

Vol. 41 (Issue 05) Year 2020. Page 10
JAIN, Vibhor 1; JAIN, Smrita 2 & RASTOGI, Prachi 3
Received: 02/10/2019 • Approved: 30/01/2020 • Published 20/02/2020
ABSTRACT: This paper studies role of emotional intelligence (EI) in career success. This research was conducted over employees of UCO Bank, Indian Bank, United Bank, Federal Bank, Central bank, OBC, Dena bank and PNB. Banking sector was selected for research because it is most lucrative sectors of economy. Sample size was 200. To assess emotional intelligence of employees, test was designed by reviewing Daniel Goleman’s emotional intelligence model. Research findings revealed a positive correlation between career success and emotional intelligence. |
RESUMEN: Este artículo estudia el papel de la inteligencia emocional (IE) en el éxito profesional. Esta investigación se realizó sobre empleados de UCO Bank, Indian Bank, United Bank, Federal Bank, Central bank, OBC, Dena bank y PNB. El sector bancario fue seleccionado para investigación porque es el sector más lucrativo de la economía. El tamaño de la muestra fue de 200. Para evaluar la inteligencia emocional de los empleados, la prueba se diseñó revisando el modelo de inteligencia emocional de Daniel Goleman. Los resultados de la investigación revelaron una correlación positiva entre el éxito profesional y la inteligencia emocional. |
At earlier career development was considered as, to be in an organization, climb the organizational ladder and move through clearly defined job positions and hierarchies for progression. However, with passage of time the term was given broader definition. According to Wendy Patton and Mary McMohan (2006) career development defined by department of education & science, in year 1989 as “multiple occupational role which an individual play throughout the life; like student, part time worker, employee and independent professional, etc”. Whereas Donald Super’s words were also quoted in the same book, where Super defined career development as “occupational and non-occupational progress of an individual through variety of roles; a student move with different levels, acquire education, learn, select a profession and grow in respective field”. In addition to this; Super had also highlighted social roles as important step at the ladder of career development. There is a direct relationship between emotional intelligence and job performance (Davar, Singh, 2014). Emotions influence professional relationships, impact service delivery and affect bank employees at an intrapersonal level (Karthikeyan, V., & Lalwani, S, 2017). Higher the levels of emotional intelligence of bank mangers the higher the levels of job performance and higher the levels of job satisfaction (Praveena, 2015). There is a connection between the skills and productivity of workers. World have started to recognize the significance of this connection and emphasis is directed to boost the workers' emotional intelligence (Anand et al. , 2019).
This is the notion of emotional intelligence referred by Jordan, Ashton-James &Ashkanasy (n.d.), from the Goleman’s work, which claims emotional intelligence is the predictor of career success. It’s been argued that cognitive intelligence can help you to get hired but to get promoted emotional intelligence plays significant role.
EI plays an equally important role in it. Researchers have discovered in past cognitive intelligence is better interpreter of professional and educational performance than EI. However according to Stys & Brown (2004) when we talk about excellence in performance or to be outstanding leader, cognitive intelligence may not be as much powerful predictor of success as emotional intelligence. Goleman has expressed EI through four factors which include: personal awareness in term of emotion and responsiveness toward feelings of other, management of personal and other’s emotions and social skills; required to better be aware of others emotions and managing other’s emotions (Gosling,2006). According to Zeidner, Matthews & Robert (2004), it’s been argued that components of emotional intelligence have great effect on one’s performance at workplace and also in developing one’s own leadership skills. And the leadership and performance are the most important ingredients in the recipe of career success.
Success of individuals contributes to development of nation but for this development, institutional frame work is equally essential. In nation’s success industries play an important role. India economy’s success is dependent upon sectors such as agriculture, textile, sport goods industry, services sector and other industries. In service industry there is great share of banking sector. Although the banking sector is moving at fast pace but this growth is leading to organizational stress. Excessive work pressure over employees leads to lower productivity and deviant behaviours which directly hamper organizational success. Here this research shall be testing how the emotional intelligence provides protection against such situations as Goleman (1998), proposed “emotional intelligence as propensity to control personal emotions and of others as well”.
At workplace employees contribute their efforts at their best but growth is not solely dependent upon performance outcome. There are several other factors that contribute to career growth and emotional intelligence (EI) is one of them. Purpose of this study is to identify, different traits of EI of employees and to explore the role of EI traits in career advancement/career success.
