

 Vol. 39 (Number 35) Year 2018. Page 1
Vol. 39 (Number 35) Year 2018. Page 1
Anara ALIMBEKOVA 1; Saltanat ABILDINA 2; Issatay UTEBAYEV 3; Kalipa ATEMOVA 4
Received: 14/03/2018 • Approved: 02/05/2018
ABSTRACT: In the article, student self-governance in the system of higher education is defined as a critical success factor for professional leadership skills of students. Building professional leadership skills is a key to increased profitability as well. The student self-governance determines and contributes to the development of professionally important skills such as organizational, communicative and personal qualities. Today it is critically important to support students to take responsibility for their work and increase their competitiveness. Since to achieve success and maintain a competitive advantage, we must be able to draw on the most important resource – the skills of the workforce. |
RESUMEN: En el artículo, la autogestión del estudiante en el sistema de educación superior se define como un factor de éxito crítico para las habilidades de liderazgo profesional de los estudiantes. Desarrollar habilidades de liderazgo profesional es la clave para una mayor rentabilidad también. El autogobierno del alumno determina y contribuye al desarrollo de habilidades profesionales importantes, tales como cualidades organizativas, comunicativas y personales. Hoy es críticamente importante ayudar a los estudiantes a asumir la responsabilidad de su trabajo y aumentar su competitividad. Dado que para lograr el éxito y mantener una ventaja competitiva, debemos ser capaces de aprovechar el recurso más importante: las habilidades de la fuerza de trabajo. |
It is quite common in today’s society that technological advancements effect on the role and functions of the universities. The university has taken a central place for ages in developing students’ core skills, cultural and education competencies.
At the first stage of adaptation and the stage of entering new professional environment the university serves a crucial role. In this education environment students become members who actively participate in meeting social needs by sharing with their knowledge. A social adjustment and psychological well-being greatly contribute to a personal and professional development in its own way. The quality education assurance for the youth is the primary requirement for highly competitiveness, cultural and economic development of independent country. In terms of promoting and creating conditions that foster student success in university has been always important. They ensure students’ creative potential, communicative skills development and increasing leadership qualities.
Professionally significant leadership qualities - intellectual, business and organizational set of qualities: critical and positive thinking, creativity, personal determination, strong-willed, well-organized, the ability to adapt and respond to changing work situations and environments, the ability to create a team, set its goals and values, a sense of partnership, the ability to define roles and distribute tasks among team members, the ability to inspire them to perform tasks and motivate, the ability to coordinate work and balance workload, support in difficult situations, the ability to control the outcome, to define a leader, performers and listeners, followers, the recognized leadership.
R. Stogdill defines «leadership» as the two persons communication in a social community. He also distinguishes the following leadership qualities like mind-decency, the desire for knowledge, responsibility, reliability, socially activeness [1].
Leadership is the specially organized process of accumulating cultural and team factors arisen in the environment. [2].
In this regard, the leadershıp is considered as a process and a quality. The leadership process The leadership process is the ongoing relationship between leaders and followers to accomplish company goals. The process of leaders and followers working together is different for each business. Leadership qualities as a system is a set of properties, a true leader is someone who inspires others to become more of who they truly are. They bring out the talent in people and have them put it to use over and over. Therefore, the development of student leadership qualities can be defined by describing the following principles:
- firstly, advanced leadership qualities are integral components of students’ professionalism, in such case, the leaders are tasked with effectively guiding organizational goal achievement. Their strategies vary from the specific features of specialty, personal competencies and experience, team behavior management, professional distinct motives;
- secondly, leadership qualities as a priority to thrive in a management position, a leader is a representative of university management function and quality depend on acts and structure.
An effective way in developing student professional leadership qualities and self – governance is to start Student Club. Students who share educational experiences and scientific interests can join the organization. It greatly contributes to their professional advancement, moral qualities development; broaden horizons, leadership qualities, logical thinking and scientific erudition. Students autonomous reading, scientific and education reports, data analysis, problem solving, critical thinking and knowledge and skills acquisition. For example, a student club "Leader" and its goal: to improve the quality training of competitive specialists by identifying and developing students leadership qualities.
According to the students interests and potentials the club operates in three directions:
1. Skillfull organisers are socially active students with good organizational skills, distinct leadership qualities.
2. Potential organisers are socially active students with organizational skills that can be observed. Easily expressed leadership qualities of students clearly.
