the country's accession to the WTO is the liberalization of the foreign trade regime. As of the beginning of 2017, China has already fulfilled most of its obligations to reduce duties.
In China, the state allows the free import and export of goods and technology unless otherwise provided by law or administrative regulations. Control over goods whose export or import is restricted is exercised in the form of quotas, licenses and other methods. Control in the form of licenses is also done in the area of technology, the export or import of which is restricted. Export and import of goods, technologies, which are subject to licensing, is carried out by the resolutions of the state Council, through the issuance of permits by the Department of the state Council, which is responsible for foreign trade, or this Department together with other relevant organizations in the state Council.
In recent years, China has reached a number of important bilateral and multilateral agreements. In particular, negotiations were held with a number of States on the recognition of the market status of the Chinese economy - currently 52 States have officially recognized the market status of the Chinese economy. Within the framework of the strategic task of creating a free trade zone around China, practical work is also being carried out on the implementation of agreements on the establishment of a free trade zone China-ASEAN (Association of South East Asian Nations), China-countries of the southern African development Community, China-countries of the Gulf cooperation Council, China-New Zealand, China-Chile, China-Australia, China-Pakistan. Practical work continued on the implementation of bilateral agreements and the establishment of free trade zones with Australia and New Zealand.
Thus, China is carrying out a comprehensive reform of the legal framework in the field of foreign trade to improve the welfare of the people of the country and the development of the economy of the state. Work is under way to expand the capacity of Chinese national industries and various enterprises in the world market, as well as to protect their interests in trade within the country and abroad.
In order to ensure the balance of socio-economic development of Kazakhstan on the basis of foreign economic relations, the state carries out: registration of participants of foreign economic activity; declares goods and other property moved across the state border; establishes the order of export and import.
One of the directions of the economic policy of the Republic of Kazakhstan in the market conditions is the liberalization of foreign economic activity in order to overcome the insolvency of the Republic, improve the position of Kazakhstan in the international division of labor, expanding markets for Kazakh goods (Naribaev, 2018).
The development of foreign economic relations requires accelerating the development of a list of investment projects with the appropriate feasibility study (FS) to attract foreign investors and creditors. It is necessary to develop bilateral agreements on mutual protection of investments with the main trade partners, at the same time to join the existing international agreements in this area.
As part of the analysis of foreign trade regulation experience, the experience of such developed countries as Japan and China is of great scientific and practical interest. Active participation of the state in the organization and implementation of foreign trade is a characteristic feature of the "land of the rising sun". The state is the main organizer, regulator and controller of foreign trade activities to ensure high efficiency through the development of science-based EEA, fully taking into account the interests and capabilities of the country at each stage of its development.
To date, in Kazakhstan, a well-developed mechanism should be the main control factor of foreign economic activity, ensuring its optimal organization, control and regulation (Fig.2).
Figure 2
The mechanism of state regulation of foreign economic activity of the Republic of Kazakhstan
(compiled by the authors on the basis of the studied material, (Ilimzhanova, Burnasheva, Gussenov, 2018)
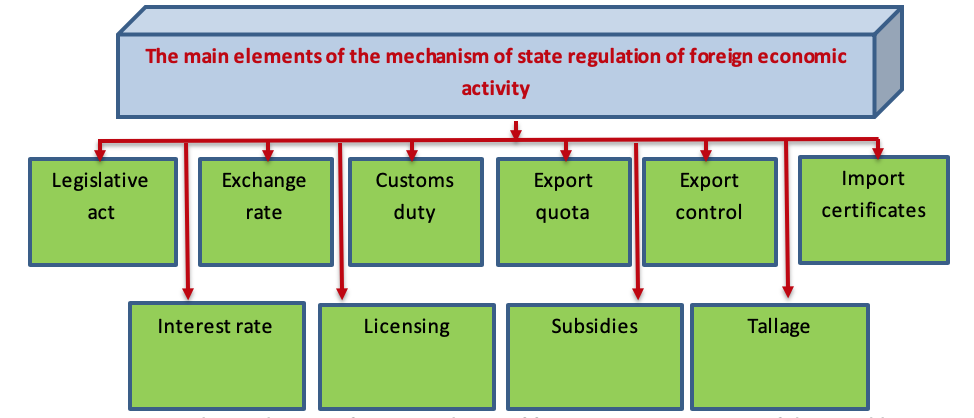
This situation was particularly relevant both in the context of the global financial and economic crisis and in the post-crisis period. At the same time, the state needs to use a wide range of tools and methods of foreign economic activity management to ensure its sufficient efficiency (NAZARBAYEV, 2018).