Objective of this study is to discover link between emotional intelligence and career success of respondents. For this research objectives are as follow:
Cognitive ability of intelligence has remained very attractive to psychologists and researchers. Psychologists have focused on memory and problem solving aspect of intelligence because in older times it was the sole paradigm for individual’s efficacy. However over the period of time focus of researchers diverted toward emotional intelligence. It refers to use of our own emotions and those of others intelligently. The term emotion is defined as “feeling arising as result of experience from external environment and self awareness.” (Mayer, Salovey & Caruso, 2008). Whereas intelligence; is the other name of cognitive ability.
Human brain’s operations are categorized in three classes known as triad; motivation, emotion and cognition. Motivations arises as result of internal and external bodily states (basic needs), emotions continuously evolve signals and respond according to the change occurring within individual and environment however third category of mental operation is cognition; which is about learning from environment and problems solving. Emotion, often defined by combining with attributes of motivation and cognition which widen its boundary. Mayer, Carsuo and Salovey (1999) proposed “feelings are resultant of a person’s internal, external environment, understanding and understanding capability”.
Though Peter Salovey and John Mayer was the pioneer of the term EI and were also the first to develop EI measure but the term really got famous in the corporate world and in 1995 when a book Emotional Intelligence by Daniel Goleman was written. Goleman proposed a model outlines four main emotional intelligence constructs: self awareness, self management, social awareness and relationship management.
Theoretical Framework
Referred to above mentioned measures of emotional intelligence, MSCEIT (Mayer, Salovey and Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test ) is the test to assess contribution of emotional intelligence in one’s ability. These factors enhance an individual’s career progression; since career success is no more confined to vertical progression in one organization only; similarly the means of progression are also being changed.
Figure 1
Theoretical Framework

Source: Authors’ adoption from MSCEIT
(Mayer, Salovey and
Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test ) & Goleman’s Test
Jain, S., Jain, V., & Das, S. (2018) proposed that service quality & emotional intelligence are related to each other. So the service quality will be affected if emotional intelligence factored by Self-management, self-awareness and social skills/networking. These are the component of emotional intelligence which serves as determinants of career success; which directs individual toward professional development Professional development refers to be having skills, knowledge, and competence in relevant field and in today’s inconsistent period to be professionally developed individual needs to be flexible to learn new skills according to need and unlearn olden practices. Bar-On has emphasized importance of emotional intelligence in his research where he equated emotional intelligence to cognitive intelligence. Boundaries of emotional intelligence are spread out not only to professional development but they also incorporate career development. Donald Super has regarded it as lifelong learning process.
This study was conducted to uncover role of emotional intelligence in career success through quantitative research method and provide empirical evidence of relation among the variables. Emotional intelligence and career success level of respondents was identified through close ended questions, the collected responses were assessed over Likert scale. To explore the relationship between the variables, relevant statistical tools including average, percentage, regression analysis and correlation analysis were used. Furthermore to identify the relation, confidence was also tested at the interval of 5%.
Sampling frame included individuals working at middle level of management in different commercial banks of Ghaziabad city for at least two years (with in the same bank for two years or more). Scope of sample for this research was confined to eight banks including, Uco Bank, Indian Bank, United Bank, Federal Bank, Central bank, Oriental bank of Commerce, Dena bank & Vijaya Bank. Emotional intelligence test was design with the help of Daniel Goleman’s model presented in his book Emotional Intelligence. The designed research tool was presented Dr. Rukhsana Haider for approval. As she has hand on Emotional Intelligence and she is working as Neuropsychologist at Dow University of health science. After conducting Emotional Intelligence test of respondents, there results were analyzed in the light of their subjective and objective career success. Collected data was processed and a detailed report was generated; representing the role of EI in respondent’s career success.
For the study population included commercial bank employees working at managerial cadre. Sampling frame only included those employees who have been working in the bank for two or more than two years. In conducting this research sampling was heterogeneous both the male and female were participant in study.
Convenient sampling method of non probability sampling was used in this study. Two hundred bank employees falling in managerial cadre of the selected commercial banks of Ghaziabad participated in the research. Sample size of two hundred was decided after reviewing past research papers Mehta, S., & Singh, M. N. (2013).
To identify emotional intelligence level of respondents EI test was designed including research regarding self awareness, self management, social skills and networking. These responses were scored over Likert scale. At earlier research plan included to conduct in depth interview with respect to supervisors of respondents, to explore success level. However due to time constraint certain question regarding career success such as, promotions, salary increment and rewards were added to survey. Emotional intelligence test was conducted and results were associated with career success level of respondents.
