

 Vol. 38 (Nº 40) Año 2017. Pág. 40
Vol. 38 (Nº 40) Año 2017. Pág. 40
R.S. SOKOV 1; R.R. GURINA 2; S.L. SOKOV 3; M.M. NAMOYAN 4; A.A. PODDUBSKY 5
Received: 29/07/2017 • Approved: 05/08/2017
ABSTRACT: The reasons of erroneous actions are considered at administering first aid to the injured in emergency situation. The authors note that emergency situations require adoption of quick and competent decisions, effective creative approach and evaluation in terms of legality. It is important to teach the student necessity for knowledge in the field of forecasting and monitoring of possible emergencies, causes of their occurrence, improving organization of response to them, including administering first aid to the injured. In class it is substantiated the necessity of using visual material, mock-ups, medical means for mastering the skills of self and mutual help. It is studied academic progress of students and showed errors reduction when using situational problems in learning process. Based on the conducted research, the authors point out the importance of teaching students by rules and basics of administrating first aid in higher education institutions. |
RESUMEN: En este trabajo se consideran las razones de acciones erróneas en la administración de primeros auxilios a heridos en situación de emergencia. Los autores observan que las situaciones de emergencia requieren la adopción de decisiones rápidas y competentes, un enfoque creativo eficaz y una evaluación en términos de legalidad. Es importante enseñar a los estudiantes la necesidad de conocimiento en el campo de la previsión y seguimiento de posibles emergencias, causas de su ocurrencia, mejorando la organización de la respuesta a ellos, incluyendo la administración de primeros auxilios a los lesionados. En clase se fundamenta la necesidad de utilizar material visual, maquetas, medios médicos para dominar las destrezas del yo y de la ayuda mutua. Se estudia el progreso académico de los estudiantes y se ha demostrado la reducción de errores al utilizar problemas situacionales en el proceso de aprendizaje. Basándose en la investigación realizada, los autores señalan la importancia de enseñar a los estudiantes las reglas y fundamentos de la administración de primeros auxilios en las instituciones de educación superior. |
According to the data of World Health Organization “injuries got in road traffic incident, drowning, intoxication, falling, burn or physical abuse, self-abuse or military activity annually cause death of about 5 million of people all over the world and inflict harm millions of people. They are causes of 9% death cases and threaten people’s health in every country” (Injuries and violence: the facts 2014).
It occurs that generally relatives, colleagues, passers-by of injured are near in emergency cases. That is why their awareness about algorithms and rules of administering first aid to the injuredare is important and influence over lifesaving and reduction of injured disability. Refusal to provide emergency medical assistance in first minutes of getting injuries due to lack of awareness and practical skills leads to increasing of public mortality (Levchyuk, Sokov, Kurochka and Nazarov 2016).
Emergency situations require quick and right decision taking, development of effective and creative approach and their evaluation as a matter of law. It is important to teach students the necessity of knowledge in the area of emergency situations forecast and monitoring of possible emergency situations, causes of their occurrence, “improvement reaction organization to the emergency situations, which includes administering first aid to the injured”.
In this article we investigate the problem of student teaching practical skills problems in administering first aid to the injured with the most frequent accident of mechanical injury, who is in need of hemostasis and transport immobilization, in which there is no necessity to do cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Regardless of conditions, leading to the injury, disturbing factor form, injury character, first aid administering should start with safety of yourself and surrounding people. Global experience shows that more and more people stand in danger of life consciously therefore the quantity of injured grows. The developed algorithms for administrating first aid to the injured increase the chances of preserving the vital organs and functions of the organism, but they do not always prove to be sufficient (Lysenko 2010; Gurina, Khairova and Fominykh 2015).
In any case, first of all it is necessary to find a way for notifying the relevant authorities about the situation.
