

Vol. 40 (Number 35) Year 2019. Page 17
GALAUTDINOVA, Victoriia V. 1
Received: 19/06/2019 • Approved: 07/10/2019 • Published 14/10/2019
2. Analysis of the Russian cheese market growth
4. Sales of chees products in the Republic of Tatarstan
5. Options of modelling of allocation of products supply flows
ABSTRACT: Issues of management accounting and analysis taking into account the specifics of agribusiness guarantee an increase in the efficiency of agricultural production. The practical significance of the work lies in the modeling of trade flows, the justification of the strategic priorities of regional policy in order to increase the competitiveness of cheese-making enterprises. The result is the formation of a sectoral profile of the territory based on a rating system; selection of competitiveness indicators and their combinations according to the intensity of their impact on competitiveness. |
RESUMEN: Las cuestiones de contabilidad y análisis de gestión que tienen en cuenta las características específicas de los agronegocios garantizan un aumento en la eficiencia de la producción agrícola. La importancia práctica del trabajo radica en la modelización de los flujos comerciales, la justificación de las prioridades estratégicas de la política regional para aumentar la competitividad de las empresas productoras de queso. El resultado es la formación de un perfil sectorial del territorio basado en un sistema de calificación; selección de indicadores de competitividad y sus combinaciones según la intensidad de su impacto en la competitividad. |
Over the recent decades tendency towards reduction of number of dairy producers and level of their competitivness has been clearly seen. In the competitive environment, problems of supporting such enterprises is the most relevant because of channels of marketing. Methods developed by foreign and domestic scientists for industrial sectors have proved the importance of improving competitiveness of an economic entity (Program of development and distribution of productive forces …, 2008).
The purpose of APK development is to move into a new phase of production and social development through introduction of high technologies and machinery. As a result of this purpose implementation, the Republic should achieve the volume in table 1. This level will be reached through development of such areas of agriculture production as program of recovery and support of land fertility, breeding, elite seed production, using food additives of new generations and support of staffing in science.
Table 1
Forecast of production volume food-industry
APK in the Republic of Tatarstan
|
I option (inertial) |
II option (innovation) |
||||||
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2030 |
2010 |
2015 |
2020 |
2030 |
|
Whole milk products, thousand tons. |
205 |
210 |
215 |
230 |
208 |
215 |
255 |
305 |
Source: Program "Development and deployment of productive forces of the Republic
of Tatarstan on the basis of cluster approach till 2020 and for the period till 2030
From 2014, Russian cheese market continues to grow (fig. 1). Along with this, reduced growth rate of cheese production has been notices in 2016 – 2017. In 2014 – 2015, annual growth rates of cheese production were about 15-18%. In 2016 and 2017 positive directions were kept, but annual increase rates were 2.8% and 1.8% respectively (Federal State Statistics Service …, 2018; Official statistical data …, 2008; Dairy news …, 2013).
Analysis of the current demand is based on dynamics of trade flows of cheese in RF entities for 2009-2017 according to the data of Federal State Statistics Service on the Republic Kazakhstan, (Official statistical data …, 2008) (table 2).
The main reasons of production slowing down are the following:
The Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 614 of August 19, 2016, mentions the consumption rate of cheese in Russia. According to this document, the consumption rate of cheese in Russia is 7 kilograms per person a year. According to the data of the Federal State Statistics Service, in 2010-2016, consumption of cheese and brynza in RF was 6.1-6.5 kilograms per person a year (Dairy news …, 2013) (Fig. 2).
Figure 1
Production and import of cheese in the RF

-----
Table 2
Geography of cheese supplies from the regions of RF
Export of cheese by manufacturers and wholesale organizations from constituent entities of the Russian Federation, tons |
|||||||||
|
2009 1 |
2010 2 |
2011 |
2012 3 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 4 |
Bryansk oblast |
17189 |
20844 |
20109 |
21759 |
20779 |
24921 |
28349 |
32678 |
45913 |
Voronezh oblast |
28058 |
29043 |
28297 |
24923 |
28803 |
36268 |
42234 |
49224 |
17294 |
Moscow oblast |
29354 |
34056 |
39323 |
47730 |
47091 |
51056 |
41092 |
40937 |
44177 |
Krasnodar oblast |
4327 |
4255 |
1797 |
2522 |
684 |
522 |
434 |
4039 |
4387 |
The Republic of Tatarstan |
9918 |
8825 |
9981 |
11054 |
7882 |
10730 |
12553 |
10504 |
17291 |
Udmurtia |
12433 |
8736 |
8127 |
8677 |
10363 |
12025 |
16851 |
22160 |
10866 |
Altay region |
4835 |
6306 |
6153 |
5626 |
4361 |
6414 |
15379 |
14084 |
11604 |
Omsk oblast |
6997 |
12666 |
15065 |
13484 |
17287 |
22408 |
26805 |
27165 |
918 |
-----
Figure 2
Consumption of cheese per person a
year in Russia and the world, kg (2017)

In the opinion of many specialists, primary tasks of the industry are: stabilisation of a raw material base, technical re-equipment and modernisation of the industry, expansion of the assortment and improvement of product quality, production of import-substituting products, maintenance of human resources (Belov et al., 2018; Bezpalov, 2014).
