

Vol. 39 (Number 48) Year 2018. Page 31
Elena Yu. AVKSENTEVA 1; Ilya B. GOSUDAREV 2; Sergey Yu. AVKSENTIEV 3; Elena Z. VLASOVA 4
Recibido: 22/06/2018 • Aprobado: 06/08/2018 • Publicado 29/11/2018
ABSTRACT: The work makes an attempt to solve the problem of classification of articles of ICCS scientific conferences in 2006-2016 by means of intellectual data analysis. To extract keywords from research articles the authors used a statistical measure, used to assess the importance of the word in the context of the TF-IDF document. For the analysis of the parts of speech, a package of libraries and programs for symbolic and statistical processing of natural language – NLTK – was used. This intellectual analysis allows predicting the basic topics and to classify research articles of scientific conference participants. In addition, visual modelling of the content of information resources is essential for solving the tasks of knowledge management in education. Frequency analysis of terms and the generation of visual models can be applied in computer-aided educational content management systems. |
RESUMEN: El trabajo intenta resolver el problema de la clasificación de los artículos de las conferencias científicas del ICCS en 2006-2016 mediante el análisis de datos intelectuales. Para extraer palabras clave de los artículos de investigación, los autores utilizaron una medida estadística, utilizada para evaluar la importancia de la palabra en el contexto del documento TF-IDF. Para el análisis de las partes del habla, se utilizó un paquete de bibliotecas y programas para el procesamiento simbólico y estadístico del lenguaje natural (NLTK). Este análisis intelectual permite predecir los temas básicos y clasificar los artículos de investigación de los participantes de la conferencia científica. Además, el modelado visual del contenido de los recursos de información es esencial para resolver las tareas de la gestión del conocimiento en educación. El análisis de frecuencia de los términos y la generación de modelos visuales se pueden aplicar en sistemas de gestión de contenido educativo asistido por computadora. |
The volume of information circulating in the world telecommunication network and stored on servers shows the explosive growth dynamics. The task of keywords and phrases extraction arises in many areas: information retrieval, electronic document management, linguistics, business process monitoring, research, education, library and patent technologies, etc. The volume and dynamics of information in these areas determine the problem of automatic keywords and phrases extraction as urgent. These words and phrases can be used to create and improve terminological resources, as well as to efficiently process documents in information retrieval systems (indexing, abstracting and classification).
The first theoretical attempts to solve the problem of keywords extraction ("supporting", "generalizing") were undertaken in the article "Inner Speech and Understanding" by A.N. Sokolov (Sokolov 1941). The fundamentals of modern understanding of keywords are presented in the works of L.V. Sakharny, S.A. Sirotko-Sibirsky, and A.S. Shtern. The fundamentals in a nutshell are (Sakharny and Shtern 1988, Sirotko-Sibirsky and Shtern 1988):
The extraction of keywords from a number of candidates includes the calculation of the informative weights, which allows assessing their relevance to each other. Here the well-known TF-IDF metric should be mentioned (Manning and Raghavan 2011).
TF-IDF (TF-term frequency, IDF- inverse document frequency) is a statistical measure used to assess the importance of a word in the context of a document that is part of a collection of documents or a corpus. The weight of a word is proportional to the amount of use of this word in the document and inversely proportional to the frequency of the word usage in other documents of the collection.
The TF-IDF measure is often used for text analysis and information retrieval, for example, as one of the criteria for the relevance of a document to a search query, when calculating the proximity of the documents of the clustering.
TF (term frequency) is the ratio of the number of term entries to the total number of words in a document.
IDF (inverse document frequency) is the inverse frequency with which a word occurs in the collection's documents.
This article analyses the data obtained from the sets of articles from the ICCS conference (International Conference on Computational Science).