Heavy mortality of the population when injured is connected with a large loss of blood that is why it is very important to stop the bleeding in the outset. The main method of stopping the bleeding in providing self and mutual assistance is a method of physical action. These are manual pressure, compressive bandage, method of twisting and applying a tourniquet. Applying a tourniquet without sufficient indications and for a long time leads to serious injuries with subsequent loss of the limb. Clinical experience shows that 75% of patients apply it without proper indications (Grigoryan 1976). The application of a tourniquet is indicated only in arterial bleeding from the great vessels. In all other cases, proper applying a compressive bandage to the appropriate place of injury provides hemostasis. Application of these methods in disease sites allows reducing the risks associated with the development of hypovolemic shock.
It is necessary to perform immobilization on top of clothes during administrating the first aid stages, thereby reducing traumatizing of the damaged area. For fractures and significant damage of soft tissues, it is reasonable to use various means of immobilization (Skoblin, Zhila and Jereley 1975). These can be such primitive methods as bandaging to a healthy part of the body, the use of improvised means, when the damaged area is bandaged to the boarded structures. Special attention should be payed to immobility of the limb in joints involved in the injury.
Often mistakes in performance of immobilization lead to serious consequences. The most common mistakes are short tires, filling of arresting bleeding tourniquet.
The introduction of disaster medicine practical lessons in the first year allowed students to study the algorithm for administering first aid to the injured. In class, when studying the nature of damages, various equipment was used such as tourniquets, scarves, bandages, mannequins. Interacting with each other in class, students studied ways of hemostasis, carrying out transport immobilization in different situations.
Work experience showed importance of studying possible mistakes connected with the implementation of practical tasks. For that end students with the teacher analyzed specific cases and mistakes that occurred as a result of using manipulation. Frequent common mistake was incorrect applying a tourniquet and immobilization dressings. Usage of these teaching methods made possible to develop students’ personal experience in this field, which increased their academic performance (Table 1).
Table. Analysis of students studying the algorithm of first aid to the wounded
Class |
Validity of Manipulation |
Mistakes of Manipulation |
Absent |
Class 1 |
4 |
287 |
9 |
Class 3 |
76 |
219 |
5 |
Class 5 |
145 |
141 |
14 |
Class 7 |
197 |
99 |
4 |
Credit |
185 |
111 |
4 |
Total: 300 students. 150 – male. 150 – female.
Important way to consolidate theoretical and practical material is to illustrate it, to apply examples of real practice from life experience of both: students themselves and the teacher. For this end, students are divided into groups and participate in the preparation of five-minute video clips, in which they describe in creative form the basic rules for the administrating of first aid during emergency situations (Gurina, Khairova and Fominykh 2015; Gurina, Khairova and Indrisova 2016). Clips are created in Russian and English languages and put on a special you tube channel for further consolidation of the material by all students. Usage of video clips in the modern conditions made possible to shorten learning period and promote abstract thinking. Annually thousands of students look through this channel for repetition of reinforced skills and learning new ones.
On final session a creative role-playing dramatization of the emergency situation is used for consolidation of students’ knowledge gained during learning and practicing practical skills in educational process. For this purpose, a corresponding material base is created which includes topographical model for emergency situations of natural, technology-related and biologically-social character, multimedia equipment, training stands, medical means and equipment, personal protective equipment, instructions, regulatory documentation. It should be noted that during some proposed creative game the student must adhere to a clear algorithm of actions and develop special stereotype of skills that will enable him to find the right solutions in his further professional activity very quickly. Emotionally active joint activity of students during the creative game contributes to the formation of their professional competencies.
Panic moods during the exam led to mistakes, which affected to the overall result and is reflected in the figure 1.