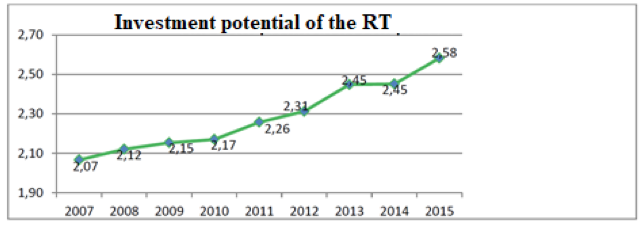
Production increase is limited by milk shortage. Growth of enterprise’s economy is directly proportional to investment aimed at overcoming of technical dependence, increase of work productivity, increase of competitiveness of products in the market, export promotion, import-substituting production, job creation, and etc. Figure 3 reflects the dynamics of investment potential in the Republic of Tatarstan (Ministry of economy …, 2000; Takhumova et al., 2016).
Figure 3
Dynamics of investment potential in the RT
In such way, in industrial police, a strategic purpose of competitiveness is suggested to be determined as an increase in demand for products due to developing competitive advantages of enterprises that provide stable social and economic development and strategic competitiveness. A. Smith thought that under market conditions, total satisfaction of consumers’ needs and the best use of resources in community in general are possible (Fatkhutdinov, 2002). Conception of forming the industrial profile is in figure 4.
Figure 4
Conception of forming the industrial profile

Evaluation of possible perspectives of competitive advantages considering influence of uncertainty factor is prior to choosing mechanisms of managing impact. Such evaluations can be obtained using scenario forecasting. To optimise a location of cheese manufacturing facilities on the territory of the Republic according to economic zones and more precise accounting of the important factor – distance between the points of production and consumption, it is necessary to model trade flows.
The Republic of Tatarstan is among the leading regions of the Russian Federation by the main macroeconomic indicators. By the gross regional product, the Republic is the six of entities of the Russian Federation, third place by agriculture, fourth place by the amount of fixed investment, fifth place by industrial production and building, eighth place by housing, and eighth place by retail trade turnover (Ministry of economy …, 2000; Ostanina et al., 2016).
Figure 5
Dynamics of GRP of the Republic of Tatarstan and GDP of the Russian Federation.

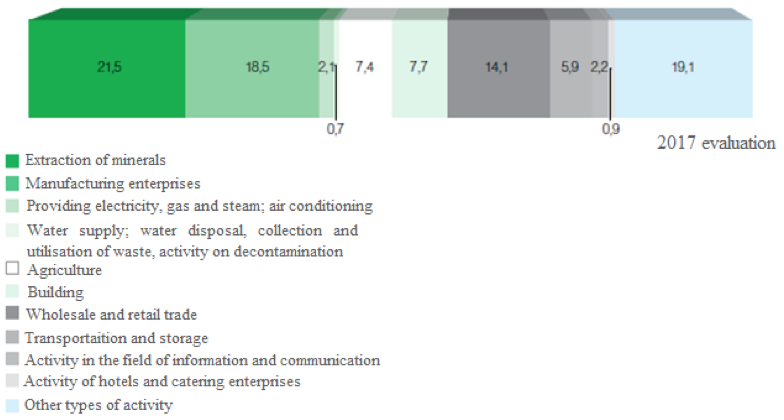
An amount of gross regional product of the Republic of Tatarstan in 2017, was 2 115.5 bln rbl, or 102.8% in comparable prices to the level of 2016 (fig.5). The main contribution to economy growth has been made by industrial production, agriculture and trade. In the structure of GRP, the main types of economic activity are extraction of minerals, manufacturing enterprises; production and distribution of electricity, gas and water; building; wholesale and retail trade; transport and connection. The structure of GRP is represented in fig. 6 (Ministry of economy …, 2000).
Improvement of competitiveness of economy of the Republic is connected to amounts of investment. Over past years Tatarstan is among the most attractive to invest regions that is due to combination of high investment potential and low investment risk. In 2017, the fixed investment was 637.6 bln rub, or 99.3% in comparable prices to the level of 2016. On January-September of 2017, by investment in fixed capital the Republic of Tatarstan was the first among regions of Volga Federal District and fourth among entities of the Russian Federation after Tyumen region, Moscow and St. Petersburg (Schoemaker, 1993; Akhmetshin et al., 2018).