Along with the positive results of foreign economic relations, there are factors that constrain the development of foreign trade. These include: a low level of coordination of joint activities between similar state bodies of the partner countries, violation of terms and conditions of implementation of agreements and arrangements, and sometimes their non-implementation, inefficiency of control of state bodies of foreign trade processes and others.
In order to improve the state management of foreign economic activity, including its efficiency and effectiveness, the following economic processes should be constantly improved. These include: improvement of the country's foreign economic policy, improvement of the legal framework of foreign economic activity, modernization of institutional support for foreign economic activity regulation, development of information and analytical support of foreign economic activity, joint activities with other countries to protect against the negative effects of foreign economic crises and overcome their possible consequences. The promotion of the competitiveness of the national economy, taking into account the changed approaches to it in the context of globalization and regional integration, should be an integral component.
Further development of foreign economic activity of our country with various foreign partners, expansion of trade, economic, scientific and technical relations not only within the framework of existing regional and integration associations, but also in the bilateral format will also contribute to strengthening the stability of the national economy, modernization, acceleration of diversification and increase its competitiveness. This approach will allow us to consider foreign economic activity from the following positions:
1. The current state of foreign economic activity, as the main form of manifestation of the IER (international economic relations) within the state, is largely determined by the state of the national economy, its indicators and development factors. The external sector of the country should be aimed at solving urgent problems of the national economy, including the acceleration of modernization, increasing its competitiveness and others. At the same time, any stage of the economic process can become an object of foreign economic activity.
2. Today, the state should be the main manager of foreign economic activity, ensuring its optimal organization, control and regulation. This situation is particularly relevant both in the context of the global financial and economic crisis and in the post-crisis period. At the same time, the state needs to use a wide range of tools and methods of foreign economic activity management to ensure its sufficient efficiency.
3. At the present stage, the instrument of international treaties, the provisions of which have priority over the norms of national legislation in accordance with international law, remains the leading, basic mechanism of development and state management of foreign economic activity (Gussenov, 2018).
4. The results of foreign economic relations, there are factors that constrain the development of foreign trade. These include: a low level of coordination of joint activities between similar state bodies of the partner countries, violation of terms and conditions of implementation of agreements and arrangements, and sometimes their non-implementation, inefficiency of control of state bodies of foreign trade processes and others. Economic cooperation of Kazakhstan in the regional format is carried out in various fields. This process is pragmatic, integration-oriented and aimed at ensuring full multilateral cooperation. The development of foreign trade of Kazakhstan in this format should be considered from the standpoint of deepening the integration processes, strengthening the role of Kazakhstan in regional cooperation and promoting sustainability, growth and competitiveness of the economy of our state.
The system of foreign economic activity should be considered as a process management system, as the establishment and development of these relations in various fields and sectors of the economy. The system must have all the required components. FEA management is carried out by the management subsystem, which acts as a set of national and supranational bodies of economic cooperation (Dyrka, 2018).
Management of foreign trade should also include the development of resolutions and decisions of the managing subsystem, binding on all parties - partners in external relations. Planning and monitoring should be an integral part of the management process, ensuring that emerging issues and issues are addressed in the process of cooperation.
In order to improve the state management of foreign trade, including improving its efficiency and effectiveness, as well as improving the foreign economic policy of the country, the state is constantly monitoring compliance with all aspects of improving the regulatory framework of foreign economic activity. The promotion of the competitiveness of the national economy, taking into account the changed approaches to it in the context of globalization and regional integration, should be an integral component (Fig.3) (Nazarbayev, 2007).
