

 Vol. 39 (Nº 01) Year 2018. Page 23
Vol. 39 (Nº 01) Year 2018. Page 23
Lyudmila I. CHERNIKOVA 1; Elena N. EGOROVA 2; Svetlana A. EVSTEFEEVA 3; Sergey S. SHCHERBAKOV 4
Received: 28/08/2017 • Approved: 03/10/2017
1. Methodological approach to managing the credit organizations
2. Analysis of sustainability of credit organizations
3. Recommendations for increase of effectiveness of credit organizations’ activities
ABSTRACT: This article views sustainability of the banking system from the point of view of bank’s providing a wide range of products and services, strengthening of own resource and financial base, and capability to oppose the risk of internal and external environment with the help of effective management. Sustainability of the banking system depends on a lot of factors, including the macro-economic ones. Study of dynamics of indicators of the Russia’s banking system’s sustainability shows toughening of the banking control policy. Sustainability of the banking system is especially actual in modern times due to the crisis in the Russian economy. Achievement of the banking system sustainability is a problem for all regions of the Russian Federation. A lot of banks seek for various means of provision of their sustainability: they increase the value of coefficients of capital adequacy, make the systems of risk management more complicated, diversify their activity according to the product and geographical principles, and implement new tools of effective management. The authors distinguish the criteria and attributes of the banking system sustainability. Study of the problems showed that the banking system is stable and sustainable, which is confirmed by the indicators of dynamics of attracted and used assets of credit organizations. The performed analysis allowed determining the main macro-economic factors of influence on the banking system functioning, which include gross domestic product, gross national products, gross accumulation, etc. The performed study showed the necessity for further study of the viewed direction and especially of its applied direction, which predetermined the topic of the research. As a result of the study, it is offered to implement changes into the banks’ credit strategies in part of correction of the system of evaluation of credit risk of borrowers in view of macro-economic and political risks. |
RESUMEN: Este artículo considera la sostenibilidad del sistema bancario desde el punto de vista del banco que ofrece una amplia gama de productos y servicios, el fortalecimiento de los recursos propios y la base financiera, y la capacidad de oponerse al riesgo del entorno interno y externo con la ayuda de una gestión eficaz. La sostenibilidad del sistema bancario depende de muchos factores, incluidos los macroeconómicos. El estudio de la dinámica de los indicadores de la sostenibilidad del sistema bancario de Rusia muestra un endurecimiento de la política de control bancario. La sostenibilidad del sistema bancario es especialmente real en los tiempos modernos debido a la crisis en la economía rusa. El logro de la sostenibilidad del sistema bancario es un problema para todas las regiones de la Federación de Rusia. Muchos bancos buscan diversos medios de provisión de su sostenibilidad: aumentan el valor de los coeficientes de suficiencia de capital, complican los sistemas de gestión de riesgos, diversifican su actividad de acuerdo con el producto y los principios geográficos e implementan nuevas herramientas de gestión de riesgos. administración. Los autores distinguen los criterios y atributos de la sostenibilidad del sistema bancario. El estudio de los problemas mostró que el sistema bancario es estable y sostenible, lo que se confirma con los indicadores de la dinámica de los activos atraídos y utilizados de las organizaciones de crédito. El análisis realizado permitió determinar los principales factores macroeconómicos de influencia en el funcionamiento del sistema bancario, que incluyen el producto interno bruto, los productos nacionales brutos, la acumulación bruta, etc. El estudio realizado mostró la necesidad de seguir estudiando la dirección vista y especialmente de su dirección aplicada, que predeterminó el tema de la investigación. Como resultado del estudio, se ofrece implementar cambios en las estrategias de crédito de los bancos como parte de la corrección del sistema de evaluación del riesgo de crédito de los prestatarios en vista de los riesgos macroeconómicos y políticos. |
Macro-economic processes determine the parameters of development of the banking sector. Their correct evaluation allows increasing the effectiveness of managerial decisions and strengthening the financial sustainability of credit organizations. Complex analysis of influence of macro-economic factors on the results of business processes allows for timely determination of negative phenomena and tendencies in the activity of the banking system.
A special role in the modern conditions belongs to development of the methodological approaches to evaluation of influence of the monetary policy of the Bank of Russia on the results of the banking activity.
There’s a necessity for additional study and improvement of the methods of correction of the parameters of the banking activity for bringing them into the comparable forms. Certain conceptual and methodological provisions are debatable, which predetermines the expedience of their detailed study. There’s a necessity for improvement of theoretical and methodological basis for the purpose of developing the practical recommendations for increasing the effectiveness of credit organizations’ management in the conditions of the crisis.