Along with this, there is the analysis to reveal potential sources to grow. Thus, in September of 2017, there was meeting of the Security Council under the leadership of the President of the Republic of Tatarstan, the result of which was developing of the set of solutions aimed at reduction of administrative barriers, optimisation of entrepreneurs’ interaction with oversight bodies. On January 9, 2018, information Internet resource “Revised business” started working. This is mutual project of Ministry of Economy of the Republic of Tatarstan and Prosecutor's Office of the Republic of Tatarstan created for entrepreneurs that contains practical recommendations on passing business inspections.
Figure 6
The structure of GRP of the Republic of Tatarstan
Priorities of state investment policy for 2018 have been determined: forming and development of competitive enterprises using advanced technologies; stimulation of development of small and medium-sized business; creating conditions to provide infrastructure for investment objects; information and staff providing of investment process ant other.
In Tatarstan, such mechanism of state support of enterprises and business as tax breaks is developed in details and actively applied. According to positions of the law of the Republic of Tatarstan dated November 25, 1998 №1872 “About investment activity in the Republic of Tatarstan”, investors implementing investment projects are provided with a reduction in the rates of regional profits taxes – up to 13.5% – channeled to the budget of the Republic of Tatarstan and reduction of tax rate up to 0.1% for property newly created or purchased by an organisation to implement a project (The law of the Republic of Tatarstan …, 1998; Shvets, 2006; Heywood and Outsourcing, 2012; Solow, 1974). These breaks are provided for entities of investment activity for the pay-back period of a project but no more than seven years, and in the engineering industries, tax breaks can be provided for a period for a period of up to 13 years from the start of investment.
Priority directions of development of investment activity in the Republic of Tatarstan are implementation of the Model “Tatarstan+5+3” (Program of development and distribution of productive forces …, 2008); Novoselov, 2007), which includes 7 directions of competition, 5 basic economic complexes and 3 areas around three agglomerations. Medium-term dynamics of development of agri-business still will depend on natural and climatic conditions, state support, internal and world market situation. According to the basic scenario, in 2020 regarding 2016, production increase of agricultural products by 5.4%, food – by 15.2% that will be connected with an increase of real income of population and recovery of demand for food in the internal market and development of new export focuses and expansion of existing export focuses on food and agricultural commodities.
According to the program “Development and deployment of productive forces of the Republic of Tatarstan on the basis of cluster approach till 2020 and for the period till 2030” (Program of development and distribution of productive forces …, 2008; Lambin, 2007), the objective of food production is to form a stable and efficient producing of food, which would provide food safety and respond to needs of citizens in food in amounts and assortment enough to form balanced meals.
Mentioned objectives imply the solution of the following issues:
To bring the share of food in the total volume of consumption produced by Republican producers to 95% (Toyne and Walters, 1989).
As it was mentioned above, in the Republic of Tatarstan, in 12 municipalities, there are cheese enterprises; they are independent in marketing policy. It is expedient to develop one sale plan of products of the whole branch network to optimise transport costs and equipment loading basing on proximity to the regions where the demand for products is highest (Filosofova, 2006; Fatkhutdinov, 2002; Lvov and Porshnev, 2004). Data on using production capacities of cheese-making factories of the Republic of Tatarstan in 2018 is represented in table 3.
Table 3
Capacity of cheese-making factories of the Republic of Tatarstan
|
Municipalities |
Production capacity, tons |
Demonstrated capacity |
1 |
Aznakayevsky |
2920 |
1460 |
2 |
Apastovsky |
1825 |
0 |
3 |
Arsky |
1095 |
0 |
4 |
Baltasinsky |
8760 |
8395 |
5 |
Bugulma |
2920 |
2555 |
6 |
Buinsky |
5475 |
3650 |
7 |
Kukmorsky |
1095 |
0 |
8 |
Leninogorsky |
912,5 |
730 |
9 |
Mamadyshsky |
13140 |
12657 |
10 |
Menzelinsky |
1825 |
0 |
11 |
Sabinsky |
3650 |
2920 |
12 |
Tyulyachinsky |
1825 |
0 |
|
45 443 |
32 367 |
|
Starting data for modelling:
To transport cheese, special conditions are necessary according to international and Russian standards: temperature (0 – 12°С), humidity (not more than 80%), mutual transportation with other products, consistent stack. Refrigerators or isotherm cars are used to transport cheese. Cheese producers to deliver products to Russian regions use hired transport (realisation by themselves is much more expensive). Transportation companies get an opportunity to price more attractively due to second loads of a car for a way back. It is worth noting that an amount of transportation does not affect pricing.