Figure 3
Institutional support for the development of foreign economic activity in the Republic of Kazakhstan
(compiled by the authors on the basis of the studied material, Nesterenko, 2013; Schwab, 2016; Sorkin, 2016)
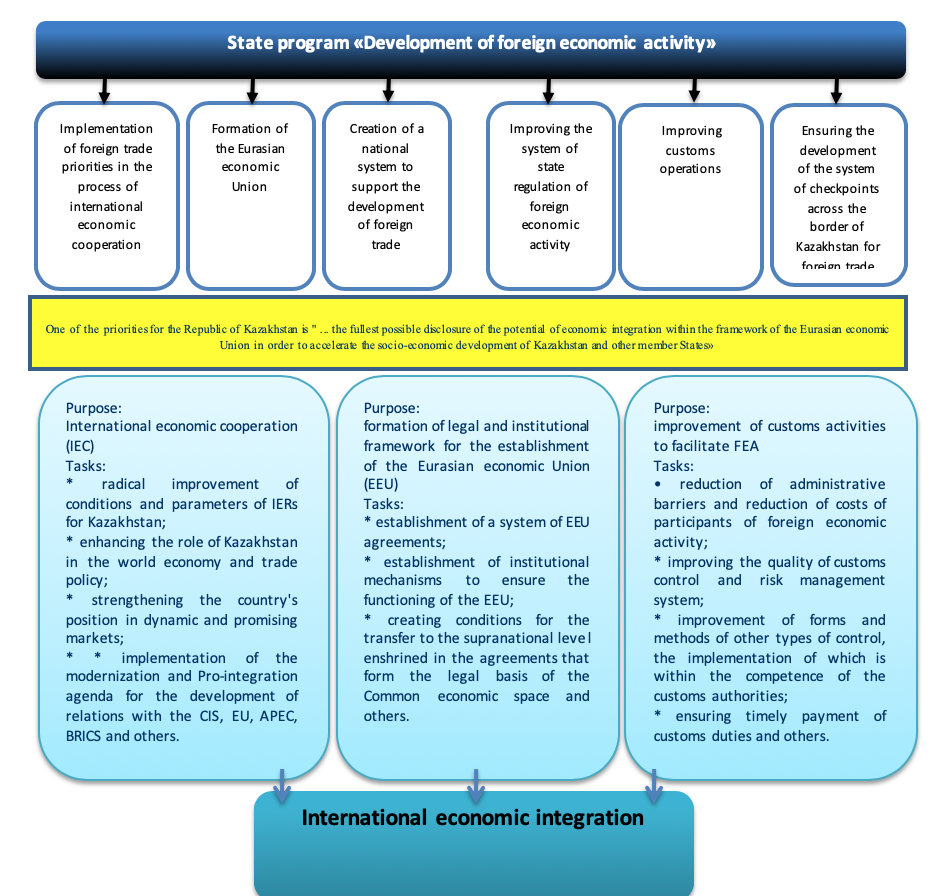
The main documents defining the order of foreign trade regulation in the Republic of Kazakhstan are:
* Constitution of the Republic of Kazakhstan of 30 August 1995;
* The customs code of the Republic of Kazakhstan of April 05, 2003 N 401-2;
* Civil Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan of 27 December 1999;
* Tax Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated January 1, 2018;
* Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 467-IV of July 21, 2011 " on amendments and additions to some legislative acts of the Republic of Kazakhstan on taxation»;
* Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 356-IV of November 26, 2010 " on amendments and additions to some legislative acts of the Republic of Kazakhstan on taxation»;
* Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan № 297-IV of June 30, 2010 " on amendments and additions to some legislative acts of the Republic of Kazakhstan on customs regulation and taxation»;
* Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "on accounting and financial reporting" 28 February 2007 № 234;
* Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "on currency regulation and currency control" of June 13, 2005 N 57-3;
* Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated January 6, 2012 № 530-IV " on amendments and additions to some legislative acts of the Republic of Kazakhstan on currency regulation and currency control»;
* The law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "On investments" dated 8 January 2003 No. 373;
* Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "on licensing" of 11 January 2007;
* Resolution of the government of the Republic of Kazakhstan "on approval of the agreement on the common commodity nomenclature of foreign economic activity of the Eurasian economic community" dated 11.06.2003 № 567;
* In accordance with the Decision of Committee of Customs Union № 859 dated 9.12.11 "On bringing normative legal base of the Customs Union in accordance with the unified Customs Union and a Single of CU, approved by the Decision of the Committee of the Customs Union dated 18.11.11, No. 850", amendments to certain Decisions of the CU Commission (130, 131, 132, 168, 257, 299, 317, 318, ...); the Document entered into force as of 01.01.2012 (Gussenov, 2018).