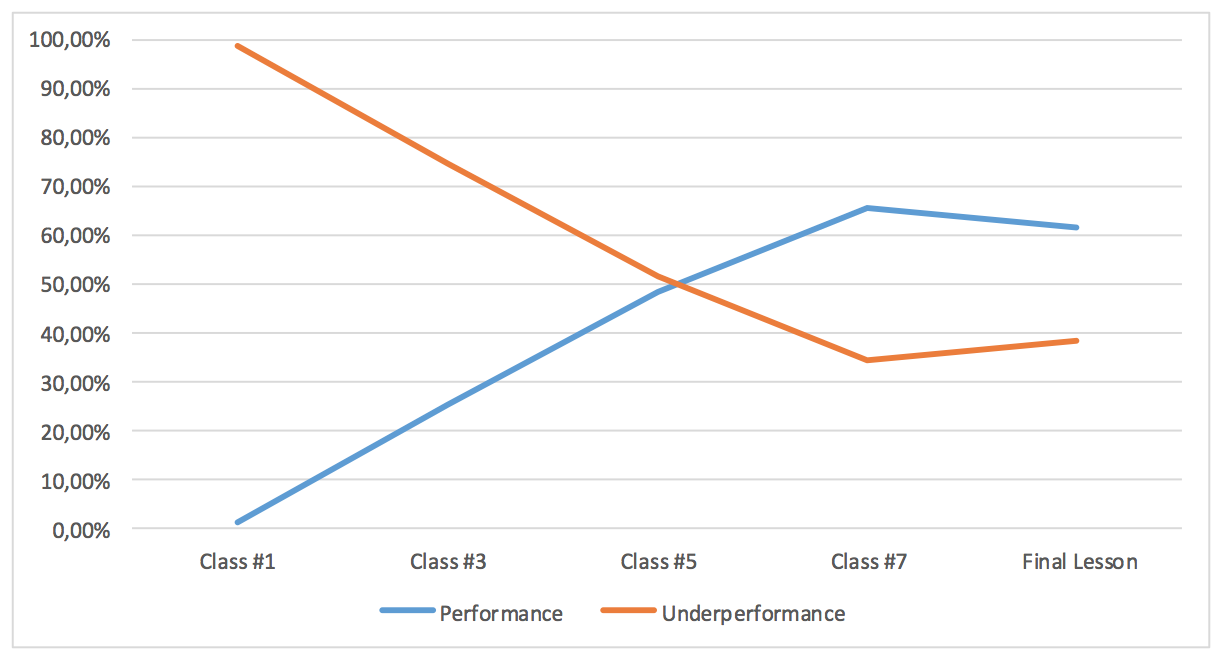
Figure 1. Students’ Performance ( % )
Practicing practical skills on each other imitates communication between doctor and patient and allows experiencing mistakes that appear in self-help and mutual assistance. Experience shows that the main problems connected with the administrating first aid when injured appear due to panic and incorrect actions. In this regard, the most important need is to organize rules and basics of first aid training for students in higher education establishments.
Grigoryan A.V. (1976). Manual for practical exercises of general surgery. Moscow: Medicine, pp. 351.
Gurina R.R.. Khairova N.I. and Fominykh Y.G. (2015). Pedagogical potential of modern concept and health and safety culture. Initiatives of XXI century, 4, 93-95
Gurina R.R., Khairova N.I. and Indrisova L.S. (2016). Methods of life safety discipline teaching at Peoples' Friendship University of Russia. Proceedings of the 1st scientific-practical conference. Moscow: Publishing office: All-Russian Research Institute of Civil Defense and Emergency Situations, Ministry of Emergency Situations of Russia, pp. 474-476.
Injuries and violence: the facts 2014. (2014). WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data, pp. 1-2.
Levchyuk I.P., Sokov S.L., Kurochka A.V. and Nazarov A.P. (2016). Administrating primary incidental medical service in emergency and extreme situations. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, pp. 288.
Lysenko M.V. (2010). Military field surgery: guide for practical exercises: a tutorial. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, pp. 576.
Skoblin A.P., Zhila Y.S. and Jereley A.N. (1975). Guide for practical exercises of traumatology and orthopedics. Moscow: Medicine, pp. 224.
1. Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), 117198, Russia, Moscow, Miklykho-Maklaya Street, 6
2. Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), 117198, Russia, Moscow, Miklykho-Maklaya Street, 6. E-mail: rina_gurinka@list.ru
3. Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), 117198, Russia, Moscow, Miklykho-Maklaya Street, 6
4. Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), 117198, Russia, Moscow, Miklykho-Maklaya Street, 6
5. Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), 117198, Russia, Moscow, Miklykho-Maklaya Street, 6