

Vol. 38 (Nº 33) Año 2017. Pág. 3
Diana Dmitrievna BURKALTSEVA 1; Lyudmila Mikhaylovna BORSCH 2; Oleg Georgiyevich BLAZHEVICH 3; Evgenia Evgenyevna FROLOVA 4; Ilya Valentinovich LABONIN 5
Received: 20/05/2017 • Approved: 01/06/2017
ABSTRACT: The rational model of institutional economics and its information analysis system are studied herein illustrated by the socio-economic analysis of the indicators of the analysis, the forecasting and planning of the spatiotemporal development, using the method of decomposition of multifactor economy as the state forecasting, the system integration of financial and economic security of business as the primary economic system in terms of epistemological position of cognition of the economic reality. The main purpose of this article is to study financial and economic security of business as a primary economic system. The main conclusions of this work are as follows: |
RESUMEN: El modelo racional de la economía institucional y su sistema de análisis de la información se estudian aquí ilustrado por el análisis socioeconómico de los indicadores del análisis, la previsión y la planificación del desarrollo espaciotemporal, utilizando el método de descomposición de la economía multifactorial como el pronóstico del estado, El sistema de integración de la seguridad financiera y económica del negocio como sistema económico primario en términos de posición epistemológica de conocimiento de la realidad económica. El objetivo principal de este artículo es estudiar la seguridad financiera y económica de los negocios como un sistema económico primario. Las principales conclusiones de este trabajo son las siguientes: |
Financial and economic security of any business is the primary element of the economic system, including the national level as well.
A significant contribution to the study of the economic security theory was made by the foreign scientists: Azoulay, Pareto, Gezau, Hager, Brown and many others (Kunitsyn 1998; Mikhalkin 1990; Romadina 2008; Yakunin, et. al. 2008; United Nations. Economic Commission for Europe, 2003; Azoulay 2010; Breidinger 2006; Brown, et. al. 2006; Sutnata & Byrd 2007; D’Agostino 2008; Murray & Grybeste 2007; Friesz 2007; Sullivaut 2007).
The study of theoretical and methodological approaches to ensure the financial security of business was carried on by the following domestic and foreign scientists such as: Baranovsky, Blank, Goryacheva, Vechkanov, Vorobiev, Gukova, Oleynikov, Papekhin, Pogosova (Baranovsky 2000; Blank 2004; Vechkanov 2007; Gukova & Anikin 2006; Oleynikov 2005; Papekhin 2007; Pogosova & Lebedev 2014) and others. But the problems of evaluation of the financial and economic security of business have been studied only partially and require further research.
The financial and economic security has already been studied at the country level; however, it is impossible without the financial and economic security of the business.
The rational model of institutional economics and its information analysis system are studied herein illustrated by the socio-economic analysis of the indicators of the analysis, the forecasting and planning of the spatiotemporal development, using the method of decomposition of multifactor economy as the state forecasting, the system integration of financial and economic security of business as the primary economic system in terms of epistemological position of cognition of the economic reality.
The previous studies carried on by the Russian scientists (Burkaltseva 2012; Borsch, et. al. 2016; Goryacheva 2006; Dudin, et. al. 2016) have shown that the maximum quality growth and business development are possible with certain components of the safety criteria, including not only the economic safety, involving financial, manufacturing, investment, food, macro-economic, social, science and technology, foreign trade, energy, demographic, institutional, but also the military, political, environmental, informational, legal and cultural safety (Fig. 1).
There are two areas of philosophy: the epistemology – that is how we perceive a thing, and the ontology – that is what a thing is in itself. Therefore, it is required to study the rational model of the institutional economics and its information analysis system, illustrated by the socio-economic indicators of the analysis, forecasting and planning of the spatiotemporal development, using the method of decomposition of the multifactor economy of the state forecasting, system integration of financial and economic security of business as the primary element of the economic system based on the internal and external risks, threats, dangers in terms of epistemological position of cognition of the economic reality.
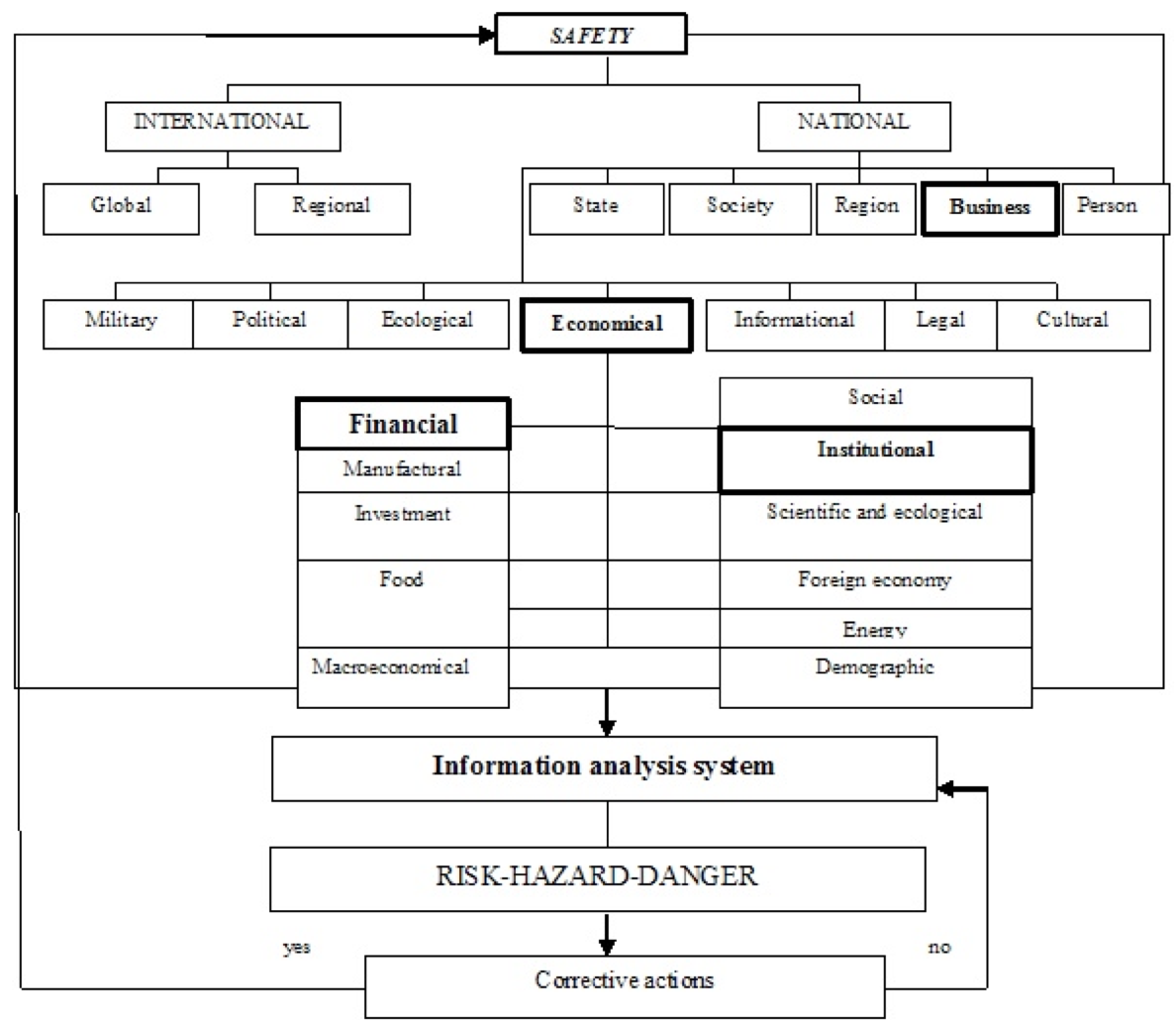
Source: compiled by the authors according to (Burkaltseva 2012; Oleynikov, et. al. 2005).