Thus, in the Republic of Kazakhstan, foreign economic activity is considered as part of the foreign policy of the state, as well as national economic policy, therefore it is subject to regulation by the state.
Foreign economic policy involves targeted actions of the state and its bodies to determine the regime of regulation of foreign economic relations and optimize the country's participation in the international division of labor. The main components of foreign economic policy are: foreign trade policy (including export and import policy), policy in the field of attracting foreign investment and regulation of national investment abroad, monetary policy.
With the help of foreign economic policy is regulated and foreign economic activity, the hallmark of which is the international sale of goods and services, international movement of material, monetary and labor resources.
Traditional instruments of foreign economic regulation used in market economies are becoming the main ones in Kazakhstan. The market economy system is more consistent with the economic instruments of foreign trade regulation, operating through the mechanism of prices (first of all, customs and tariff regulation is allocated here). When using economic instruments, the buyer retains the freedom of choice between imported and similar domestic goods, which is one of the most important conditions for the functioning of market relations. During periods of significant deterioration in the economy, inflation and sharp differences between domestic and world prices of the government (and this is evidenced by international experience) for the mobilization and better use of limited resources are forced to resort to administrative instruments of regulation.
Thus, the mechanism of legal regulation of foreign economic activity consists primarily of a variety of legal means that perform their inherent functions in the system of legal regulation of foreign economic relations. State regulation of foreign trade includes the following components: the nature, specific directions, forms and scale of state intervention in this area, which are determined by the nature and severity of the world economic problems of Kazakhstan. At present, foreign trade activities are carried out by a wide range of subjects, while there is no centralized state management of this activity, since state regulation of foreign trade is carried out by special state institutions and includes a system of measures, legislative, executive and supervisory impact in order to ensure effective foreign economic development, stimulate the development of exports and imports, as well as increase the inflow of foreign capital.
Artemov, N. M. (2016). Financial and legal regulation of foreign trade activities. Moscow. Methodical center of educational and practical literature. p.249.
Balabanov, I. T. & Balabanov, A. M. (2015). Foreign economic relations. Book. Moscow: Finance and statistics. P. 264.
Batizi, E. (2015). Management of foreign economic activity of economic entities in Russia: Studies allowance. Moscow. Infra publishing house. P.147.
Bayanova, S. (2014). Economy. Book. Moscow: Ladoga, p. 245.
DYRKA, S. & GUSSENOV, B. Sh. (2018). THE MAIN ASPECTS OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF FOREIGN ECONOMIC ACTIVITY IN THE ERA OF
GLOBALIZATION. BULLETIN OF NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE REPUBLIC OF KAZAKHSTAN. Volume 6, Number 376, 234 – 238. https://doi.org/10.32014/2018.2518-1467.50. http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0275-8029 .
Gussenov, B. Sh. (2015). Development of foreign economic activities in the age of globalization Tutorial LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, p. 316.
Gussenov, B.Sh. (2017). Regional aspects of implementation of foreign economic activities of Almaty region. Scientific achievements and discoveries of modern youth, collection of articles of the winners of the International scientific and practical conference: in 2 parts. P. 551-553.