3. The non-experienced organisers are students with poor organizational skills and slightly noticeable leadership qualities.
The members of second and third groups were able to participate in organizing local events to some extent and successfully operated within their programmes. Club Members met once a week and held various events. All the special university occasions were held according to the plan. At the early stage each group worked separately from each other. The exclusion of certain groups may even lead the dominant group to reassert its own identity and power over other groups.
The tasks were given with the reference to the students’ wishes and interests and due to that all the necessary changes were made.
It is of primary significance to figure out the content and outline forms and methods:
- social skills training;
- role - playing and team games;
- conferences, projects, presentations and etc.;
- group discussions and debates;
- readers workshops;
- online conference;
- meetings.
Such events have a big practical value since they assist in developing self-determination, personal traits, moral qualities, to reveal talents and offer conditions to acquire essential skills for leadership effectiveness in diverse workplace development. A variety of meeting with people of strong leadership skills serves as a great tool for motivating students.
Meeting is the place where the group revises, updates, and adds to what it knows as a group. Every group creates its own pool of shared knowledge, experience, judgment, and folklore. But the pool consists only of what the individuals have experienced or discussed as a group. This pool not only helps all members to do their jobs more intelligently, but it also greatly increases the speed and efficiency of all communications among them. The group knows that all special nuances and wider implications in a brief statement will be immediately clear to its members. Group activities improve students’ leadership qualities to a certain degree. There are three types of leadership styles depending on social roles:
1. Business leadership. Learning to be a leader is not easy because it takes a conscious commitment and consistent effort to develop one's business leadership skills. And as good business leadership is critical to business success, your efforts to improve your leadership skills will be amply rewarded. The following properties are of primary significance high competence, cool-headed, farseeing, visionary, courageous reputation, authority, experience, etc. Strong business leadership promotes efficiency and results;
2. Emotional intelligence in leadership. Different styles of leading have different effects on the emotions of the target followers. An “emotional” approach can be a very important step of the process (to evoke trust in people, create friendly environment);
3. Situational leadership (business and emotional) refers to a leader or manager who adjusts his style to fit the development level of the followers he is trying to influence. It is up to the leader to change his style, not the follower to adapt to the leader’s style. It provides leaders with an understanding of the relationship between an effective style of leadership and the level of readiness followers exhibit for a specific task.
One of the most effective forms for professional leadership development is a student self-governance.
We must envision education as the foundation for developing citizen-leaders. As students live and learn in a residential community built on six core values: academic rigor, honor and integrity, student self-governance, service, diversity and inclusion, and health and wellness. From their first day on the Grounds, students become part of a strong residential community based on student self-governance, an experience that builds knowledge, character, and independence.
Self-governance means that students have significant freedom to develop their talents and make decisions that matter to University life. With that freedom come high expectations of responsibility. Students are expected to hold themselves and their peers to high standards inside and outside the classroom, and to engage ethically in their local, national, and international communities. Within the framework of student self-governance, students have the latitude to be creative, assume ownership, develop leadership, take risks, and learn from their mistakes. At the same time, the University provides support and guidance.
Student self-governance and major initiatives:
1. within the framework of student self-governance to enhance creative and innovative capacities, develop scientific- professional potentials, to build cross- cultural relationships;
2. student self–governance prepares a new generation and a new nation to govern and to lead—producing a culture that places responsibility, along with the power to change, directly in students' hands.
3. student self-governance at universities is an integral part of educational system. Students' self-government includes young people, who try to solve their problems by themselves, but also with support of administration. They take an active stand in the life of the university and their personal lives;
4. university students implement decisions to achieve publically significant objectives;
5. students initiate a study-friendly environment, protect students’ interests and rights, thus prepare themselves for adulthood;
6. as independent governing body it has its own administrative system that works well;
7. the culture of self-governance gives graduates a lasting sense of initiative, decisiveness and self-confidence.
Student self-governance in institutions of higher education covers all spheres of modern life. In other words, student self-governance and student alliances greatly contribute in enhancing graduates self-confidence, initiative, social activity as the effective method for socialization.
