

Vol. 40 (Number 35) Year 2019. Page 28
NOVIKOV , Sergey V. 1
Received: 13/06/2019 • Approved: 11/10/2019 • Published 14/10/2019
ABSTRACT: The problem of strategic choice is being under study on the example of aviation-industrial complex enterprises, creating the capital goods and determining the technological structure of the country's economy. In the sphere of industrial production, a special place is occupied by the aviation industry, which ensures the country's competitiveness on the global stage. In the article a mechanism that integrates strategic, project and operational-tactical planning is proposed, which allows organically combine the strategic guidelines for the development of consolidated enterprises and their practical implementation. |
RESUMEN: El problema de la elección estratégica está siendo estudiado sobre el ejemplo de las empresas del sector industrial de la aviación, creando bienes de capital y determinando la estructura tecnológica de la economía del país. En la esfera de la producción la industria de la aviación ocupa un lugar especial que garantiza la competitividad del país en el escenario mundial. En el artículo se propone un mecanismo que integra la planificación tanto estratégica de proyectos como operacional-táctica que permite combinar orgánicamente las directrices estratégicas para el desarrollo de empresas consolidadas y su implementación práctica. |
Strategic changes in the modern world are caused by the urgent need not only for the successful functioning of the subjects to management, but also for their survival, the threat of which is due to objective circumstances: The XXI century brought humanity very close to turning points of “saddle” development. The need for effective change management and the theoretical lack the issues’ essence of strategic changes development, the procedures for their formation and justification, the specifics for large-scale systems of organizational and economic type put them among the most relevant.
Stabilization of the situation and further production increase implies the implementation of an integral set of changes in the activities of industrial enterprises and, above all, in its knowledge-intensive, high-tech industries, such as aviation. These changes, obviously, should be of fundamental nature, since they are caused by the necessity of strategic needs’ solving. Strategic changes in the aviation industry are carried out now in the form of the aviation assets consolidation within the framework of core integrated structures and the modernization of consolidated enterprises. The method of forming specialized integrated structures is based on the principles of constructive and technological proximity between the developed types of high-tech products (HTP), which, as a rule, is characterized by a long-life cycle and involves consistent structural integration of the following stages:
It is necessary to note the ongoing modernization of consolidated enterprises, i.e. legally independent organizations created on the basis of control of rights increase the degree of influence in subsidiaries and affiliates acting as a single business unit and implementing a common financial and economic policy in order to maximize economic benefits. The goals on this path are the substantiation of different hierarchical level project solutions, the alignment of implementation steps into a single interconnected contour within the development perspectives of consolidated enterprises as a single large-scale organizational and economic system (LOES). Thus, the problem of getting out of the current situation is the change management of large-scale organizational and economic systems challenge, where the strategic change forecasting is being the primary goal, and the solution tool for this problem are social needs’ research and regulatory forecasts – the aim of fundamental and applied sciences. The understanding of changes essence, how to plan them and in what order to carry out – this article is devoted to these issues.
Strategic changes are changes in the behavior of the system within the framework of the developed strategy, as a rule, they are optimally when they have a manageable design character. Project activities are dual in nature. On the one hand, this activity is ideal, because it is associated with planning for the future. On the other hand, it is a technological activity, as it reflects the processes of implementing what is intended. The analysis of various literary sources allows us to highlight the main features of the project:
The disadvantages of the existing practice of substantiation and implementation of strategic changes at facilities of such complexity as enterprises and associations of the knowledge-intensive industry sector remain:
As known, if there is no clarity in the definitions, there cannot be any clarity in the discourse. Therefore, to make clear the essence of the project change management, it is necessary to clarify the project concept.
There are two approaches that give the definition to project: narrow – in the theory of project management and broad – in the general theory of management. The definition of the project in the framework of the first approach is given through the components of the “deadline – goal – resources” in the standards of IPMA (International Project Management Association), PMBOK (Project Management body of knowledge) – a manual to the body of knowledge on project management (international standards for project management, USA).