Fig. 1. Rational model of decomposition of the security.
Having applied the basic epistemological strategies for cognition of the economic reality, associated to the problem of the manner of relation between the human knowledge, which is always subjective and limited in nature, with the objective order of things, the following must be distinguished: the cognitive optimism, where the world is knowable; the agnosticism (in Greek "a" means a denial, "gnosis" means knowledge), where the world to infinity is unknowable; skepticism, doubting the knowability of the world, where it is necessary to identify uniquely the cognitive optimism in terms of determination of the economic condition and the reality at the micro and meso levels. The skepticism at the macro level is in the search for solutions, the adoption of strategies, corrective actions, claiming the authoritarianism of truth, often taking into account the impossibility of adoption and implementation of the sharp decisions, at the level of institutions, taking into account the centuries-old ways orders, cultural heritage, traditions and mentality. The agnosticism at the mega-level is limited by the sphere of human subjectivity. The cognition cannot trespass beyond the human subjectivity; therefore, it cannot judge the objective situation in the international scale of socio-economic relations. By absolutizing sensual experience as a source of cognition, David Hume considers the truth only as the usual number of associations, easily refuted by the first exception to the general rule. According to Kant, the objective world exists as the world of "things-in-themselves" and is knowable only in the boundaries, determined by the ability of the mind, the transcendental foundations of which enable the science. In both cases, the truth in no way can serve as the compliance of the knowledge to the reality, because we can be sure only in our own experience, but not in the world that exists outside and independent of us.
The following spatial socio-economic development of the temporal dynamic changes in the normal development processes and political deformation should be distinguished: corruption, shadow economy, capital outflows, raiding. It is the complex nature of the deformations, which in many ways are a means of changing traditional political institutions, forced to adjust to the needs of their time, while being formal and informal, and, at the same time, the factors and the sources of impact.
In terms of the epistemological position of cognition of the economic reality, in our view, it is necessary to consider the following institutional priorities: protection of social human rights, environmental protection, protection of the historical monuments, and the supervision over the legality of the use of budgetary assets.
Such guarantees should be provided by the legal institutions, represented in the activities of the authorities at different levels, with the regulations to determine the general trends in the policy and to set the rules of interaction between different institutions.
For the purposes of stability of the security system, including the economic safety, and its effective functioning, the correct and accurate state regulation and control are required to prevent the onset of chaos in the current economic system.
The need appears for institutionalism as the main controller and the new vector of social and economic development, the institutionalization of the state security system in a completely new process in the system of new generation. The application of the institutional approach to the study of government activities regarding the implementation of the socio-economic reforms provides the following capabilities: to assess objectively the ideology, policy and practice of the reforms; to analyze and to identify the range of subjects that are able to ensure the strengthening and development of the statesmanship, the civil society and the civilized market; to raise the question of the compliance of the reforms under implementation (communication protocols in new generation system) to the values, economic and legal and institutional framework, recognized by us as the institutional framework and the infrastructure of the said reforms.
Instead of the unification of the terms "institutionary" and "institutional", the authors distinguish the differences and give a definition.
The interaction of the forms of functional and elemental structures, that is, the institutions and the organizations, results in the institutions and the bodies of the economic system. The institutional organization becomes the institution and the organized institution becomes the body (Fig. 2). The institute acts as a functional organization that provides the implementation of a specific system of similar institutions. Therefore, the category of "institutional" is much larger than the category of "institutionary".
The institutions are the social forms of typification of the functions of the economic entities, determining their status and role in the society, creating a system of relations of the functional structure of the society. The institutionalization of the social and economic relations is the process of improvement of the forms and methods of regulation of the relations between the economic entities, capable of providing the dynamic balance, as well as the coordination of the socio-economic interests, modification of the economic order. The institutionalization of the social and economic systems is a process of establishment of the interconnected social institutions, accompanying the formation of a new socio-economic system and ensuring its mechanisms of functioning. This is the process of establishment of the certain types of regulation of the social and economic activities as the social institutions.
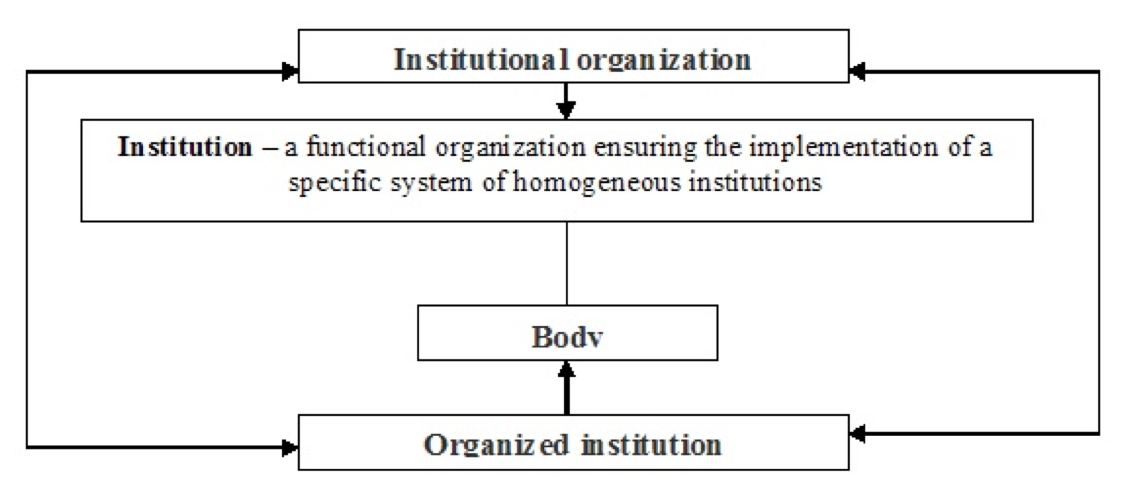
Source: compiled by the authors according to (Kunitsyn 1998).