Student self-governance coordinates various social initiatives :
1. Industralization
2. Educational organization
3. Welfare issues
4. Partnership (with other institutions of higher education)
5. Entertainments
6. Cultural-cognition projects
7. Charity events
Below is a list of competences graduates develop within the framework of student self-goverance:
- acquire skills in dealing with social and welfare issues;
- experience in education assistance program;
- acquire skills for organizing various important event and occasions;
- have valuable expertise and help other students to develop the confidence
- advocate humanism and healthy life style, to evoke patriotic citizenship, to promote ethics;
- get acquainted with various extracurricular activities;
- improve communication skills in relationship with students from different universities,
- assist in training others and etc.
Implementation of socially significant youth initiatives, both individual and collective through student organizations (clubs): pros and cons? What are the chances and opportunities? We can answer these questions by analyzing the experience of Leader club.
The club operates according to the plan for each academic year.
The set of projects planned within the framework of student self-governance:
1. Scientific-researches
2. Educationalprojects
3. Student self-administrating
Aim: to develop professional leadership qualities of students
Tasks:
- develop the system of human values;
- improve students research skills and facilitate professional growth in the future.
- to acquire learning and research skills and better understanding of methods and techniques.
- to enhance self-management and teamwork skills, creative potentials, such traits as responsibility, perseverance.
The members of the club protect and support the academic and personal interests of the students. The club members get acquainted freshmen with the teachers and the way the club operates. To find out personal traits, creative potentials of each student there is an opinion poll held amid students. For example, A question is «Do you consider yourself a leader?» and options to choose «Yes, I do», «No, I don’t», «I’m focused on my study», «My single goal is to graduate well». It is rational to raise such questions amid young people that recently finished school. As they are unaware of the tradition of higher education need to know about the local administration and condition the university ensures for their successful study. Most of them study hard to meet parental expectations. In this regard the role of students alliance is rather crucial to coordinate newbies to adapt well in academic environment.
Basic requirements aimed at developing professional leadership qualities amid students are the following: attendance of all members. The questionnaire shows that some students (total number of students is 62) initially showed no interest in organize and coordinating different events. Regular meetings and discussions made them reconsider their views, helped to establish friendly relationship with other students. The student body requires a responsibility from each member. The teenage years are when young people begin to master the skills that will enable them to be fully independent in adulthood. As the local body we encourage independence in our students, while keeping them safe and supported. We look at ways to encourage them to be confident, independent and responsible.
There is a distinct structure of student self-governance that must be mentioned. The Chairman and his functions:
1) Student Council plans shall be subject to the approval;
2) members of student body organize different events;
3) hold regular meetings, coordinate goals accomplishment;
4) university is expected to give recommendations to student council;
5) attend all mandatory meetings of student council;
6) appoint tutors to the first year student groups;
7) to select department principals, vice-principals, secretaries, to consider each candidate in the student council meeting agenda;
8) to give instructions to all members of student council;
9) control over the tasks execution;
10) monitoring of student council members' progress;
11) university administration is required to participate in all important events;
12) members are encouraged to assist to university administration;
13) do trainings, workshops, hold cultural events, conferences, competitions etc.
The leader club provides a wide range of opportunities for students to get involved. It has a significant impact in providing effective learning environments for students, preparing them to live and work in a global community. In addition to building lasting friendships, student organization provides many benefits including serving as a medium for academic discourse, personal growth, leadership development, intercultural understanding and community engagement, to exchange information, get job.
Moreover, students perform better academically and are more likely to graduate. Members of the club work due to their personal interests in different sectors. Such as:
Culture section. Graduates hold different events, contests, classroom meetings, evenings, concerts, holidays, competitions and etc. The events always bring much joy and fun, writing scripts, playing games and other activities that reflect students’ professional interests.
Students in Art. Inspire students who are good at drawing and decorating. We have come to derive aesthetic pleasure that are beneficial to our primary sense’s functioning (a variety of photo exhibitions, art galleries, art posters, decorate the classroom for a special occasion).
Sport clubs - voluntarily organized for the purpose of furthering and promoting students interest in a particular sport or athletic activity. The purpose of the club should be to promote, practice, and further the skills and collective interest in a particular sport or athletic activity and advocate a healthy lifestyle. To encourage students play outdoor games. For example, to play ballgames and celebrate «World Health Day».
News blog – requires high skills to operate with different kind of information and share with verified through education platforms, news blogs, announcements, invitations. Official university website and catalogues with specialties. To inform about upcoming events, post ads on social communities, upload photos and video reports.