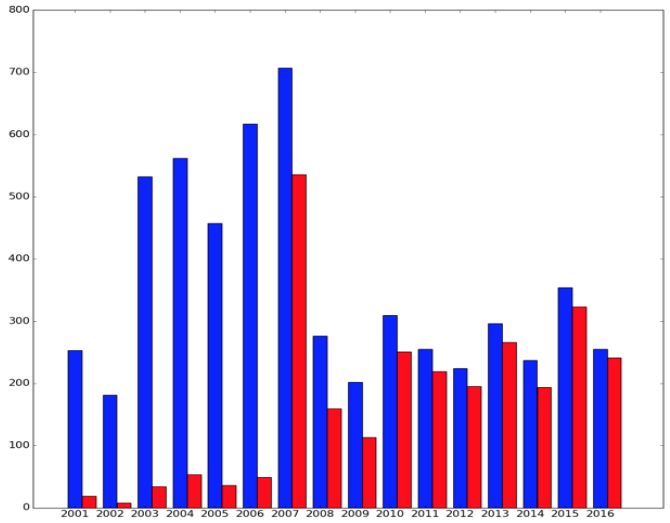
The data used for the study is a set of articles from the ICCS (International Conference on Computational Science), which consists of 5717 articles. 3021 articles of them do not have keywords from authors. The average number of articles per year is 357.
The histogram (Fig. 1) shows the distribution of articles over several years:
- red colour shows the number of articles with keywords from authors;
- blue colour shows the total number of articles.
Figure 1
Distribution of articles by years
In order to correctly extract keywords, the analysis of parts of speech for authors’ keywords was carried out. It allowed determining the fact that the length of the most popular key phrases does not exceed three words. It was also determined that most key phrases have several most commonly used combinations of parts of speech (for example, a phrase consisting of two nouns).
To analyse keywords the NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) package was used. NLTK is a package of libraries and programs for symbolic and statistical processing of natural language written in the Python. NLTK contains graphical representations and sample data. This package is convenient because it is accompanied by comprehensive documentation, including a book explaining the basic concepts behind the tasks of natural language processing that can be performed by this package (Bird 2009).
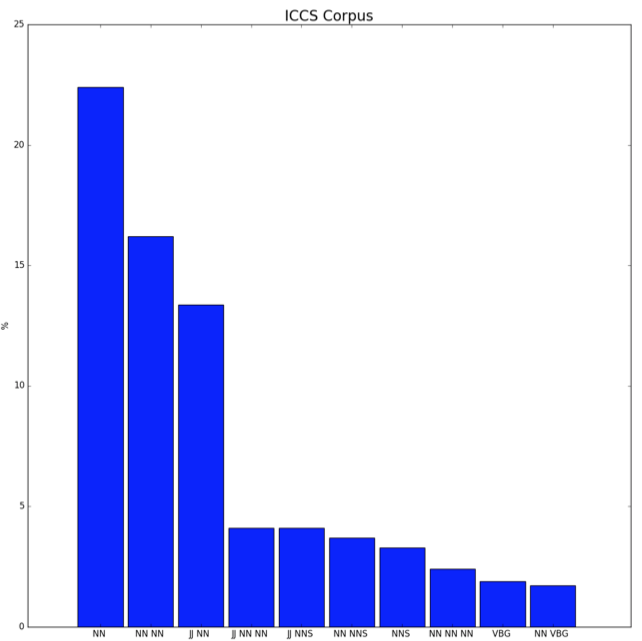
A histogram with the results obtained after determining the parts of speech is shown in Fig. 2. This diagram shows the distribution of the parts of speech of all articles of the ICCS for 2006-2016.
The notation conventions used in the histogram:
NN - nouns;
NNS - plural nouns;
JJ - adjectives;
VBG - gerund.
Figure 2
The histogram of the distribution of parts of speech
Also, based on the extracted data, the graphs were constructed, with the keywords of the authors as nodes. The graph with the keywords of the articles of the 2013 conference is shown in Fig. 3.
The figure shows that the graph consists of a number of densely connected components with a small average clustering coefficient and a small average path length inside the component.