Fig. 2. Interaction between the forms of functional and elemental structures – the institutions and the organizations.
Therefore, the institutional system (the system of institutions) of state security is a system of social forms of behavior and the actions of the existing economic entities, and the applied "rules of the game", defining their status and role in society, which, in turn, creates a system of relations of the functional structure of society, as the basis for the formation of the institutionalization (entrenchment of the "rules of the game") of the state security system (Fig. 3).
To ensure the stability and the effective functioning of the security system, the correct actions of the state are required to prevent the onset of chaos in the current economic system. Therefore, there is a need for the process of institutionalization of the state security system (the system of institutions), as well as for the formation of a system of functional, regulatory and property relations in society, including the processes of development of base and the creation of new social, economic, military, political, environmental, informational, legal, cultural institutions to ensure the systematicity and comprehensiveness in the state security in the face of uncertainty, risk, and threats of internal and external nature (Fig. 2).
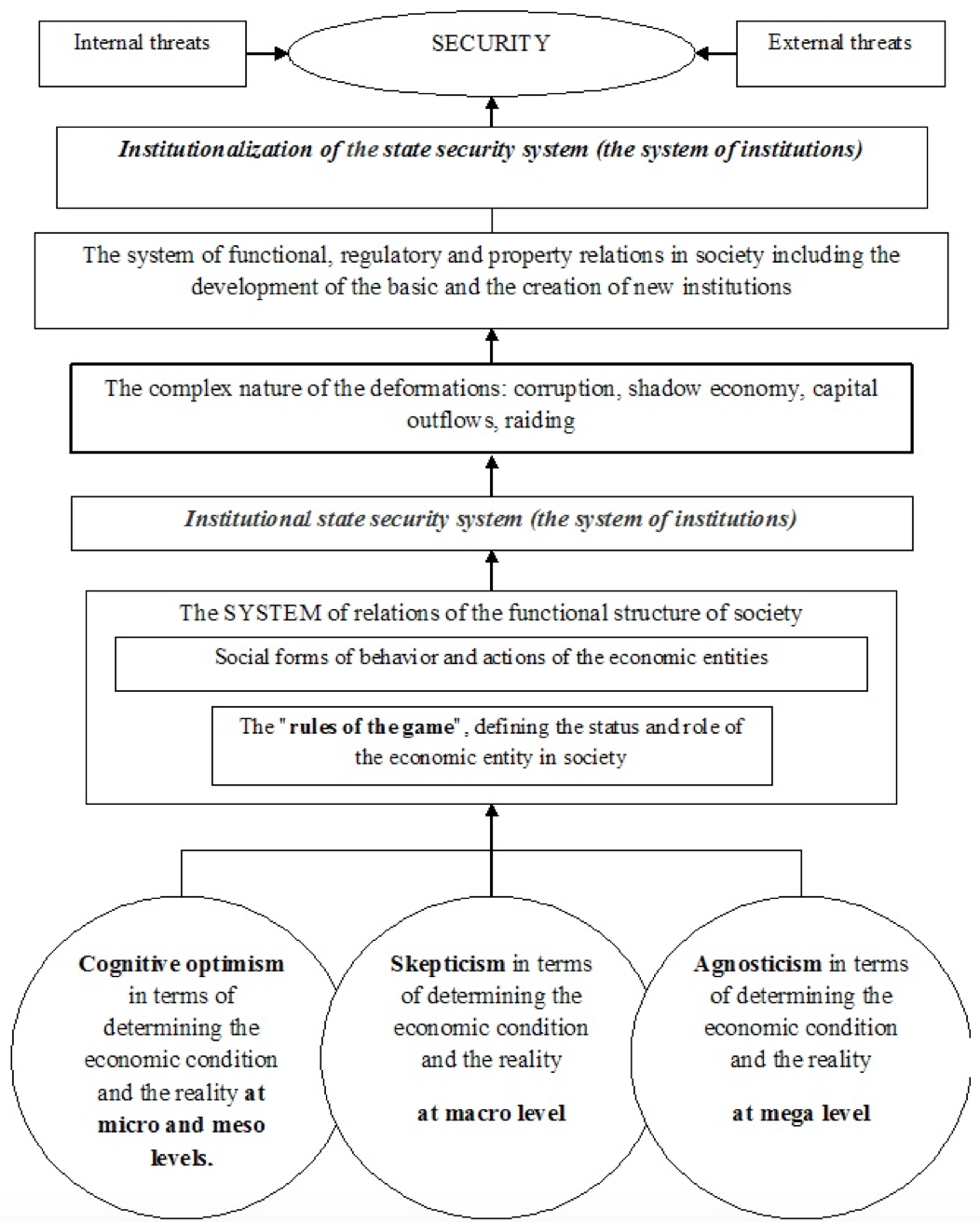
Source: compiled by the authors according to (Burkaltseva 2012)
Fig. 3. The process of institutionalization of the state security system in the spatial socio-economic development of the temporal dynamic changes in the normal development processes, in terms of epistemological position of cognition of the economic reality.
The essence of the institutionalization of the state security system is the establishment of the institutions, norms and rules, increasing the independence, stability and adaptability of the national economy and the state as a whole, through creation of the conditions for high-quality socio-economic growth and the implementation of the national economic interest, the protection against the actual and potential threats to the security of the state.
At the same time, it is integrated into the concept of institutional organization of public relations in the framework of redistributive and market economies (Fig. 4). Its significance is a promising methodology for the analysis of the Russian society and economy, and this theory, in our view, significantly complements and extends the categorical apparatus of study of market and non-market economic system not only for Russia but also for other countries, because the institutions regulating the economy are represented in the concept.
In the course of the analysis of the nature of economic security (Burkaltseva 2012; Oleynikov, et. al. 2005; Dudin, et. al. 2014; Burkaltseva, et.al. 2016), the authors give a concise definition of financial and economic security as the sustainable quality economic growth with financial components in the absence of internal and external threats. Given this definition of financial and economic security, the institutional support of the financial and economic security is especially important at all levels of this multi-factor and polysystem phenomenon.
Taking into account the maximization of utility, the economic system makes effective decisions towards the reduction in its maintenance costs. At the same time, the implementation and the use of the revolutionary "blockchain" technology allow to reduce the costs by up to 80%.