Table 4
Cost of 1 t/km production from the municipalities of
the Republic of Tatarstan to points of consumption
Municipalities |
Cost of 1 t/km from municipalities of the Republic of Tatarstan where factories are located to points of consumption |
||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
9 |
|
Bryansk oblast |
Moscow oblast |
Voronezh oblast |
Belgorod oblast |
Altay region |
Pskov oblast |
Udmurtia |
|
Aznakayevsky |
60 |
40 |
50 |
70 |
175 |
65 |
45 |
Apastovsky |
60 |
40 |
50 |
70 |
175 |
65 |
45 |
Arsky |
55 |
35 |
45 |
65 |
170 |
60 |
40 |
Baltasinsky |
70 |
50 |
60 |
80 |
185 |
75 |
55 |
Bugulma |
60 |
40 |
50 |
70 |
175 |
65 |
45 |
Buinsky |
55 |
35 |
45 |
65 |
170 |
60 |
40 |
Kukmorsky |
70 |
50 |
60 |
80 |
85 |
75 |
55 |
Leninogorsky |
60 |
40 |
50 |
70 |
175 |
65 |
45 |
Mamadyshsky |
62 |
45 |
53 |
73 |
178 |
70 |
50 |
Menzelinsky |
62 |
45 |
53 |
73 |
178 |
70 |
50 |
Sabinsky |
70 |
50 |
60 |
80 |
185 |
80 |
60 |
Tyulyachinsky |
55 |
37 |
47 |
65 |
170 |
60 |
40 |
-----
Table 5
Calculation of a supply route
|
Municipalities |
Cost of 1 t/km from municipalities of the Republic of Tatarstan where factories are located to points of consumption |
|||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|||
Bryansk |
Moscow |
Voronezh |
Krasnodar |
Barnaul |
Omsk |
Izhevsk |
|||
1 |
Aznakayevsky |
1550.7 |
1138 |
1180.5 |
1859.9 |
2453.5 |
1569.6 |
321 |
|
2 |
Apastovsky |
1219.8 |
859 |
963.6 |
1691.5 |
2881.4 |
1997.5 |
604 |
|
3 |
Arsky |
1276.6 |
881 |
1099.4 |
1859.4 |
2751.2 |
1867.3 |
345 |
|
4 |
Baltasinsky |
1303.7 |
925 |
1135.8 |
1895.8 |
2670.5 |
1839 |
383 |
|
5 |
Bugulma |
1463 |
1141 |
1135.5 |
1814.9 |
2443.6 |
1559.7 |
345 |
|
6 |
Buinsky |
1200.3 |
825 |
931.8 |
1659.6 |
2909.2 |
2025.3 |
543 |
|
7 |
Kukmorsky |
1372.2 |
1020 |
1195 |
1955 |
2682.4 |
1798.5 |
304 |
|
8 |
Leninogorsky |
1521.5 |
1131 |
1129.8 |
1809.2 |
2473.3 |
1589.5 |
366 |
|
9 |
Mamadyshsky |
1387.2 |
994 |
1210.1 |
1931.6 |
2613.8 |
1729.9 |
233 |
|
10 |
Menzelinsky |
1511.4 |
1113 |
1287.8 |
1967.2 |
2479.6 |
1595.7 |
245 |
|
11 |
Sabinsky |
1321.7 |
926 |
1144.5 |
1904.5 |
2718.4 |
1834.5 |
342 |
|
12 |
Tyulyachinsky |
1299.2 |
906 |
1122.1 |
1882.1 |
2711.5 |
1827.6 |
321 |
|
-----
Table 6
Consumer prices for 1 kg of cheese less transport
expenditures and contribution margin*
|
Municipalities |
Average annual production capacity, tons |
Consumer prices for 1 kg of cheese less transport expenditures and contribution margin |
||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
9 |
|||
Bryansk oblast |
Moscow oblast |
Voronezh oblast |
Belgorod oblast |
Altay region |
Pskov oblast |
Udmurtia |
|||
1 |
Aznakayevsky |
2920 |
398.6822 |
478.5164 |
424.128 |
364.062 |
263.6418 |
446.0206 |
427.7846 |
2 |
Apastovsky |
1825 |
398.68 |
478.52 |
424.13 |
364.06 |
263.64 |
446.02 |
427.78 |
3 |
Arsky |
1095 |
403.38 |
483.22 |
428.83 |
368.76 |
268.34 |
450.72 |
432.48 |
4 |
Baltasinsky |
8760 |
389.28 |
469.12 |
414.73 |
354.66 |
254.24 |
436.62 |
418.38 |
5 |
Bugulma |
2920 |
398.68 |
478.52 |
424.13 |
364.06 |
263.64 |
446.02 |
427.78 |
6 |
Buinsky |
5475 |
403.38 |
483.22 |
428.83 |
368.76 |
268.34 |
450.72 |
432.48 |
7 |
Kukmorsky |
1095 |
389.28 |
469.12 |
414.73 |
354.66 |
348.24 |
436.62 |
418.38 |
8 |
Leninogorsky |
912,5 |
398.68 |
478.52 |
424.13 |
364.06 |
263.64 |
446.02 |
427.78 |
9 |
Mamadyshsky |
13140 |
396.80 |
473.82 |
421.31 |
361.24 |
260.82 |
441.32 |
423.08 |
10 |
Menzelinsky |
1825 |
396.80 |
473.82 |
421.31 |
361.24 |
260.82 |
441.32 |
423.08 |
11 |
Sabinsky |
3650 |
389.28 |
469.12 |
414.73 |
354.66 |
254.24 |
431.92 |
413.68 |
12 |
Tyulyachinsky |
1825 |
403.38 |
481.34 |
426.95 |
368.76 |
268.34 |
450.72 |
432.48 |
Total |
45442.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*data as of December 31, 2018 (Federal State Statistics Service … 2018).