This research will deal with an independent variable (also known as a predictor variable) and a dependent variable. In this study, the independent variable was emotional intelligence EI and dependent variable was career success. The purpose of the study was to determine whether the independent variable (EI) is positively related to the dependent variable (career success).
As per research plan, analysis was to be conducted over two hundred respondents. However despite of circulating four hundred questionnaires only one hundred and ninety four questionnaires were received which is near to the estimated sample size of 200 and analysis was conducted over one hundred and fifty four responses. Certain responses were eliminated as respondents did not belonged managerial cadre. Analysis was done in SPSS-22 for regression, correlation, factor análysis & descriptive statistics. Graphical image are drawn by Origin Pro.
Questionnaires were circulated among bank employees regardless of employee’s gender.
Data analysis reveals there is great proportion of male gender in managerial cadre than female in selected commercial banks of Ghaziabad. From the sample of two hundred respondents 81% were male belonging to different managerial level ranging from cash officer to Assistant Vice President (AVP), however only 19% were female.
Review of age of respondents, shows most of the respondents belonged to the age brackets of twenty five to thirty five years which indicates that respondents tend to have greater flexibility in their behaviors. 68% of respondents belonged to the age group of twenty five to thirty five years, 14% of respondents were below the age of twenty five years, 9% of respondents fall in the age bracket of thirty five to forty five years while remaining was above the age of forty five years.
In term of experience most of the respondents fall in category of two to five years of experience. Only 9% of respondents had over the eleven years of experience.
Key objective of the study was to explore emotional intelligence of respondent and for this purpose certain questions were designed based upon Daniel Goleman’s model. Parameters of emotional intelligence include self –awareness, self-management, social skills and net-working. The collected data revealed that most of the respondents possess above average level of emotional stability. However number of respondents at the extremes of high and average level of emotional intelligence was very low, and even there was not a single respondent having low level of emotional intelligence.
As per this research emotional intelligence, does not possess any relation to the level of experience. Respondents having experience from two to eleven years had almost same level of emotional intelligence. Although individuals having eight to eleven years of experience had lesser emotional intelligence as compared to the rest, however individual falling in this category of experience was very low to draw significant conclusion.
Moreover analysis of emotional intelligence with reference to hygiene and motivation factors reveals individuals, who prefer hygiene factors are more emotionally intelligent than those who prefer motivational factors.
Analysis of average emotional intelligence level of female versus male shows women were more emotionally intelligent rather than male respondents.
Other variable of this research was career success. Analysis of career success shows most of the respondents were satisfied with their career achievements. However a very few respondents fall in the category of not successful or in other words as not satisfied as here emphasis was given to subjective success rather than objective success and subjective success is associated to motivational factors. In this research parameter of success included salary and benefits, environment/working condition, work life balance, quality of supervision, job responsibility and recognition.
Analysis of career success to the age shows positive relation among two. Individual falling in age bracket of 35-45 years and over the age of 45 years possess more success.
The above result could be attributable to decreasing motivational level with increasing age. Analysis of career success with reference to experience also shows positive relation.
Moreover analysis of average career success to gender shows, female respondents were more successful than male respondents. They were satisfied with their achievements and they also had higher level of emotional intelligence.
A further analysis of career success was carried out through hygiene and motivational factors. Average was taken of collected data and it showed individuals who preferred motivational factors were slightly more successful than those preferred hygiene factors.
Till yet it was an independent overview of career success and emotional intelligence level of respondents. However the essence of study depends upon the relationship between career success and emotional intelligence. Regression analysis of variables reveals a relationship between emotional intelligence and career success.
Figure 2
Regression Graph showing Relationship between
Career Success and Emotional Intelligence Level
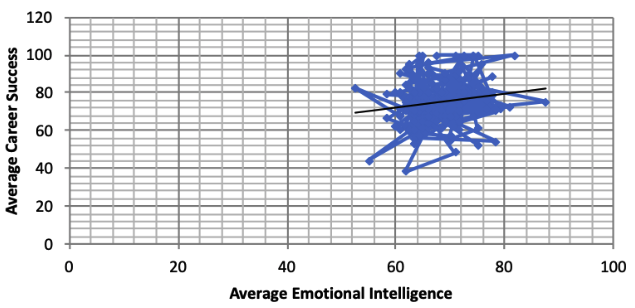
To explore the nature of relationship between two variables, correlation analysis was conducted which revealed, relation of 0.18. It indicates a positive relation among the variables. But this relation is not as strong as individual component of emotional intelligence contributes to career success. Following table below shows strong relationship of networking and social skills with Career Success.