In the era of modern technology, many economic and business processes undergo a cycle of automation through technical innovation. The automation of production (as well as the record keeping) processes is carried on everywhere – including the small businesses and the large corporations. However, the technical innovation at this stage of development of the society is being changed significantly upon entering a new stage of technological evolution. The new technology, which riveted the attention of the world's largest financial institutions (such as the world banks, large IT-corporations and the government), is called "blockchain". This technology represents a revolutionary solution that will help to get rid of the majority of intermediaries, and the enforcement mechanisms for control over the execution of production and record keeping processes, reducing the costs at the same time (Kosten 2016).
The technological achievements in terms of means of production are the result of the changes in the existing system of social and economic relations, due to reduction of the transaction costs and corruption, shadow economy, raiding, capital outflow.
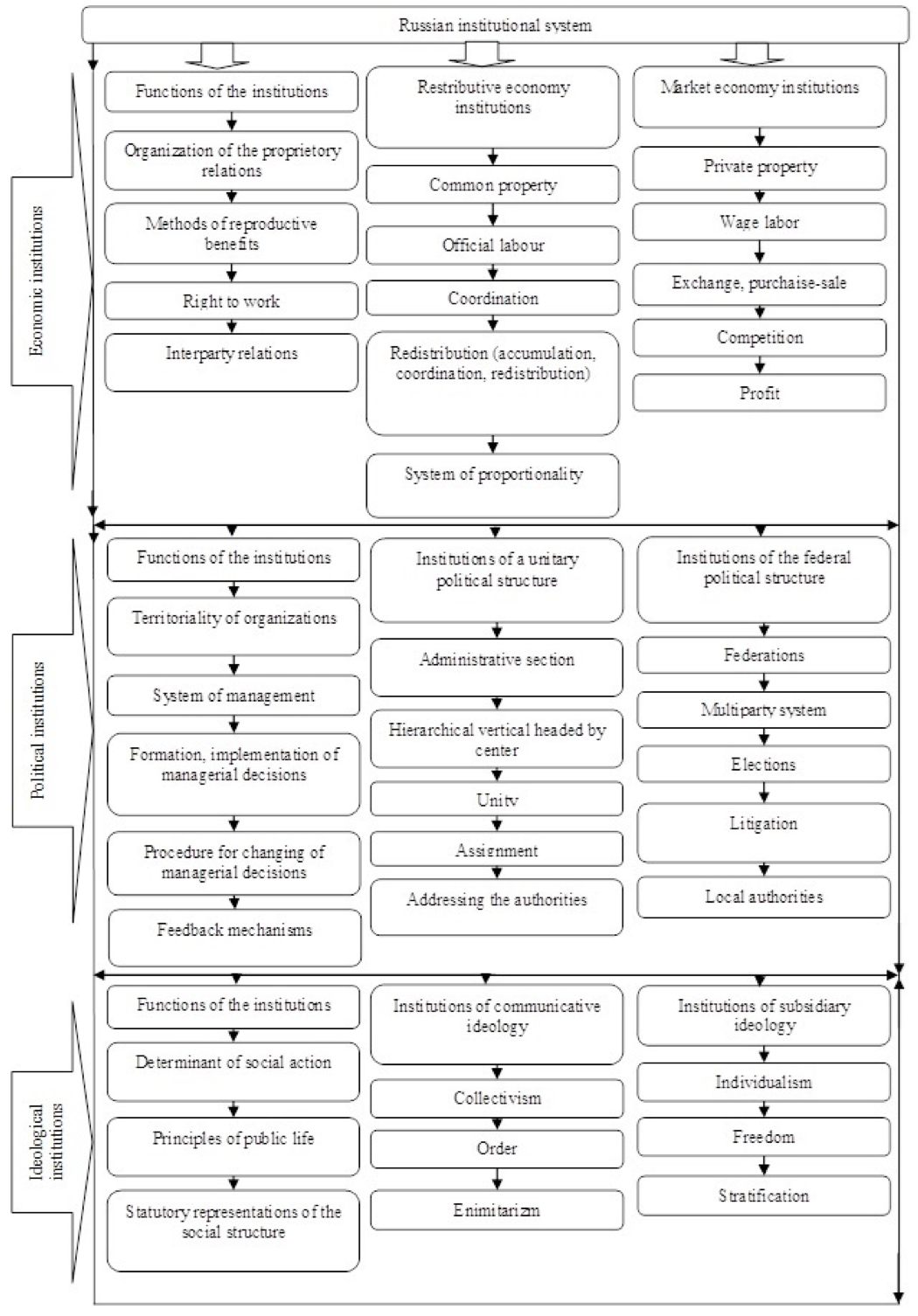
Source: (Borsch 2015; Borsch, et. al. 2016).
Fig. 4. The concept of the institutional organization of public relations, market and redistributive economies.
When using the principal scheme of the institutional provision of financial and economic security in the conditions of application of the blockchain technologies (Fig. 5), it is required: to consider the triad (risk-threat-danger) in the course of provision of security (Fig. 6), as well as the formulation and accurate implementation of the following algorithm.
1. The goal, the objectives, the functions, the principles of financial and economic security in the conditions of application of the blockchain technologies;
2. The definition and the use of the group of indicators, defining the financial and economic security in the use of blockchain technologies;
3. The establishment of the thresholds and limit values for which the financial and economic security becomes unsecure in conditions of the use of blockchain technologies;
4. The selection of a facilitating mechanism, depending on the level of financial and economic security in conditions of the application of the blockchain technologies, the in time decision-making and its institutionalization should be divided by taking into account the external and internal threats, respectively, into: strategic, tactical, operational, according to the different economic levels (micro, meso, macro);
5. The monitoring – the conduct of the on-line systematic monitoring;
6. To take the corrective measures to achieve the sustainable level of financial and economic security in conditions of the application of the blockchain technologies taking into account the external and internal threats.
Fig. 5 represents a model of institutional provision of financial and economic safety in conditions of the application of the blockchain technologies. This model is universal due to the fact that its basis is applicable at any level of the economic system.