The advantage of this method is accounting of a distance between human settlements where cheese making factories are located and regions where product is sold according to road infrastructure of Russia. This distance has been formed with a use of special calculation programs in the Internet presenting an optimal transport routes in accordance with modern navigation systems that consider the diversified network of road infrastructure of Russia. A distance is calculated between human settlements and capital cities of regions, because there is a wide network of shops to sale products, road traffic junctions and in capital regions the bigger part of population is concentrated, consequently, consumption of cheese is bigger than in a periphery. Structure of sale of Tatarstan cheese and cheese product in 2017 is represented in tables 7, 8.
Table 7
Structure of sale of Tatarstan
cheese in 2017
Types of product and Russian regions |
Export form Republic |
Import into Republic |
Cheeses, t |
17291.4 |
3383.4 |
Bryansk oblast |
‒ |
1812.7 |
Moscow oblast |
11600.5 |
243.3 |
Ryazan oblast |
70 |
25 |
Moscow city |
419.7 |
19.3 |
The Komi Republic |
128 |
‒ |
Pskov oblast |
5 |
‒ |
St. Petersburg |
1545.9 |
‒ |
Republic of Adygea |
‒ |
4.3 |
Krasnodar oblast |
856 |
‒ |
Republic of Bashkortostan |
102.3 |
24 |
Mari El Republic |
5.6 |
149.7 |
The Republic of Mordovia |
‒ |
23.1 |
Udmurtia |
137 |
1013.6 |
Chuvash Republic |
0.5 |
‒ |
Perm oblast |
2.1 |
2 |
Kirov oblast |
102 |
2.4 |
Samara oblast |
75 |
‒ |
Saratov oblast |
68 |
‒ |
Ulyanovsk oblast |
39.2 |
‒ |
Sverdlovsk oblast |
1193.4 |
32 |
Tyumen region |
0.9 |
‒ |
including: |
||
Khanty – Mansiysk |
||
Autonomous Region Ugra |
0.9 |
‒ |
Chelyabinsk oblast |
910.3 |
‒ |
Novosibirsk oblast |
30 |
32 |
------
Table 8
Structure of sale of Tatarstan
cheese product in 2017
Cheese products, t |
180.8 |
2005.2 |
Ryazan oblast |
‒ |
299 |
Tambov oblast |
‒ |
64.6 |
Yaroslavskaya oblast |
‒ |
15.4 |
Novgorod oblast |
5 |
‒ |
Republic of Bashkortostan |
45 |
‒ |
Mari El Republic |
‒ |
122.4 |
The Republic of Mordovia |
‒ |
1 |
Udmurtia |
48 |
328 |
Chuvash Republic |
1 |
‒ |
Perm Krai |
‒ |
363.8 |
Sverdlovsk oblast |
38 |
‒ |
Chelyabinsk oblast |
43.8 |
‒ |
Omsk oblast |
‒ |
811 |
Structure of sale of Tatarstan cheese and cheese product in 2018 is represented in tables 9, 10.