The banking sector is an inseparable part of modern economic systems. Serving the bong the depositors and borrowers, the banking system performd the role of a financial intermediary, thus being the key element of the market economy.
Instability of the macro-economic environment can negatively influence the state of the banking system. In its turn, instability of the banking system can negatively influence the state of economy and lead to a crisis. Sustainable state of the banking system is supported by means of stable work of certain banks, in particular, large and strategic. From this point of view, it is possible to say that stable functioning and well-being of certain banks is a necessary condition for prevention of escalation of crisis phenomena in the economy.
Study of the issue of sustainability acquired a special significance in the modern times. The category “sustainability” is actively used in various spheres of science, related to study of functioning of various systems, including the banking system. Studying the influence of the macro-economic conditions on sustainability of the banking system in the conditions of the modern state of Russia’s economy is very important. This research seeks the following goals:
- analyzing the dynamics of indicators of the banking system’s activity, which characterize the modern state of the banking system;
- studying the peculiarities of influence of macro-economic conditions on sustainability of the banking system.
A lot of banks look for various means of providing their sustainability: they increase the value of coefficients of capital adequacy, make the systems of risk management more complex, diversify their activity according to the product and geographical principles, and implement new tools of effective management.
Development of the methods of evaluation of the macro-economic situation’s influence on the banking sector includes a list of very complex issues that explain the mechanism of formation and functioning of the banking capital.
Sustainability of the banking system could be viewed according to several criteria. According to them, the following types of sustainability of banking system are distinguished: financial, economic, political, moral, directions of activity, operational, time, personnel, and organizational. A special type of sustainability is financial sustainability of the banking system. It is closely interconnected to other types of sustainability. The bank’s financial state determines all other aspects of the banking activity. The bank’s financial sustainability determines sustainability of the banking system as a whole (Kryukova et al., 2016).
Thus, the following attributes of sustainability of the banking system could be distinguished: lack of crises in the banking system; a certain number of banks disappear from the market, a tendency for growth of indicators of banks’ activity grows; if the negative external influences on the banking system grow, the balance in its developed is preserved; the possibilities for evaluating the risks of the banking activity and their effective management (Nemchinova, 2012).
The Russian Federation is peculiar for an opposite situation due to financial sanctions from the leading countries of the world, which makes it vulnerable to macro-economic shocks. The crisis phenomena that appeared in late 2014 and their consequences influence various sides of economy – primarily, the banking sector, stability of which is guaranteed by the normal functioning of economy and distribution of financial resources. In this work, the econometric methods help to analyze the sustainability of the Russian banking sector against the influence of macro-economic shocks.
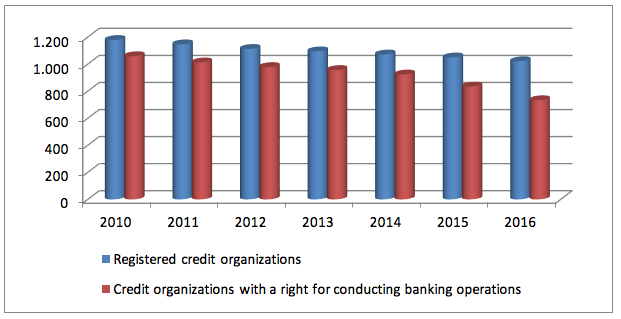
For studying the influence of macro-economic factors on sustainability of the banking system, it is necessary to view the modern state of the Russia’s banking system. The Central Bank of the RF conducts the policy of strict control over activities of commercial banks – which is shown by dynamics of several indicators. Thus, Figure 1.1 shows dynamics of registered and existing credit organizations.
Figure 1
Dynamics of the number of existing and registered credit organizations in the Russia’s banking system
Source: https://bankirsha.com/uroven-inflyacii-v-rossiyskoy-federacii-po-godam.html.
Based on the data of Figure 1.1, it is possible to see that the dynamics is negative according to two indicators. At that, the rate of growth of the registered credit organizations constitutes 86.6% - i.e., the reduction in 2010-2016 by 13.4%. The growth rate of the number of credit organizations, which have a right for conduct of banking operations, constitutes 69.3% - i.e., over the analyzed period the number of existing credit organizations reduced by 30.7%. Analysis of the cause of negative dynamics of these indicators shows the tendency for licenses withdrawal with the banks due to non-conformity to the requirements of the Bank of Russia, and, as a consequence, reduction of the quality of provided banking services (Figure 1.2). Besides, credit organizations do not correspond to the requirements of sufficiency of own capital (Zaernyuk et al., 2015).