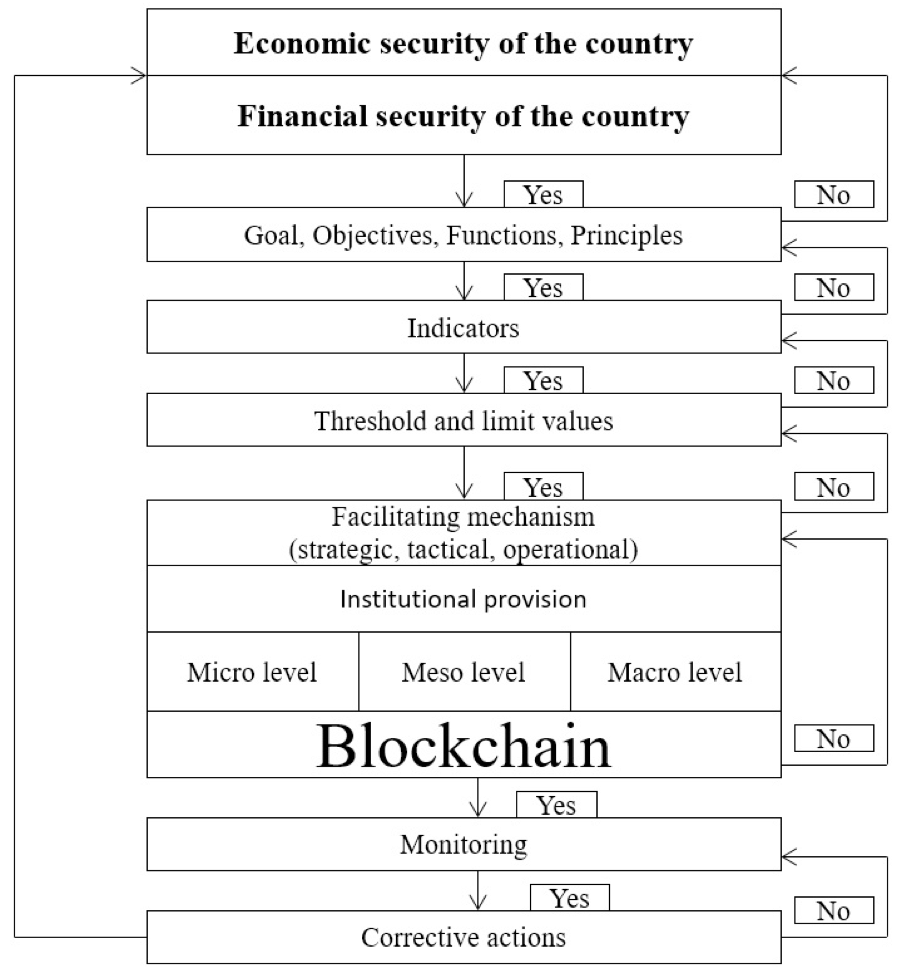
Source: compiled by the authors according to (Burkaltseva 2012; Burkaltseva, et.al. 2016).
Fig. 5. The model of institutional provision of financial and economic safety in conditions of the application of the blockchain technologies.
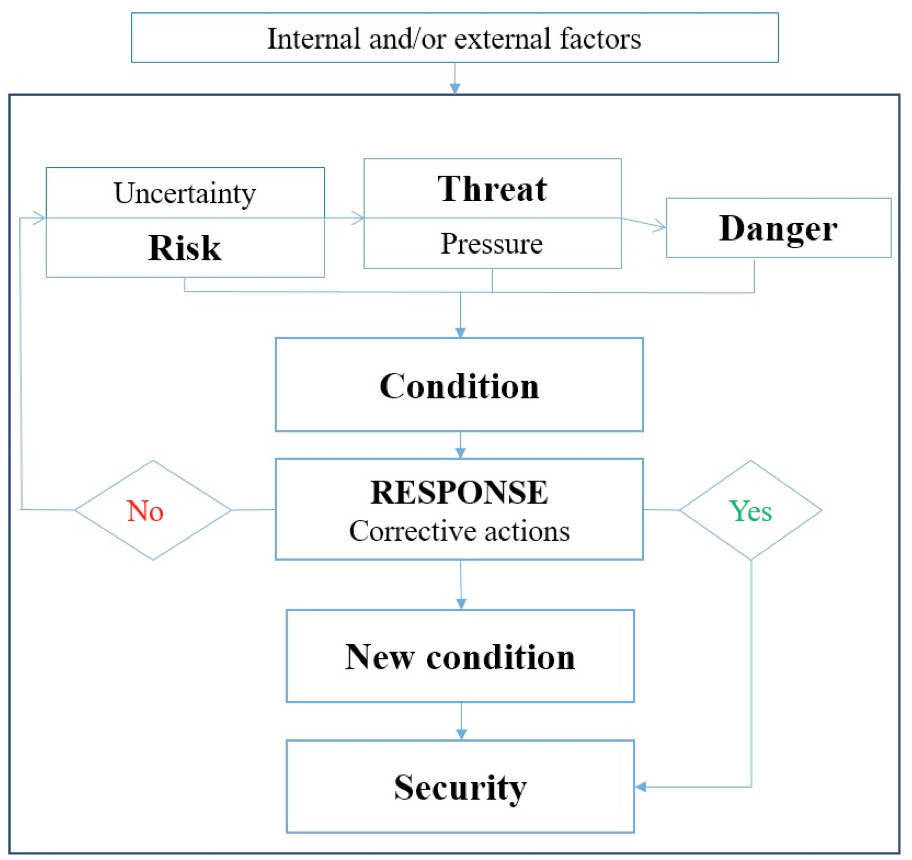
Source: proposed by the authors.
Fig. 6. Security management taking into account the triad: risk-threat-danger.
The economic security of business is a system integration of the rational model of decomposition of the security, the indicative forecasting and planning of the institutional economics through the system hierarchy, the protection against any possible internal and external threats. Considering the institutionalism as the main regulator associated to the time and the situation of analysis, prediction and planning of the socio-economic development, based on the model of "organized complexity", where the principle is the systemic hierarchy, emphasizing the rationality of the security, through the reconstruction of the economic knowledge axiomatic model. In the framework of the economic system, the business structures and their level of financial and economic security depend on the extent of the efficiency of the managerial actions on avoidance of any the possible internal and external risks, threats, dangers and, consequently, on elimination of the negative effects of the negative phenomena of the external and internal factors or on mitigation of these effects by reduction of the risks.
These are the proposals for the establishment of the institutional and investment platforms for spatiotemporal socio-economic development for the purposes of definition and development of the dynamic changes in the processes of normal development.
There is no consensus on the concept of economic security of business (Fig. 7).
The above-mentioned events would provide an opportunity to achieve the goals and objectives set, through a comprehensive study of the foundations of the social and economic development based on the rationality, associated with the ordering of formal, informal, voluntary, involuntary negative phenomena, bound to the time and situation, taking into account the indicative planning of the development of the institutional hierarchy of the economy through the system of financial and economic security of business.