A project (from the Latin projectio – throwing forward) is a one-time set of actions and tasks, which has a number of distinctive features: novelty of goals and objectives, limited time and resources, isolation from other actions and tasks, uniqueness of conditions in their combination, specific implementation organization process. Thus, the project is associated with changes. Projects can be diverse and multifaceted. However, they all have the following common characteristics:
In modern management theory, a project refers to the purposeful, pre-designed and planned creation or modernization of physical objects, technological processes, technical and organizational documentation for them, material, financial, labor and other resources, as well as managerial decisions and measures for their implementation. Such conception of the project is perpresented in Porshnev A.G., Rumyantseva Z.P., Salomatina N.A. and others. The essence of any project is activity, but for it to be successful, careful and thoughtful management of this project is necessary, which serves as a guarantee of effective activity and its focus on achieving the goal. Project management is a practical application of knowledge, skills, tools and methods to the project to meet the requirements of the project.
Project changes are those changes in the common state of the entire large-scale organizational and economic system and (or) its individual subsystems (enterprises, organizations, industries) under the influence of new requirements. The most significant (basic) transformation of LOES is the portfolio diversification of its business units, when individual enterprises (organizations) are acquired (created), liquidated (sold) or the core strategic assets of high-tech enterprises are reorganized as a result of their restructuring. The resources used to implement the project changes are long-term, that means strategic investments. Thus, project changes are strategic, aimed at solving prospective problems (as opposed to operational-tactical organizational-technical measures that solve current nature problems). Nowadays the innovative strategic are extremely important when investments are aimed at creating or reproducing the organization’s knowledge assets. Managing project changes implies not only forecasting future social needs, but also managing the generation of project ideas, their rationale and practical implementation. The acceptability of strategic changes is carried out in the form of technical and economic project study or in the form of business plans today. At the same time, point to the fact that existing practice, a crucial disadvantage is the connection loss between the organizational strategic planning and project management (Mindlin, Novikov, Kireev, Adamenk, Belitskaya, 2016).
The consequence of such situation was the strategic insufficiency of projects included in the investment and innovation plans of organizations, which essentially means the abandonment of their strategic development plans. For large-scale organizational and economic systems, it causes exceptionally negative effect.
In the theory of project management, business justification is not paid due attention. The emphasis is mainly made on managing the already accepted for execution project. This happens because the rationale, like the project initiation, is by far the most difficult issue of a creative nature. There is also no unambiguous definition of the notion “business plan”. It is used in very diverse ways.
For an adequate and unambiguous reflection of the project business planning essence, let’s give it the following definition: business planning is a special management function dealing with detail and justify the acceptability of strategic business changes associated with the costs of investment resources. This definition allows you to formulate the main goals of the business plan as a strategic document and help in the development of enterprise development strategies. (Sozinova, Novikov, Kosnikov, Nemchenko, Alenina, 2016). Strategic goals of business planning include:
1. Assessment of project compliance with the goals and strategies of the enterprise.
2. Assessment of the feasibility of the project.
3. Assessment of the acceptability of the project.
Development of a business strategy development can be carried out in two key areas: diagnostics of the external and internal environment: Diagnostic features of the external environment will include: PEST-analysis (political, economic, social, technological factors), consumer analysis, industry analysis, competitive analysis and analysis market. In turn, the diagnosis of the internal environment involves conducting: SNW-analysis (strong, neutral, weak factors of the internal environment of the enterprise), determining the key competencies of the enterprise and conducting financial analysis.
A business plan is a strategic document that transforms individual strategic changes into tactical planning activities. Depending on the purpose, the business plan performs various tasks. Business plan for a new project is the following:
Business planning can be considered as a business idea projection into the business environment in order to justify its success. The horizon period of business planning depends on the nature of the project and, above all, on the duration of its life cycle, including the economic life (the period of time when the project will generate net profit), the product life cycle or innovation (determined by the period of moral and physical deterioration of the invested object), the period of time when the project is managed, and for LOES projects – and the life cycle of the industry (industries, sub-sectors, sectors). The duration of the business planning horizon period for small and medium-sized projects should be no less than 3-5 years, and for large-scale projects from 10 to 15 years or more, which corresponds to the horizon period of the whole LOES and its individual enterprises strategic planning. The shorter horizon period of strategic planning is fraught with disastrous consequences; this was clearly demonstrated by recent crisis events in the automotive industry of the West, where five-year plans were considered as strategic plans. Taking into account that the accumulated net flows of the project’ genuine money are a function of the time period (economic life of the project), the horizon period can have a significant impact on the financial analysis results, therefore its definition is an important task in developing a business plan. The business plan precedes the direct detailed planning of the project, is developed at the initiation stage and represents its justification (FS – Feasibility study – a technical and economic study of the feasibility of the project). The feasibility study includes:
There are the following points of view:
1. The business plan has replaced the technical and economic feasibility study of the project – the most common version.
2. A business plan is a plan of any small and medium company that is used in a fundamental change in policy or the creation of a new enterprise (Mitrofanova, Demjanchenko, Novikov, Rudakova, Shmanev, 2017).