Figure 3
The graph of keywords for 2013
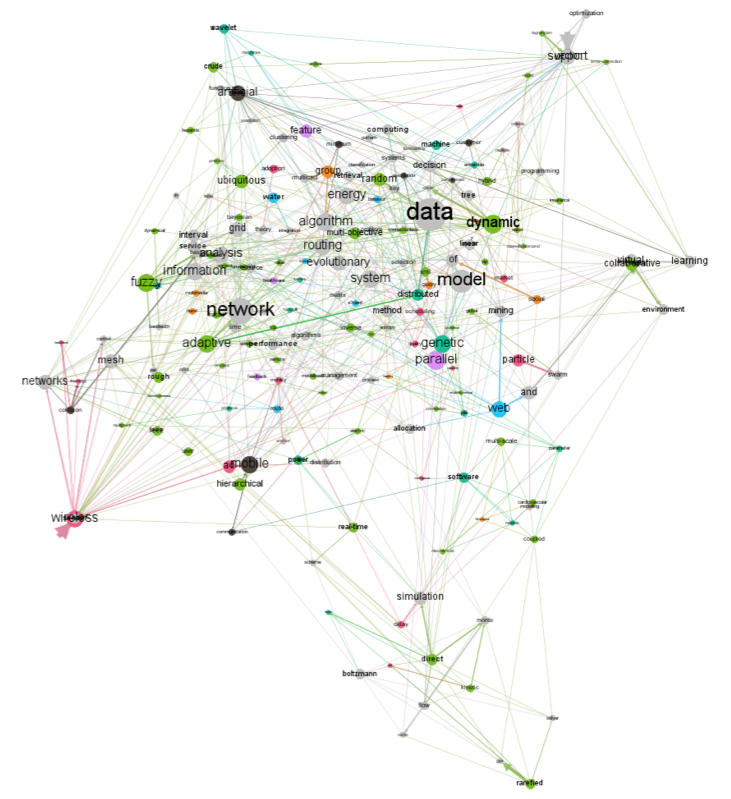
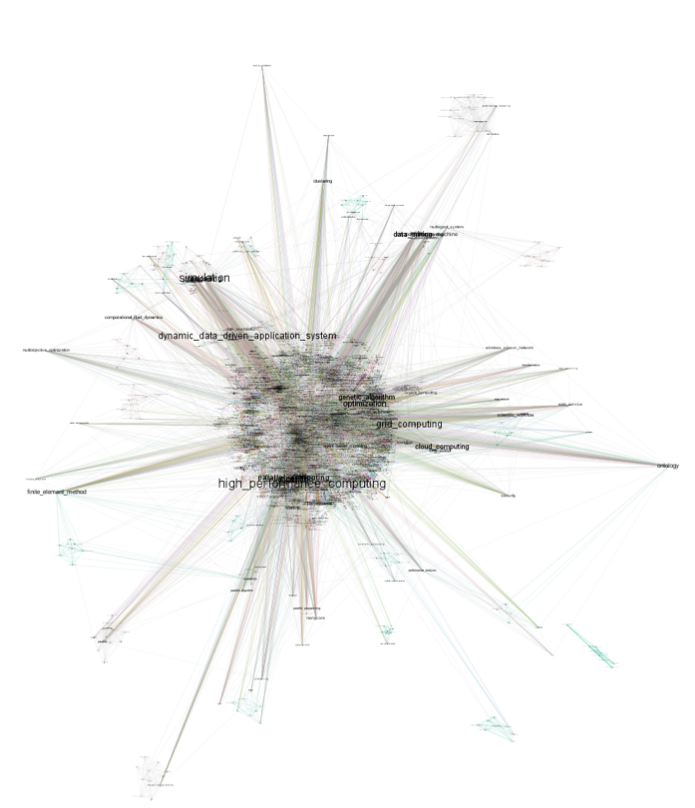
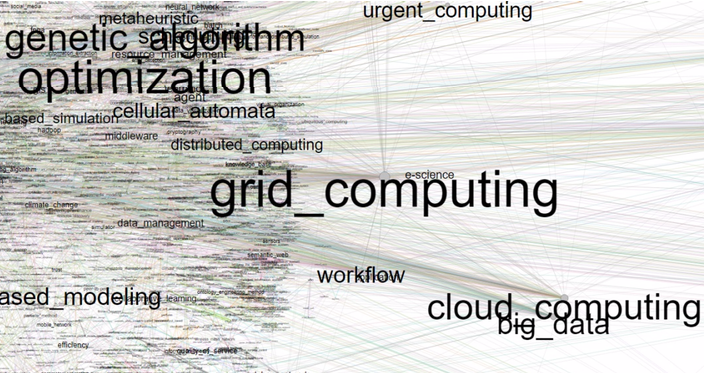
Figure 4 shows a graph consisting of the keywords of the conference articles for 2006-2016. The keywords with the largest number of connections are highlighted with a larger font on the graph.