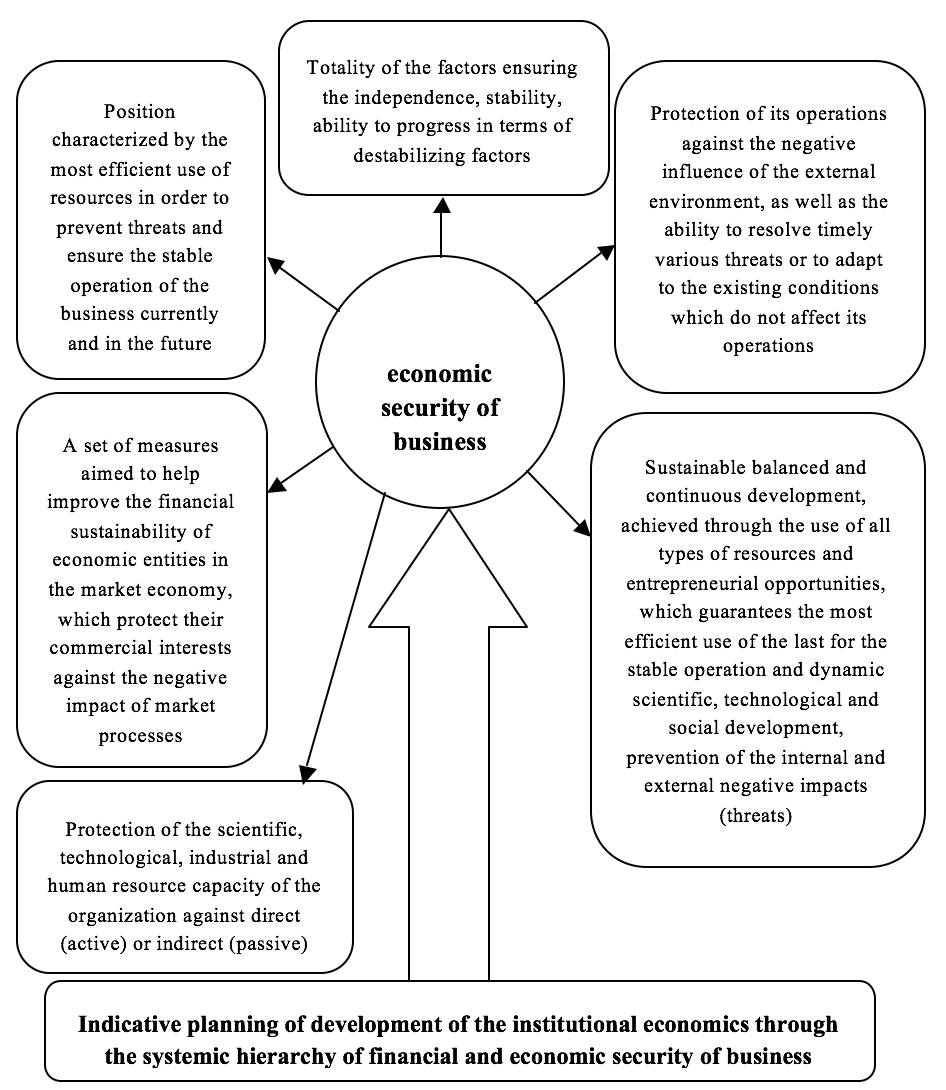
Source: developed by the authors according to (The Main Components and
the Direction of Ensuring the Economic Security of the Enterprise, 2016).
Fig. 7. The model of organized complexity of the economic security of business.
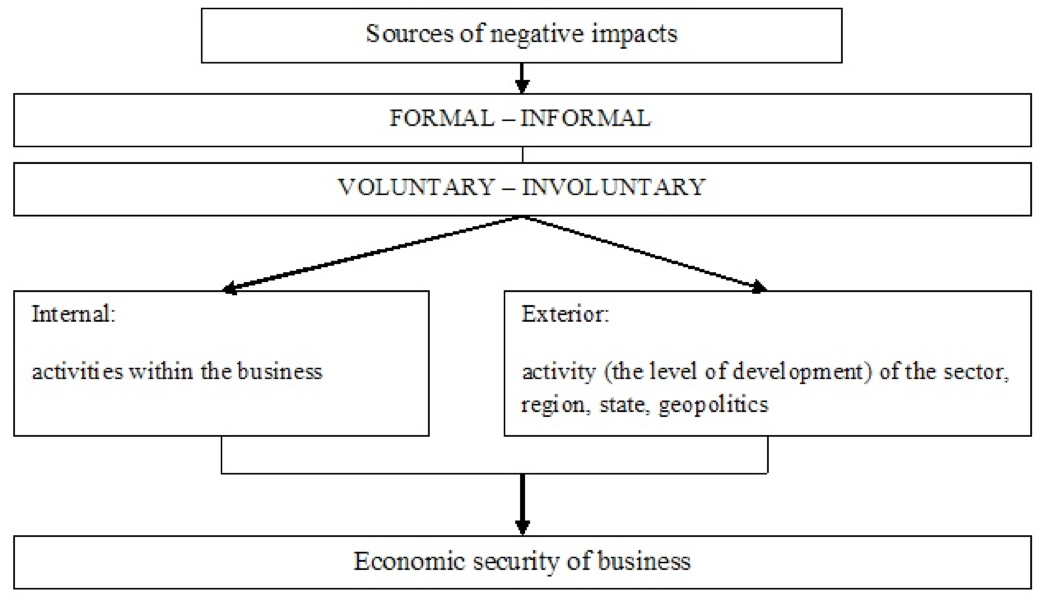
Fig. 8 shows the sources of negative impacts on the economic security of business.
The sources of negative impacts on the economic security of business should include: the formal and/or informal, voluntary and/or involuntary actions of individual officials and business entities (public authorities, international organizations, business competitors); the coincidence of all sorts of objective circumstances (condition of the financial situation of the business market, scientific discoveries and innovation, force majeure, etc.).
The security management in general, including the management and the strategy for provision of the economic security of business, involves the consideration of the variability in time, the transition from one qualitative state in a new qualitative state followed by the appropriate response and corrective actions, taking into account the triad: risk (uncertainty) – threat (pressure) – danger.