-----
Table 9
Structure of sale of Tatarstan cheese in 2018
Sold production in January-September of 2018 |
|||
In total |
including |
||
Export to regions of the Russian Federation |
Sold in the Republic of Tatarstan |
||
Cheeses |
11368.5 |
9995.4 |
1373.1 |
Cheese product |
9536.7 |
4789.6 |
4747.1 |
Types of products and Russian regions |
Export form Republic |
Import into Republic |
|
Cheeses, tons |
9995.4 |
2797.9 |
|
The Central Federal District |
8472 |
1429.8 |
|
Bryansk oblast |
‒ |
1110.5 |
|
Kaluga oblast |
‒ |
2 |
|
Moscow oblast |
8472 |
194 |
|
Ryazan oblast |
‒ |
58 |
|
Tambov oblast |
‒ |
0.1 |
|
Yaroslavskaya oblast |
‒ |
0.5 |
|
Moscow |
‒ |
64.7 |
|
Northwestern Federal District |
85.4 |
0.3 |
|
The Komi Republic |
7.4 |
‒ |
|
Pskow oblast |
‒ |
0.3 |
|
St.Petersburg |
78 |
‒ |
|
South Federal District |
929 |
7.9 |
|
Republic of Adygea |
‒ |
7.9 |
|
Krasnodar oblast |
929 |
‒ |
|
Volga Federal District |
186.9 |
1315.3 |
|
Republic of Bashkortostan |
18.5 |
106 |
|
Mari El Republic |
2.5 |
122 |
|
The Republic of Mordovia |
‒ |
67.2 |
|
Udmurtia |
121.6 |
999.5 |
|
Perm kray |
‒ |
17.8 |
|
Kirov oblast |
17 |
1.6 |
|
Nizhny Novgorod oblast |
7 |
‒ |
|
Samara oblast |
17 |
1.2 |
|
Ulyanovsk oblast |
3.3 |
‒ |
|
Ural federal district |
322.1 |
27.4 |
|
Sverdlovsk oblast |
239.5 |
27.4 |
|
Chelyabinsk oblast |
82.6 |
‒ |
|
Siberian Federal District |
‒ |
17.2 |
|
Omsk oblast |
‒ |
17.2 |
|
-----
Table 10
Structure of sale of Tatarstan
cheese product in 2018
Cheese products, tons |
4789.6 |
2219.7 |
The Central Federal District |
1670 |
284.1 |
Bryansk oblast |
‒ |
14.2 |
Kaluga oblast |
10 |
‒ |
Moscow oblast |
855 |
‒ |
Ryazan oblast |
88 |
235 |
Tambov oblast |
‒ |
17.9 |
Tver region |
58.5 |
‒ |
Yaroslavskaya oblast |
‒ |
8.4 |
Moscow |
658.5 |
8.6 |
Northwestern Federal District |
572.2 |
‒ |
The Komi Republic |
76.2 |
‒ |
St.Petersburg |
496 |
‒ |
South Federal District |
17 |
‒ |
Rostov District |
17 |
‒ |
Volga Federal District |
1021.8 |
774 |
Republic of Bashkortostan |
32.3 |
‒ |
Mari El Republic |
10 |
7.8 |
Udmurtia |
88.4 |
227 |
Chuvash Republic |
2.8 |
‒ |
Perm kray |
‒ |
539.2 |
Kirov oblast |
25.6 |
‒ |
Nizhny Novgorod oblast |
2.7 |
‒ |
Samara oblast |
48 |
‒ |
Saratov oblast |
785 |
‒ |
Ulyanovsk oblast |
27 |
‒ |
Perm kray |
‒ |
|
Ural federal district |
1463.6 |
|
Sverdlovsk oblast |
850.8 |
|
Tyumen oblast |
13.2 |
|
Chelyabinsk oblast |
599.6 |
|
Siberian Federal District |
45 |
1161.6 |
Novosibirsk oblast |
45 |
‒ |
Omsk oblast |
‒ |
1161.6 |
Allocation of flows has been modelled based on demonstrated capacity of production capacities (in total 32 367 tons a year). To solve this problem in Excel using “Find solution”, it is necessary to make two matrixes, the first contains starting data, the second – to calculate and reflect results.