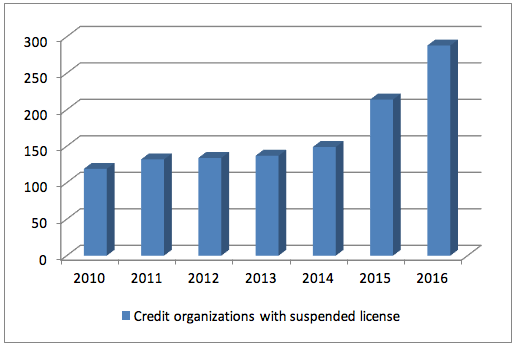
Figure 2
Dynamics of licenses suspended with credit organizations
Source: bankirsha.com/uroven-inflyacii-v-rossiyskoy-federacii-po-godam.html
Thus, Figure 1.2 shows the dynamics of reduction of existing credit organizations, as over the period of 2010-2014 the indicator of licenses withdrawal was at a stable level, increasing by 2 times beginning from 2015. This was caused by the strict policy of the Central Bank of the RF, aimed at toughening the control over credit organizations.
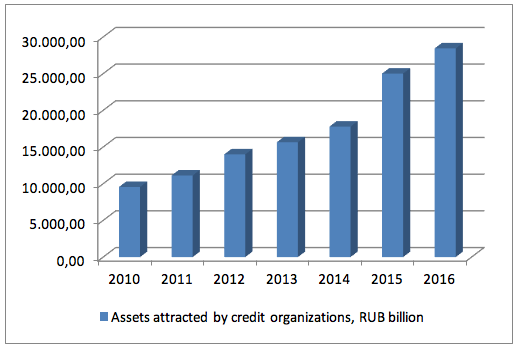
Figures 1.3 – 1.4 shows the dynamics of attracted and used assets of credit organizations.
Figure 3
Dynamics of attracted assets by credit organizations
Source: http://www.cbr.ru/statistics/?PrtId=pdko
-----
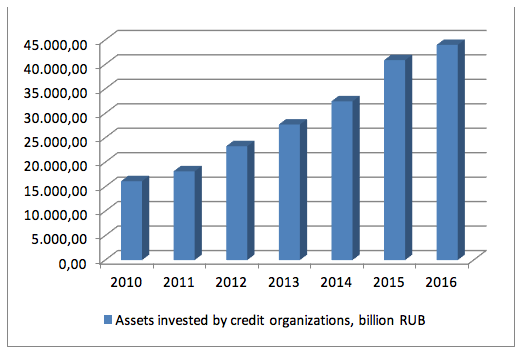
Figure 4
Dynamics of invested assets of credit organizations
Source: http://www.cbr.ru/statistics/?PrtId=pdko
This empirical study shows that 2010-2016 marked the increase of the volume of attracted and used assets of credit organizations. This shows the development of the Russian credit market.
Studying the modern state of the banking system, it is possible to say that the banking system was stable and sustainable in 2016, which is proved by the indicators of dynamics of attracted and used assets of credit organizations and by the tendency of reduction of existing credit organizations, caused by strict requirements to credit organizations for the purpose of increase of sustainability of their work in the crisis conditions.
At that, the functioning of the banking system is influenced by a lot of macro-economic factors – e.g., gross domestic product, gross national product, gross accumulation, etc. (Chernikova et al., 2012).
Figure 1.5 shows dynamics of GDP which will allow proving the influence of GDP on sustainability of the banking system.
Figure 5
Dynamics of Russia’s GDP, USD billion
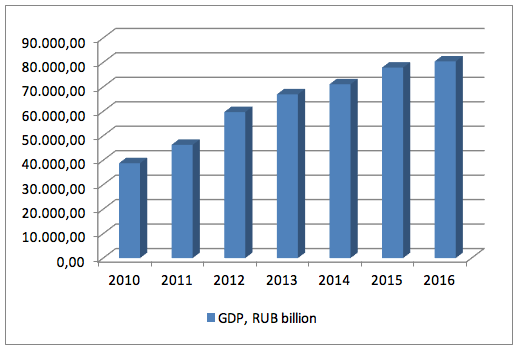
Source: http://www.cbr.ru/statistics/?PrtId=pdko
The data of Figure 1.5 allows concluding on the direct connection between GDP and sustainability of the banking system. The sense of this interconnection consists in the fact that sustainability of the banking system shows the sustainability of investment component of the banking system, which can be achieved only under the condition of growth of GDP – therefore, the connection between these indicators is direct.