In practice, there is no contradiction in these statements, since in both cases the subject matter of planning is the same – strategic changes that are implemented at objects of different nature. In fact, the business justification – the strategic changes planned by the organization and fixed in its strategic plans, and at the output – a quantitative assessment of the necessary investment resources performance indicators.
The process of business planning is like scientific research, during which the construction and implementation of a multi-criteria investment decision-making model is carried out. The purpose of business planning is to assess the feasibility of obtaining an investment, develop plans, draw up a system of numerical estimates of economic and financial indicators, which can be used to judge the degree of success of an enterprise. The field of business planning research, as a scientific discipline, are the processes of making project decisions related to investments. In modern business practice, a business plan is no longer considered as a document solely for attracting investment funds to the enterprise. Now its functions are much wider, it is a key element for achieving the goals of strategic and financial management, therefore, before starting the development of a business plan, it should be justified:
The criterion of project’s acceptability (optimality) is the main feature based on which its quality is assessed, according to which the evaluated project is recognized as the best of all possible options. In practice, there is no unambiguous criterion for optimality (rationality). The criteria for project’s acceptability at different stages of business justification are diverse: at the first stages they are, as a rule, descriptive (qualitative), expressed by the ratios “better – worse”; then, at subsequent stages, quantitative certainty is obtained and expressed in quantitative terms. Criteria reflect the set goals’ achievement degree. Projects are initiated due to the needs that can be satisfied. These needs are expressed by a system of quantitatively defined goals that must be achieved as a result of the project implementation. Objectives are determined by a combination of different groups’ interests. The project analysis’s core point are cost-oriented stakeholders’ interests (monetary theory), when the main goal is to maximize the cost of equity, and the main target indicators of business are contribution indicators to cost (economic added value), return on capital, cost of capital based on discounted deposits in cost or discounted free cash flow. Reduction in the effectiveness of traditional cost management tools (represented by the systemic crisis of world economies) led to the appearance of the idea of the need to strengthen the role of non-monetary targets in a strategic analysis and achieve a balance in the entire system of indicators (the concept of managerialism). In accordance with the managerialism concept, project acceptability, along with financial indicators, is also determined by many other factors that may be crucial to the project (Nedelkin, Novikov, Titov, Mikhailova, Popova, 2017).
In accordance with the societal marketing concept, changes in business should occur not only taking into account the momentary desires of consumers, the requirements of the company itself, but also the long-term interests of consumers, as well as the long-term interests of society as a whole, taking into account possible contradictions between the desire of individual consumers and public interests. When making changes, this concept calls for a balance between the company’s goals in achieving maximum profit, the consumers’ needs and the public interests. At the same time, the task of the investment project is to create for clients an ever-higher customer value, “but not to give him the last shirt”. The task of any project justification is to balance the process of creating a product’s higher customer value (cost) with the investment profitability. The task of a project’s multi-criteria balanced justification is performed by the business planning toolkit.
The problem of justifying strategic change has another very important issue that is not given due attention: what is the main idea of strategic change (projects). It can be stated unequivocally that the main goal of a business project is to make a profit by meeting any identified (or created) need. Consequently, the main idea of any business project is product offering. If the product offering was not initially appreciated, then the financial, intellectual, material and labor costs of the project become unjustified. The connection between the project idea with the evolution of marketing views is presented in Figure 1. This situation indicates the need for a more thorough study of the project marketing, to which both in theory and in practice insufficient attention is paid (Novosadov, Burtseva, Repetskaia, Novikov, 2017).
Figure 1
The main idea of the project in accordance
with the evolution in marketing

This is especially referring to MIC companies, where part of the products cannot be directly treated as a product. The universality of the marketing approach consists in the understanding that any project activity is aimed at satisfying any need, which is explored in the project marketing. At the same time, any product offering in the form of good, service, real estate, intellectual property, an integrated transport (for example, aerospace) system, its’ individual elements, etc. can be considered as a product. Features of the product offering affect the idea of business plan developing, its structure and presentation format (Novikov, 2018).