Restrictions of production capacities imply that calculated values cannot exceed existing. Thus, for production capacities of Baltasinsky district, this limitation can be represented as follows:
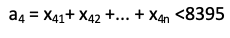
Restrictions on the volume of satisfied demand imply the achievement of a level not less than the actual value of the implementation; for the Moscow oblast the restriction looks like as follows:
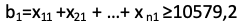
Consequently, target function that minimises transport costs will be as follows:

Table 11
Allocation of flows according to the first option of modelling
Municipalities |
Allocation of flows, tons |
|||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
9 |
||
32 367.00 |
Bryansk oblast |
Moscow oblast |
Voronezh oblast |
Belgorod oblast |
Altay region |
Pskov oblast |
Udmurtia |
|
1 460.00 |
0.00 |
1 460.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
Aznakayevsky |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Apastovsky |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Arsky |
8 395.00 |
0.00 |
1 963.46 |
0.00 |
1 050.57 |
2 778.85 |
0.00 |
2 602.12 |
Baltasinsky |
2 555.00 |
0.00 |
75.60 |
2 479.40 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Bugulma |
3 650.00 |
0.00 |
3 650.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Buinsky |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Kukmorsky |
730.00 |
0.00 |
510.16 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
219.84 |
0.00 |
Leninogorsky |
12 657.00 |
10 994.95 |
0.00 |
1 662.05 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Mamadyshsky |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Menzelinsky |
2 920.00 |
0.00 |
2 920.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Sabinsky |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Tyulyachinsky |
10 994.95 |
10 579.22 |
4 141.45 |
1 050.57 |
2 778.85 |
219.84 |
2 602.12 |
|
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
100% |
||
Maximum income |
12850370.86 |
|||||||
Basing on calculations of option 1 of modelling, it is expedient to export product only from 7 municipalities: Aznakayevsky, Baltasinsky, Bugulma, Buinsky, Leninogorsky, Mamadyshsky, Sabinsky (table 11). The following geography of supplies is expedient economically: producers of Mamadyshsky to Bryansk oblast (87% of production volume), Aznakayevsky – to Moscow oblast (100% of demonstrated production capacities in 2018), Baltasinsky – to Moscow (22%) and Belgorod (12%) oblasts, Altay (33%), Udmurtia (33%), Bulguma – to Moscow (3%) and Voronezh oblasts (97%), Buinsky – in 2018, all capacities to Moscow, Leninogorsky – to Moscow (70%) and Pskov oblasts (30%), Sabinskiy – in 2018, all capasities to Moscow oblast.
Max income= SUMPRODUCT (H45:N56; H28:N39) = 12 850 370,86
Allocation of flows has been modelled based on demonstrated capacity of production capacities (in total 45 442,5 tons a year). To solve this problem in Excel using “Find solution”, it is necessary to make two matrixes, the first contains starting data, the second – to calculate and reflect results.
Restritions of production capacities imply that calculated values cannot exceed existing. Thus, for production capacities of Baltasinsky district, this limitation can be represented as follows:
a4 = х41+ х42 +... + х4n <8760
Restrictions on the volume of satisfied demand imply the achievement of a level not less than the actual value of the implementation; for the Moscow oblast the restriction looks like as follows:
b1=х11 +x21 + …+ х n1 ≥14 852,98
Table 12
Allocation of flows according to the second option of modelling
|
Municipalities |
|
Allocation of flows, tons |
||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
9 |
|||
45 442.50 |
Bryansk oblast |
Moscow oblast |
Voronezh oblast |
Belgorod oblast |
Altay region |
Pskov oblast |
Udmurtia |
||
4 015.00 |
0.00 |
4 015.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
||
1 |
Aznakayevsky |
3 650.00 |
0.00 |
617.98 |
515.09 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
2 516.93 |
2 |
Apastovsky |
2 920.00 |
0.00 |
2 920.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
3 |
Arsky |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
4 |
Baltasinsky |
4 380.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
4 380.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
5 |
Bugulma |
7 300.00 |
0.00 |
7 300.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
6 |
Buinsky |
3 901.44 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
3 901.44 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
7 |
Kukmorsky |
1 825.00 |
905.59 |
0.00 |
919.41 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
8 |
Leninogorsky |
14 531.06 |
14 531.06 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
9 |
Mamadyshsky |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
10 |
Menzelinsky |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
11 |
Sabinsky |
2 920.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
1 474.98 |
0.00 |
308.65 |
1 136.38 |
12 |
Tyulyachinsky |
15 436.65 |
14 852.98 |
5 814.50 |
1 474.98 |
3 901.44 |
308.65 |
3 653.31 |
|
100.0% |
100.00% |
100.00% |
100.00% |
100.00% |
100.00% |
100.00% |
|||
Maximum income |
18 563 505.90 |
||||||||
Basing on calculations of option 2 of modelling, it is expedient to export product only from 7 municipalities: Aznakayevsky, Apastovsky, Arsky, Bugulma, Buinsky, Kukmorsky, Leninogorsky, Mamadyshsky, Tyulyachinsky (Table 12). The following geography of supplies is expedient economically: producers of Mamadyshsky – to Bryansk oblast (100% of production amount), Aznakayevsky – to Moscow oblast (100% of demonstrated production capacities in 2018), Apastovsky – to Moscow (14%) and Voronezh (14%) oblasts, Udmurtia (69%), Arsky – to Moscow oblast (100%), Bugluma – in 2018, all capacities to Voronezh oblast, Tyulyachinsky – to Belgorod (51%), Pskov (10%) oblasts and Udmurtia (39%), Buinsky – to Moscow oblast (100% of demonstrated production capacities in 2018).