Community service - is work done by the club members that benefits others. Community service can help many different groups of people: children, senior citizens, people with disabilities, even animals and the environment.
Students in science - to contribute to wider scientific studies by holding conferences, various olympiads, scientific forums and students, help to monitor active participation in the events.
«Leader» сlub is composed of students, with adults as advising figures to maintain the functionality of club. Club primarily focus on four aspects: blognews, community service, scientific interest, and interpersonal dynamics (also known as group dynamics). Many teenagers join the clubs because it tends to focus around culture, social dynamics, and self-interest. The club looks to satisfy the needs and demands of teenagers, based on environment, tradition, and culture. Teaching young people effective decision-making is a big step in preparing them for independence. By allowing them to work things out for themselves they develop an ability to identify and solve problems. Professional and innovative modifications are based so need to meet students academic and social interests.
As a sample the structural framework of the club:
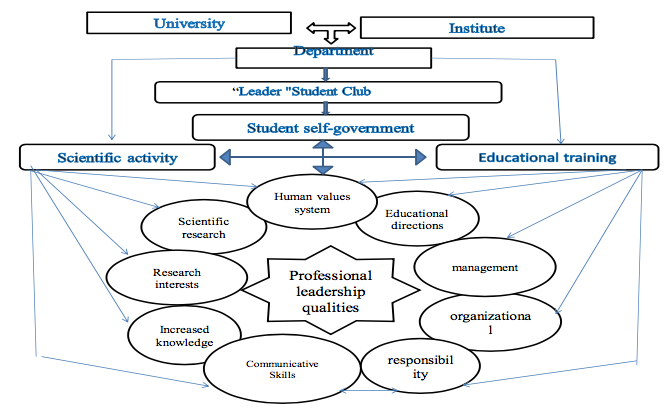
Summing up, the process of encouraging students to get engaged in research work and enhance necessary skills at the institutions of higher education plays an important role in the leadership qualities development. Leader club guarantees the insurance of regular work. The following leadership qualities to embody: personal qualities; socio-psychological qualities; organisational skills, self-development. Higher Education Institutions prepare students for the real world. Attaining a higher education is a ticket to a bright future. As people embrace new innovations and technologies, higher educational institutions must also learn how to keep up. The future of not only their students but also of the economy lies on their hands in preparing students for a globally competitive workforce. Strong professional leadership competencies can contribute to success.
The framework for developing student leadership skills at institutions of higher education considers the implementation of continuous scientific work and learning, self-governance within the structure of «Leader» club. Effective implementation of the framework can ensure students with strong leadership qualities (educational and scientific environment, great motivational impact, upbringing process, advancement). The club members encourage students to distinguish and later improve leadership compentencies; to develop self-motivation and self-perfection. Successful members in the class in the classroom and out of the classroom employ a variety of strategies to promote responsible decision-making and create self-reliant students.
Leadership in students qualities development at institutions of higher education ensures personal development based implementing various pedagogical assistance by skillful organisers ( high level of leadership development); potential organisers (middle level), non- experienced organisers (low level). Effective cooperation with skillful organisers greatly contributes to the spiritual growth in students.
Stogdill R.M. Handbook of Leadership. A survey of theory and research. - N.Y., 1974. – 362 р.
Pettrullo, L. Leadership and International Behavior [Text] / L. Pettrullo, B. Bass, - N. Y., 1964. - pp. 5-67.
C.F. Achua, R.N. LussierEffective leadership. (3rd ed.), Thomson South Western, Canada , 2007.
Anderson et al., What works for you may not work for (Gen)Me: Limitations of present leadership theories for the new generation. 2017 The Leadership Quarterly , pp. 245-260
Alvesson, M., & Sveningsson, S. Changing organizational culture: Cultural change work in progress. London, UK: Routledge. 2015.
Amabile, T. M., Schatzel, E. A., Moneta, G. B., & Kramer, S. J. Leader behaviors and the work environment for creativity: Perceived leader support. The Leadership Quarterly, (2004). 5–32.
1. Kazakh National Pedagogical University named after Abai, Almaty, Kazakhstan aaalimbekova@mail.ru
2. Academician E.A. Buketov Karaganda State University, Karaganda, Kazakhstan.
3. Academician E.A. Buketov Karaganda State University, Karaganda, Kazakhstan.
4. International Kazakh-Turkish University Named after Khoja Ahmed Yasawi, Turkestan,Kazakhstan.