To clarify the structuring of the marketing project a three-level presentation of good will be used. The first level of the good – the core product is determined by the type of activity or sector profile of the business (business project). The type of activity or industry is analyzed and justified as of perspective attractiveness in the first section of the business plan “Enterprise and Industry”. Next, a detailed elaboration of the good’s concept as actual product (second level) and augmented product – the third level of the product offering.
Thus, when justifying a project in the business plan, the idea of the product offering is detailed in accordance with the three-level concept of the product, figure 5.
This approach systematizes the project marketing, makes it possible to purposefully and reasonably take the main strategic decision on the project, logically develop the entire marketing system, subordinating its ideas to the product offering and the possibility of selling really good on the forecasted sales markets.
Business planning as a process of detailing and justifying strategic change deals with a complex logically consistent project decision-making technology. In concept the business planning logic is the following: objectives, strategy, resources (Kraev, Tikhonov, Novikov, 2018).
The business plan covers all the links of this chain, transforming the strategic aspects of investment projects into resource tactical plans for their implementation, including a number of stages, which, according to the content of the tasks to be solved, can be combined into three blocks or modules, figure 2:
Figure 2
Three-level product’s concept in project’s
business planning (project marketing)
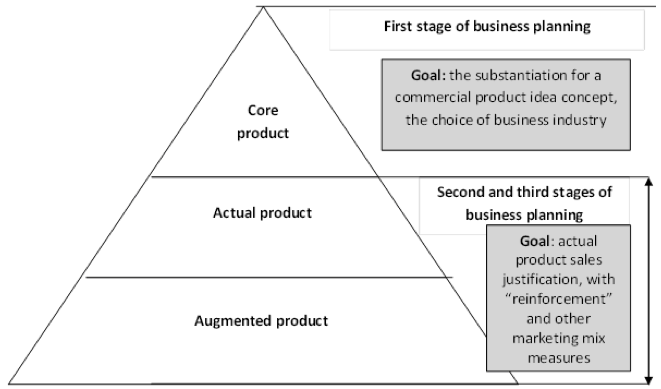
First stage. Marketing justification of the project (project marketing). The marketing rationale permeates through the entire content of the business plan and it is on a par with the financial plan and the production plan of one of its supporting structures.
Second stage. Resource planning. The purpose of resource support planning is the systematic formation of the enterprise resource base to ensure its continuous operation. Planning tasks include determining the means, risks, and alternatives to achieving the planning goals. In this case, the business plan should contain:
Third stage. Organizational planning. From the point of view of the organizational structure, special departments (bureaus) or individual specialists are engaged in planning at the enterprise. The functions of the current in-plant planning are usually performed by the planning and economic department and the economists of the departments, the sales and supply department (on special issues), the technical departments regarding the development of measures to improve the technical level, etc.
The main task of project marketing is to substantiate and elaborate the concept of a commercial product and market idea, to justify the compliance of the goals and strategies of the project with the goals and strategies of the enterprise (strategic marketing). Along with this, the project marketing goals also are:
The purpose of resourcing is to justify the feasibility of the project from the standpoint of resource capabilities. The importance of resourcing is that the bulk of the project investments is related to the resources necessary for its implementation (Novikov, Dmitriev, 2018).
Planning the organizational and legal project support provides it with a risk-free (or minimal risk) implementation in the environment: there are developed organizational and legal project action plans in the business plan, taking into account measures to reduce or prevent project risks.
The sections mix of a specific plan is refined (individualized) in accordance with the goals and specifics of the project being developed. In any case, the business plan integrates the tasks of strategic and tactical planning in the field of marketing, resource and organizational and legal support, describing the internal and external variables of a commercial, economic, technical and technological, and socioeconomic order. Historically, resourcing for the domestic economy from a methodological standpoint is the most developed issue in the entire system of planned calculations (Novikov, 2018).
The proposed systematization of business planning technology stages and their correlation with the business plan’s sections is presented in figure 3.