The threats to the economic business security include the following (The Main Components and the Direction of Ensuring the Economic Security of the Enterprise, 2016):
the unsystematic and inadequate regulatory legal provision of the regulation of the economy; high-risk credit policy of the government in the banking sector, on the stock and currency markets;
the rising inflation and the lack of a normal investment climate in the real economy, the advantage of the current expenditures at the expense of the capital ones;
the destruction of the system for reproduction of the production capacity (firstly, its active part) due to the decrease in the investment activity;
the weak embeddedness in the global economy (the discrepancy of the scientific and technical level of the majority of industrial products to the advanced foreign models, a low share of foreign subsidies in national wealth);
the discrimination (and in fact, the economic war) on the part of some countries of the international community in trade with Russia, and in its efforts to enter the international markets, the strengthening of the regional and national separatism;
the inefficient and unfair privatization of state property, public property;
the creation of conditions conducive to appropriation and export of financial resources; the loss of state control over the natural monopolies, the weakening of the regulatory role of the state in their pricing policy;
the bad faith actions of many economic actors on the markets of Russia, their low legal discipline, lack or total absence of the economic ethics at all levels of management. Depending on the subjective conditionality, the negative impact on the economic security can be objective and subjective in nature. The objective impacts are such negative influences that do not occur at the behest of a particular company or its employees. The subjective impacts occur due to inefficient operation of the business as a whole or its individual employees (especially managers and functional managers). The main objective of the economic security of business is to ensure its stable and the most efficient operation currently and a high potential for development in the future. The main functional objectives of the economic security are (The Main Components and the Direction of Ensuring the Economic Security of the Enterprise, 2016):
to provide high financial efficiency, as well as the financial stability and independence of the business;
to ensure the technological independence and to achieve high competitiveness of technical potential of the business;
to achieve a high efficiency of the management, the optimal and effective organizational business management structure;
to achieve a high level of qualification of the personnel and its intellectual potential;
to minimize the devastating impact of the results of production and business activities on the environment;
the high-quality legal protection of all aspects of business operations, the protection of the information field, of the trade secrets and to achieve the necessary level of information support for the work of all departments and divisions in this business;
the effective organization of security of the personnel, capital assets, property as well as the commercial interests of the business.
The definition of the factors, particular indicators of financial security.
The definition of the factors (groups), particular indicators of financial security that should reflect the condition of the financial system of the business, to serve as a basis for appropriate adjustments of its development, if necessary, deserves special attention. The choice of them is conditioned by the fact that all the indicators in the complex should define the economic security of business. The factors of the economic security of business are ordered on the basis of expert method. Such factors as the indicators of economic security of business as the liquidity, financial stability, business activity, profitability should be adopted (Vivchenko 2013).
In the current economic conditions, financial stability is the most important economic and financial characteristics of the organization, the economic security of any business as a whole. Quality management, which includes the investments, choice of suppliers, selection of qualified personnel, etc., is the most important advantage of a financially sustainable business, along with a less financially sustainable business of the same scope. At the same time, it pays taxes without delays, as well as makes timely social security contributions to the funds, staff salaries, dividends to shareholders; in turn, it guarantees the return of loans to financial institutions, and the payment of interest on them. The higher is the level of financial sustainability of the business, the more independent it is regardless of the abrupt change in market conditions, and therefore, the lower is the level of risk to be on the verge of bankruptcy, the higher is the level of economic security of business (Burkaltseva, et. al. 2016).
The sustainability of business is influenced by various factors, which can be divided into two groups: internal and external (Fig. 9).
The country's economy, covered by the unity of the economic knowledge, is in the phase of the economic cycle at the macro level. The developed concept of state regulation plays a great role in the financial stability and security of business. In times of crisis, there is a lag between the pace of sales of products and the pace of production; a reduction in the investment in inventories takes place, resulting in the reduction in sales, business income, the volume of profits, as well as the increase in the number of bankruptcies; the fall in the effective demand leads to the increase in non-payments, and to the increase in the competition.
The exacerbation of the competition is expressed in a dynamic model of system management through the mechanism of state regulation; it is an important external factor of the financial sustainability of business.
The established state institutional platforms for spatiotemporal socio-economic development define the dynamic changes in the normal development processes.
The significant macroeconomic factors of financial sustainability of business are the development of tax and credit policies, the degree of development of the insurance market, the degree of external economic relations, the development of the financial market, the exchange rate; the position and the abilities of the professional unions.
The external and the internal factors affecting the financial stability of the business, as well as their diversity, divide the sustainability of business by type, namely:
1. The internal sustainability of business is the overall financial health of the business, which provides a stable high output for its functioning based on the principle of active respond to the changing internal and external factors.
2. The external sustainability of business is due to the stability of the economic environment in which its economic activities is carried out through the appropriate market economy management system at the macro level.
3. The total (price) sustainability of business is the cash flows, providing a constant excess of the inflows (income) over their expenditures (expenses).
4. Financial sustainability of the business is the reflection of a stable excess of the revenues over the expenditures, it guarantees free maneuvering with the monetary assets of the business and contributes to the business development through the effective use of them. Therefore, the financial sustainability is formed in the entire course of production and business activity, and is a major component of the overall business sustainability.
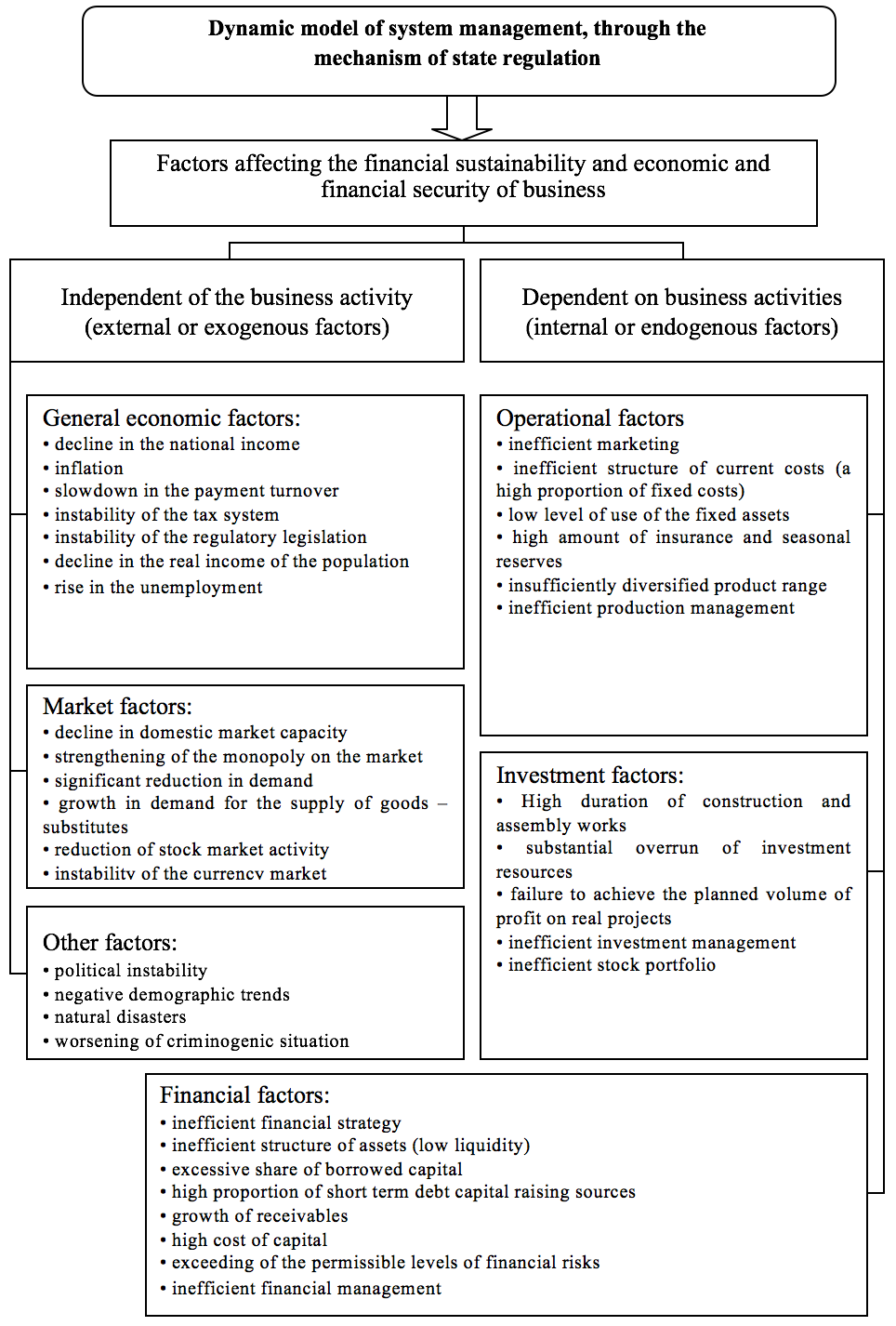
Source: compiled by the authors according to (Burkaltseva, et. al. 2016).