Max income =SUMPRODUCT (H45:N56;H28:N39) = 18 563 505,90
Initially, modelling of trade flows is aimed at determining manufacturing facilities on the basis of accounting of consumption, production capacities, optimisation of transport costs. However, transport costs in monetary terms can be corrected in value of any other costs directly connected with manufacturing facilities allocations. The advantage of this method is the ability to take into account factors affecting cost of manufacturing facilities allocation (for example, capital investment or advantages of system of preferences given on this territory) by correcting a sum of transport costs. Also, transport modelling allows considering and comparing economic benefits of introduction of certain productions.
Further, it is necessary to consider which municipal areas have opportunities for the development and placement of cheese production. For this purpose, republics should be evaluated and combined in similar or complementary clusters. Based on the results of the application of the proposed methodological approach and toolkit for the “cheese” product group, proposals on forming the industrial profile of the Republic of Tatarstan and recommendations on territorial development of this production inside the Republic, which may be strategic and tactical focus of industrial policy of a territory, have been developed.
Akhmetshin, E.M., Vasilev, V.L., Mironov, D.S., Zatsarinnaya, Е.I., Romanova, M.V., Yumashev, A.V. (2018). Internal Control System in Enterprise Management: Analysis and Interaction Matrices. European Research Studies Journal, 21(2), 728-740.
Belov, A.S., Zhebit, M.E., Moskovskova, E.A., Neutov, ETC. (2018). The dairy industry 2018-2019. Moscow: Nattsionalny souz proizvoditeley moloka. Available at: https://milknews.ru/redaktsiya/zakazat-mo-2018/
Bezpalov, V.V. (2014). Diagnostics methods for purposes of restructuring of regional management system. Life Science Journal, 11(9 SPEC. ISSUE), 9, 56-59.
Dairy news (2013) Available at: www.dairynews.ru
Fatkhutdinov, R.A. (2002). Competitiveness: Economics, Strategy, Management. St. Petersburg: Piter.
Federal State Statistics Service (2018). Retrieved from: www.gks.ru
Filosofova, T.G. (2006). Managing Competitiveness in World Markets. Moscow: Nauchnay kniga.
Heywood, J.B. (2012) Outsourcing: in Search of Competitive Advantage. Moscow: Williams.
Lambin, J.J. (2007). Market-Driven Management. St. Petersburg: Piter.
Lvov, D.C. and Porshnev, A.G. (2004). Managingof Socio-Economic Development of Russia: Concepts, Goals, Mechanisms. Moscow: Economica.
Ministry of economy of the Republic of Tatarstan. (2000). Retrieved from: http://mert.tatarstan.ru/
Novoselov, A.S. (2007). Regional Market System: Problems of Theory and Practice. Novosibirsk: Publishing House of the IEOPP, SB RAS.
Official statistical data. (2008). Retrieved from: www.fedstat.ru
Ostanina, S.S., Avilova, V.V., Aleksandrov, A.Y., Makhotkina, L.Y., Pugacheva, A.S. (2016). Institutional aspects of economic systems management. Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 7(1), 84-92.
Program of development and distribution of productive forces of the Republic of Tatarstan on the basis of the cluster approach to 2020 and 2030. (2008). Retrieved from: http://mert.tatarstan.ru/programma-razvitiya-i-razmeshcheniya.htm?pub_id=22656
Schoemaker, P.J.H. (1993). Multiple scenario development: its conceptual and behavioral foundation. Strategic Management Journal,14(3), 193–213.
Shvets, I.Yu. (2006). Analysis of the development of the theory of competitiveness. Problems of Economics and Management, 3, 44-49.
Solow, R.M. (1974). The Economics of Resources or the Resources of Economics. Lection in honour of Richard T. Ely. Milestones of Economic Thought, 2, 304-311.
Takhumova, O.V., Lovyannikova, V.V., Konovalova, I.A. (2016). Innovative mechanism for increasing the efficiency of regional agroindustrial sector. Actual Problems of Economics, 184(10), 228-234.
The law of the Republic of Tatarstan of November 25, 1998 No. 1872 “About investment activity in the Republic of Tatarstan”. Retrieved from: http://docs.cntd.ru/document/424031935
Toyne, B., Walters, P. (1989). Global Marketing Management: A Strategic Perspective. Massachusetts: Allyn & Bacon, pp. 55–78.
1. Center for Advanced Economic Research of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Tatarstan. Kazan. Russian Federation; LLC “Azbuka Syra”. Kazan. Russian Federation. E-mail: galvika26@yandex.ru