After the adoption of the project, the task of its practical implementation (the stage of economic exploitation of investments) arises. The tool for implementing strategic change is the enterprise’s tactical and operational plans system. Domestic theory and practice of planning has developed a powerful toolset for plans development. However, it is still not adapted to market conditions. Foreign experience is used in isolation from the Russian. It stands for project planning, including business planning, as well as marketing and financial planning (or budgeting) (Fedotova, Tikhonov, Novikov, 2018). At the same time, the strategic plans of individual subsystems (enterprises and organizations), integrated with the strategic plan of LOES, are being further developed in the business plans for project changes. Then the projects approved for implementation are included in the operational-tactical innovation and investment plans of individual enterprises: detailed planning of projects is carried out, action plans are drawn up as guides to the action of the management apparatus in the current period (Novikov, Veas Iniesta, 2018). The organizational and technical measures developed in this current period (the domestic prototype of the kaizen system) to improve the current stable activity of the enterprise are connected to the activities of individual projects. Thus, the investment phase of each project life cycle is implemented. Next comes a system of operational tactical plans, which provides for the activities of the operational (production) phase of the individual projects’ life cycle, as well as measures for the current stable activity of the enterprise (Pinkovtskaia, Balynin, Arbeláez Campillo, Rojas-Bahamón, 2019).
Figure 3
Connection of business planning process stages
and typical sections of the business plan

To create the effective mechanism for innovative development, the enterprise needs a concentration of intellectual, material, financial, and managerial resources, their effective combination in space and time.
To ensure strategic survival and further effective development of the domestic industry and first its high-tech, and therefore particularly complex industries, such as aviation, an efficient, adequate to the subject to management system is necessary based on justification and implementation of strategic changes.
The work presents the systematization, refinement and detailed elaboration of the existing developments in the domestic and foreign theory and practice in this area, which allowed the authors:
The proposed solutions for improving the substantiation and implementation of strategic changes will allow integrating strategic development plans of enterprises with the plans of individual projects, as well as with operational and tactical planning of their activities, substantiate and implement strategic changes in accordance with their future plans. As a result of the proposed solutions there will be the increased investments’ efficiency in the ongoing strategic changes by growing of their justification and streamlining implementation.
1. Fedotova, M.A., Tikhonov, A.I., Novikov, S.V. (2018). Estimating the Effectiveness of Personnel Management at Aviation Enterprises. Russian Engineering Research. 38(6), 466-468.
2. Kanashchenkov A.I., Matveev A.M., Minaev E.S., Novikov S.V. (2017). New Generation Compact Integrated Radar Systems for Aerial Vehicles. Russian Aeronautics. 60(4), 647-652.
3. Kraev V.M., Tikhonov A.I., Novikov S.V. (2018). Economic Conversion in the Aviation Industry. Russian Engineering Research. 38(4), 330-333.
4. Mindlin Y.B., Novikov S.V., Kireev S.V., Adamenk, A.A., Belitskaya O.V. (2016). Innovative territorial clusters. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues. 6(8), 251-256.
5. Mitrofanova S.V., Demjanchenko N.V., Novikov S.V., Rudakova O.V., Shmanev, S.V. (2017). The role and characteristics of the enterprises' working conditions before and after the transition to market relations: A view from macroeconomic perspective. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research. 15(13), 63-72.
6. Nedelkin A.A., Novikov S.V., Titov V.A., Mikhailova A.V., Popova L.N. (2017). Development of human resources of agro-industrial complex. Journal of Applied Economic Sciences. 12(7), 1932-1942.
7. Novikov S.V. (2018). Russian Support for Innovation and Export Growth. Russian Engineering Research. 2018. 38(4), 305-308.
8. Novikov S.V. (2018). Strategic Analysis of the Development of High-Technology Manufacturing Facilities. Russian Engineering Research. 38(3), 198-200.
9. Novikov S.V., Dmitriev O.N. (2018). Vision of Genesis of Presentation of Hi-Tech Project during Competitive Selection. Russian Engineering Research. 38(4), 320-322.
10. Novikov, S.V., Veas Iniesta, D.S. (2018). State regulation of the development of the connectivity of the Russian territory. Espacios. 39(45), 8.
11. Novosadov S.A., Burtseva T.A., Repetskaia N.V., Novikov S.V. (2017). The formation prospects of the command culture of the organization management thinking in the new paradigm of social and economic development of the society. Journal of Applied Economic Sciences. 12(7), 1996-2002.
12. Pinkovtskaia I.S., Balynin I., Arbeláez Campillo D.F., Rojas-Bahamón M.J. (2019). Small business development in Russia: results of the assessment of sectoral structure and number of employees. Espacios, 40(7), 6.
13. Sozinova A.A., Novikov S.V., Kosnikov S.N., Nemchenko G.I. Alenina E.E. (2016). Peculiarities of isolated clusters operation. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues. 6(8), 19-23.
1. Moscow Aviation Institute (MAI), 125993, Russia, Moscow, Volokolamskoe highway, 4. E-mail: ncsrm@mail.ru