Gussenov, B. Sh. (2018a). Theoretical features of development of foreign economic activity in the context of globalization of the economy.OPEN INNOVATION, collection of articles of the III International scientific-practical conference. P. 124-127.
Gussenov, B.Sh. (2018b). The concept of monitoring of foreign economic activity of the region on the example of Almaty region. ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT: PROBLEMS AND INNOVATIONS, collection of articles of the II International scientific-practical conference. P. 41-44.
Gussenov, B.Sh. (2018c). Systematization of evaluation of the region development efficiency in the conditions of globalization as a subject of foreign economic activity. Priority directions of development of science and education, collection of articles of the International scientific and practical conference. In 2 parts. P. 171-175.
Gussenov, B. Sh. N. B. Korabaeva, G. A. Zhunusova, A.G. Tolamisova, S. N. Aitkulova. (2018). The development of foreign trade in the era of globalization. Espacios. Vol. 39 (Number 47). Page 22. http://www.revistaespacios.com/a18v39n47/18394722.html
Ilimzhanova, Z. А., Burnasheva, V. R., Gussenov, B. Sh. (2018). Trends in the development of fiscal authorities of Kazakhstan. Espacios. Vol. 39 (Number 12). Page 26.
Kurnickaya, K. Yu. (2018). The fourth industrial revolution and innovative trends in the world economy. Economic science and practice: materials VI international. scientific. Conf. (Chita, April). Chita: publishing house of the Young scientist. P. 16-19. URL https://moluch.ru/conf/econ/archive/265/14072/ (accessed: 11.10.2018).
Kushlin, V. I. (2016). State regulation of market economy: Textbook. Ed. 3rd, supplemented and processed. Under the general ed. RAGS publishing house. Chapter 27. P. 268.
Message of The President of The Republic of Kazakhstan N. Nazarbayev to the people of Kazakhstan strategy “Kazakhstan-2030 " at the New stage of development of Kazakhstan, December 14, 2012.
Naribaev, M. K. (2018). The Current state of foreign economic activity in Kazakhstan and ways to improve it. Statistics, accounting and audit. No. 1 – 4. P. 82 – 89.
Nazarbayev, N. A. (2007). The strategy of Kazakhstan's entry into the number of 50 most competitive countries in the world. Kazakhstan is on the threshold of a new leap forward in its development: message of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan to the people of Kazakhstan dated 1 March 2006. Kazakhstan-2030. Almaty: Lawyer. P. 38-57.
Nesterenko, A. I. (2013). Economy. Moscow. Vlados, p. 189.
Schwab, K. (2016). the Fourth industrial revolution. Klaus Schwab. Eksmo-Top Business Awards. 208 p.
Sorkin, S. L. (2016). Foreign Economic activity of the enterprise: Economics and management: textbook. Minsk: Modern. P. 283.
State regulation of foreign economic activity in the conditions of industrial and innovative development of the economy: regional aspect (on the example of East Kazakhstan region). Proceedings of the III international scientific and practical conference "Science and education in the modern world", MESI. Ust-Kamenogorsk. 2017.
1. C.e.s. Zhetysu State University named after I. Zhansugurov. The faculty of law and economics. Taldykorgan. Republic of Kazakhstan.
2. Senior lecturer. Zhetysu State University named after I. Zhansugurov. The faculty of law and economics. Taldykorgan. Republic of Kazakhstan.
3. Senior lecturer. Zhetysu State University named after I. Zhansugurov. The faculty of law and economics. Taldykorgan. Republic of Kazakhstan.
4. Senior lecturer. Zhetysu State University named after I. Zhansugurov. The faculty of law and economics. Taldykorgan. Republic of Kazakhstan.
5. Master of law. Zhetysu State University named after I. Zhansugurov. The faculty of law and economics. Taldykorgan. Republic of Kazakhstan.
6. Master of economics. Zhetysu State University named after I. Zhansugurov. The faculty of law and economics. Taldykorgan. Republic of Kazakhstan. king_bara@mail.ru
[Index]
revistaespacios.com

This work is under a Creative Commons Attribution-
NonCommercial 4.0 International License