Table 1
Co-relation Matrix show relationship
between EI, Components of EI and CS
Correlation Matrix |
||||||
Variables |
EI |
CS |
SA |
SM |
SS |
N |
Emotional Intelligence(EI) |
1 |
|||||
Career Success(CS) |
0.18 |
1 |
||||
Self awareness(SA) |
0.60 |
-0.01 |
1 |
|||
Self management(SM) |
0.65 |
0.03 |
0.30 |
1 |
||
Social Skills(SS) |
0.57 |
0.17 |
0.30 |
0.21 |
1 |
|
Networking(N) |
0.70 |
0.23 |
0.18 |
0.21 |
0.22 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-----
Table 2
Co-relation Matrix showing relationship
between CS, Components of CS and EI
Correlation Matrix |
||||||||||||
Variables |
EI |
CS |
SD |
WLB |
VP |
R |
J |
LW |
PB |
G |
||
Emotional Intelligence(EI) |
1 |
|||||||||||
Career Success(CS) |
0.18 |
1 |
||||||||||
Self-development at work(SD) |
0.05 |
0.38 |
1 |
|||||||||
Work-life balance(WLB) |
0.09 |
0.43 |
0.33 |
1 |
||||||||
Vertical Progression(VP) |
0.02 |
0.49 |
0.34 |
0.40 |
1 |
|||||||
Recognition( R ) |
0.03 |
0.42 |
0.25 |
0.35 |
0.65 |
1 |
||||||
Job itself(J) |
0.01 |
0.36 |
0.44 |
0.19 |
0.44 |
0.40 |
1 |
|||||
Learning at workplace(LW) |
0.03 |
0.33 |
0.31 |
0.16 |
0.25 |
0.28 |
0.39 |
1 |
||||
Pay & Benefits(PB) |
0.08 |
0.40 |
0.28 |
0.18 |
0.58 |
0.41 |
0.39 |
0.24 |
1 |
|||
Above table shows relationship between career success components and Emotional intelligence, although relationship is not strong, but yet there is positive relation. A general overview of relationship between career success and emotional intelligence level of respondents was presented, however results of male and female respondents separately were as follow:
Table 3
Co-relation Matrix showing relationship
between EI and CS of Male Respondents
Correlation Between Career Success and Emotional Intelligence of Male Respondents |
Average |
Emotional Intelligence |
68 |
Career Success |
75 |
Correlation |
0.11 |
Self-Awareness |
-0.10 |
Self-Management |
0.01 |
Social Skills |
0.17 |
Networking |
0.16 |
Analysis male respondent’s career success to emotional intelligence indicates a positive relation of 0.11. Also the relation between career success and networking and career success and social skills is much positive as compare to self-management.
Table 4
Co-relation Matrix showing relationship
between EI and CS of Female Respondents
Correlation Between Career Success and Emotional Intelligence of Female Respondents |
Average |
Emotional Intelligence |
70 |
Career Success |
76 |
Correlation |
0.43 |
Self-Awareness |
0.28 |
Self-Management |
0.09 |
Social Skills |
0.15 |
Networking |
0.48 |
Strong correlation of Emotional intelligence level to the career success level was observed in female respondents. Overall observation shows a positive relationship between career success and emotional intelligence, which further proven from the results of female respondents.
By applying coefficient of determination r2=.03 = 3% was obtained. This value indicates that the 3% variance in career success due to variance in emotional intelligence level can be defined and vice versa. To further test the validity of result, it was tested at confidence level of 5%.
For this research following hypothesis was constructed.
H0: There is no relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Career Success.
H1: There is relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Career Success.
To test the hypothesis F-test was used.
Table 5
Table for F-test
Sum of Squares(SS) |
d.f |
Mean Square |
F=statistic |
F-test(at .05) |
p-value |
|
Explained Regression |
12.61 |
1 |
12.61 |
11.66 |
254 |
0.23 |
unexplained (error) |
22043.32 |
150 |
146.96 |
|||
Total |
22055.93 |
As per the findings p-value was greater than .05 (level of significance) and the value of f-test was greater than f-value, which indicates that null hypothesis may not be rejected. It indicates there is no relationship between emotional intelligence and career success level of respondents. Hypothesis may be rejected at the confidence level 95% however correlation analysis shows the minor but positive relationship between emotional intelligence and career success.