Besides, sustainability of the banking system is influenced by inflation. Banking system is the only sector of economy for which inflation to a certain crisis level is the higher the better, for, the lower the inflation and the rates of growth of money supply, the slower the growth of passives and the lower the rates of assets – so, the margin grows as well (Chernikova et al., 2016).
A large growth of money supply leads to inflation, and this, in its turn, influences the companies of the real sector which take credits. Nominal credit rates are high during high inflation, and not all companies can cope with high interest rates, which reduced the demand for credits. The situation is similar for consumer crediting. High inflation, high interest rates, and reducing margin of companies lead to reduction of crediting. The level which exceeds the expectation as to inflation and growth of money supply will be critical.
Apart from the general economic factors, sustainability of commercial banks is influenced by financial factors – primarily, the state and development of the financial market. The state of the financial рынка is determined by the following factors: money emission, rates of inflation, interest on credits, changes of state regulation in foreign economic activity, country’s old and foreign currency reserves, the volume of foreign debt, and the state of the stock market.
Besides, in 2016 sustainability of the banking system was confirmed by the indicators of dynamics of attracted and used assets of credit organizations, with the tendency for reduction of the number of working credit organizations, caused by strict requirements to credit organizations for the purpose of increase of sustainability of work in crisis. At that, functioning of the banking system is influenced by a lot of macro-economic factors – e.g., dynamics of GDP, GNP, gross accumulation, etc. The main conditions of macro-economy that influence the sustainability of the banking system are the volume of GDP and the level of inflation. Thus, it is possible to distinguish the following attributes of sustainability of the banking system:
During development of macro-economic scenarios, the Bank of Russia uses the forecast of the most probable development of external conditions and the supposed action of a range of internal factors that are outside of influence of the monetary policy – in particular, state policy and structural characteristics of economy. All viewed scenarios suppose preservation of external sanctions against the Russian economy over a three-year period without significant change of the scale or character of their action. The restraining influence of sanctions on the Russian economy will be translated through the increase level of economic uncertainty, preservation of limited access of Russian companies and banks to external financing and using the import of high-tech products for investments.
Preservation of moderate dynamics of internal consumer demand as to the stable course dynamics and inflation expectations with lack of unexpected inflation risks will ensure the successive reduction of the inflation level and its entering the target level of 4% in 2017 – 2018.
The offered measures, aimed at development and increase of effectiveness of the banking sector and financial markets, optimization of approaches to their regulation, increase of accessibility and level of distribution of financial services and financial knowledge of population and business will stimulate the well-balanced development of the financial system on the whole and improvement of conditions of realization of the monetary policy, increasing the efficiency o the transmission mechanism.
Zaernyuk V.М., Chernikova L.I. Economic model of development the banking services market: a conceptual approach. Finance and credit. No. 7 (487). P. 41-48.
Zaernyuk V.M., Bokareva E.V., Chernikova L.I., Kryukova, E.M. A study of the theoretical approaches to the banking financial intermediation and its development trends. World Applied Sciences Journal. 2014. V. 30. No. 12. P. 1723-1725.
Zaernyuk V.M., Chernikova L.I., Leonova V.P., Mukhomorova I.V., Belokhvostova N.V. Stress testing as a tool for assessing systemic risk of organizations of the Russian banking sector. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences. 2015. V. 6. No. 3 S3. P. 157-164.
Kryukova Е.М., Mukhomorova I.V., Egorova Е.N. Modern social problems of the banking crediting of individuals in Russia. Actual problems of the Russian law. 2016. No. 14. P. 70-73.
Nemchinova Y.V. Sustainability of the banking system and factors of its provision / Managing the economic systems: scientific E-journal. – 2012. – No. 42(6).
Pakhomova S.А. Factors of financial sustainability of a commercial bank / Young scholar. – 2015. – No. 24(104).
Chernikova L.I., Shcherbakov S.S., Evstefeeva S.А. Past-due debt as an indicator of the banks’ state. Money and credit. 2016. No. 5. P. 53-56.
Chernikova L.I., Egorova Е.N., Zaernyuk V.М., Faizova G.R. Institutional evaluation of the banking services market. Moscow, 2012.
Chernikova L.I., Faizova G.R., Egorova E.N., Kozhevnikova N.V. Functioning and development of retail banking in Russia. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences. 2015. V. 6. No. 6 S4. P. 274-284.
https://bankirsha.com/uroven-inflyacii-v-rossiyskoy-federacii-po-godam.html
1. Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia. e-mail: tariff2004@mail.ru
2. Russian State Social University, Moscow, Russia. e-mail: egelni@yandex.ru
3. Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia. e-mail: s.evst969@mail.ru
4. Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia. e-mail: shcherbakovs.s@yandex.ru