Figure 4
The graph of keywords for 2006-2016

For a better visual expression Fig. 5 shows an enlarged fragment of the graph.
Figure 5
The fragment of the graph
This work analysed the parts of the speech of the authors' keywords. In future, this analysis will allow considering frequently used parts of speech in authors’ keywords when extracting keywords from the articles.
Based on the extracted keywords, a graph was constructed with keywords as nodes. According to the characteristics of the graph, it is possible to make conclusions about the main topics and classify the research articles of conference participants.
The visual modelling of the information resources content is of significant importance for solving the problems of knowledge management, including the areas of e-learning and corporate training. Frequency analysis of terms and generation of visual models can be used to build computer-aided components of content management systems, bibliographic lists, and tasks for trainees. The experience of using these tools in working with master’s degree students of the study program "Corporate e-Learning" (Herzen State Pedagogical University of Russia, 2017-2018) has shown a stable positive dynamics of the formation of knowledge components of study and research competency of students (Barakhsanova et al. 2016).
Barakhsanova E.A., Savvinov V.M., Prokopyev M.S., Vlasova E.Z. and Gosudarev I.B. (2016). Adaptive Education Technologies to Train Russian Teachers to Use E-Learning. IEJME: Mathematics Education, 11(10), 3447-3456.
Bird S. (2009). Natural Language Processing with Python. O'Reilly Media Inc. ISBN 0-596-51649-5.
Bolshakova E.I., Klyshinski E.S., Lande D.V., et al. (2011). Avtomaticheskaya obrabotka tekstov na estestvennom yazyke i kompyuternaya lingvistika [Automatic processing of texts in natural language and computer linguistics: Textbook]. Moscow: MIEM.
Manning K.D. and Raghavan P. (2011). Vvedenie v informatsionny poisk [Introduction to information retrieval]. Translation from English. Moscow: Vilyams.
Sakharny L.V. and Shtern A.S. (1988). Nabor klyuchevykh slov kak tip teksta [A set of keywords as a type of text]. Leksicheskie aspekty v sisteme professionalno-orientirovannogo obucheniya inoyazychnoy rechevoy deyatelnosti. Perm: Perm Politechnical University.
Sirotko-Sibirsky S.A. and Shtern A.S. (1988). K izmereniyu kachestva raboty predmetizatora [On measuring the quality of the work of the prefabricator]. Predmetnyj poisk v tradicionnykh i netradicionnykh informatsionno-poiskovykh sistemakh, 8. Leningrad: GPB.
Sokolov A.N. (1941). Vnutrennyaya rech i ponimanie [Inner speech and understanding]. Uchenye zapiski Gosudarstvennogo nauchno-issledovatelskogo instituta psihologii, 2, 99–146.
1. St. Petersburg National Research University of Information Technology, Mechanics and Optics, 197101, St. Petersburg, Kronversky prospect, 49, Russia. E-mail: avksentievaelena@rambler.ru
2. St. Petersburg National Research University of Information Technology, Mechanics and Optics, 197101, St. Petersburg, Kronversky prospect,
3. Saint Petersburg Mining University, 2, 21st Line, St Petersburg 199106, Russia
4. Herzen State Pedagogical University of Russia, 6 Kazanskaya (Plekhanova) St., 191186, St. Petersburg, Russia