On the basis of designed model, positive relation between career success and emotional intelligence appears. An important finding of this study was strong relation between emotional intelligence and career success of female respondents. Moreover to test the validity of relation hypothesis was generated and tested at the confidence interval of 95% through F-test. H0: There is no relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Career Success. H1: There is relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Career Success. Based upon the designed model, hypothesis test showed there is no relationship between the variables. However correlation analysis revealed positive relation between career success and emotional intelligence; even individual component of emotional intelligence showed a very strong correlation to the career success level. The essence of research shows emotional intelligence cannot be referred sole parameter of career success as there are various other factors which influence and in this study great emphasis was over subjective success rather than objective success as well.
This study has uncover new horizon for further researches over role of emotional intelligence in objective success, relationship between emotional intelligence and employee performance, relation between emotional intelligence and age, relation between emotional intelligence level and gender. Moreover finding of this study can also be tested through different models of emotional intelligence. This study is also in line with Goleman’s secret of success in career. According to Goleman (2011) the success of career depends on how you handle the situation in career’s different stages. This is implicated by this study where it is found that female employees are more emotionally stable in banks to deal with different situations which eventually helped them in career development. So, it can be said that this might be the reason of more recruitment of female officers in Indian Banks at various positions.
Anand, D. S., Ali, F., Panwar, D. D., & Singhal, K. (2019) Analysis of emotional intelligence of bank employees in Dehradun district: a comparative study of private and public sector banks.
Davar, S. C., & Singh, N. (2014). Emotional intelligence & job performance in banking & insurance sector in India. The Indian Journal of Industrial Relations, 722-733.
Goleman, D. (2011). Working With Emotional Intelligence. Bantam.
Gosling, M. (2006). Measuring emotional intelligence of managers in Singapore and the application of emotional intelligence for individual and organization effectiveness [pdf]. School of Management, PhD thesis, University of South Australia. <www.goslings.net/pdf/Dr_Mike_Gosling_Doctoral_Thesis_2006.pdf>
Jain, S., Jain, V., & Das, S. (2018). Relationship analysis between emotional intelligence and service quality with special evidences from Indian banking sector. Revista ESPACIOS, 39(33). Page 3 Retrieved from http://www.revistaespacios.com/a18v39n33/18393303.html
Karthikeyan, V., & Lalwani, S. Emotional Intelligence in Banking Sector–An Integrative. IOSR Journal of Business and Management Volume 19, Issue 10. 2017
Mayer, J. D., Caruso, D. R., & Salovey, P. (1999). Emotional intelligence meets traditional standards for an intelligence. Intelligence, 27(4), 267-298.
Mayer, J. D., Salovey, P., & Caruso, D. R. (2008). Emotional intelligence: New ability or eclectic traits?. American psychologist, 63(6), 503.
Mehta, S., & Singh, M. N. (2013). Development of the Emotional Intelligence Scale. International Journal of Management & Information Technology, 8(1), 1252-1264.
Patton, Wendy and McMahon, Mary (2006) The Systems Theory Framework Of Career Development And Counseling: Connecting Theory And Practice. International Journal for the Advancement of Counselling 28(2):pp. 153-166.
Praveena, S. (2015). Emotional Intelligence on Job Performance of Bank Managers in Sri Lanka.
Stys, Y., & Brown, S.L. (2004). A Review of the Emotional Intelligence Literature & Implications for Corrections, Research Branch, Correctional Service of Canada. < https://www.csc-scc.gc.ca/research/r150-eng.shtml>
Zeidner, M., Matthews, G., & Roberts, R. D. (2004). Emotional intelligence in the workplace: A critical review. Applied Psychology, 53(3), 371-399.
1. Associate Professor, Department of Management Studies (TMIMT), Teerthankeer Mahaveer University, Moradabad. Email- vibhorjain7@gmail.com
2. Assistant Professor, MIT College of Management, Moradabad. Email id- smritagupta29@gmail.com
3. Assistant Professor, Department of Management Studies (TMIMT), Teerthankeer Mahaveer University, Moradabad, Email id – rastogi.prachi24@gmail.com
[Index]
revistaespacios.com

This work is under a Creative Commons Attribution-
NonCommercial 4.0 International License