Fig. 9. The dynamic model in the process of system control and the factors
affecting the financial sustainability and the economic security of business.
The analysis of the financial stability of the business as of a particular date allows the manager to find out if the financial management was proper during the period prior to that date. The condition of the financial resources should be in line with the market requirements and meet the business development needs, as the lack of financial stability can lead to the insolvency of the business and its shortage in the funds necessary for the development of production, and excessive one may prevent the development, burdening the business costs with the excess inventory reserves.
The financial stability of business is characterized by the condition of its own and borrowed assets, and can be determined by the effective formation, distribution and use of financial resources, taking into account the internal and external factors.
The external manifestation of the financial sustainability of business is the solvency of the business, i.e. the ability to execute timely and fully the payment obligations arising from the trade, credit and other business operations of payment nature.
The adequate mathematical models for the economic security management require the comprehensive accounting of the uncertainty factors related to the characteristics of the operation of the business in the current economic conditions. The impact of these factors makes it difficult to make the required correct and informed decisions, determines the practical importance of processing of the fuzzy data and the need for the application of the fuzzy-multiple approach (Vivchenko 2013).
Many different methods can be used to determine the level of the economic security. The indicator approach is the most appropriate for the calculation of the integral index of economic security. This approach uses the ratio analysis method in which the indicators show the proportions between the various financial items of the financial statements of the enterprise (Dudin, et. al. 2015).
The country's economy, covered by the unity of the economic knowledge, is in the phase of the economic cycle at the macro level. The developed concept of state regulation plays a great role in the financial stability and security of business. It is revealed that the increased competition is the important external factor in the financial sustainability of business. In times of crisis, there is a lag between the pace of sales of products and the pace of production, a reduction in the investment in inventories takes place, resulting in the reduction in sales, business income, the volume of profits, as well as the increase in the number of bankruptcies; the fall in the effective demand leads to the increase in non-payments, to the increase in the competition.
The following spatial socio-economic development of the temporal dynamic changes in the normal development processes and political deformations, including: corruption, shadow economy, capital outflows, raiding can be distinguished. It is the complex nature of the deformations, which in many ways are a means of changing traditional political institutions, forced to adjust to the needs of their time, while being formal and informal, and, at the same time, the factors and the sources of impact.
It is defined that the significant macroeconomic factors of financial sustainability of business are the institutional tax and credit policy, the development of the institutions of the insurance market, the degree of foreign trade institutions and their relations, the degree of development of the financial market institutions, the institutional policy of the Central Bank of Russia, regulating the exchange rate, the position and the possibilities of the public institutions, the development of positions and the opportunities of the public institutions.
The proposals on the establishment of the institutional platforms for spatiotemporal socio-economic development, defining not only the dynamic changes in the normal development processes, but also a strategy for the economic security of business involving the temporal dynamic changes, the transition from one qualitative condition to a new qualitative condition with an appropriate response and corrective actions, taking into account the triad risk (uncertainty) – threat (pressure) – danger, are developed.
Further studies. As a part of the strategy of socio-economic development, it is necessary to determine the trends in the dynamics of institutional regulation of the socio-economic processes and phenomena; to develop the recommendations for the institutional consolidation of the state regulation of the financial and economic security of business, taking into account the systematization of formation of the system of socio-economic indicators of the economic security of business with the application of the neural networks in the future, as the primary element of the economic system; to develop the proposals on improvement of the institutional framework, the strengthening of the state regulation and control over the financial and economic security of the industries of the next generations.
This article was written under the grant of the Russian State Scientific Fund, registration number NIOKTR AAAA-A16-116040410178-5 of 04/04/2016.
The authors would like to thank the colleagues who are not the authors of this article, for their assistance in this study.
Azoulay, G. (2010). Globalisation des echanges et securite alimentaire mondiale a l'horizon 2010. Revue Tiers Monde, 39(153), 25-43.
Baranovsky, O.I. (2000). Fіnansova bezpeka v Ukraїnі (metodologіya otsіnki ta mekhanіzmi zabezpechennya) [Financial Security in Ukraine (Methodology and Evaluation Mechanisms) (Doctoral Thesis Abstract)]. Institute of Economics and Forecasting of NAS of Ukraine, Kiev.
Blank, I.A. (2004). Upravlenie finansovoi bezopasnost'yu predpriyatiya [Financial Enterprise Security Management]. Kiev: Elga, Nika-Tsentr.
Borsch, L.M. (2015). Kontseptsiya institutsional'noi organizatsii obshchestvennykh otnoshenii ridistributivnoi i rynochnoi ekonomik [The Concept of the Institutional Organization of Public Relations in Redistributive and Market Economies]. Aktual'nye problemy gumanitarnykh i estestvennykh nauk, 8-1, 144-151.
Borsch L., Burkaltseva D., Vorobyov Yu., Vorobyeva E., Chepurko V. (2016) The dichotomy of opposites and the unity of the market and capitalism: the forecast and plan (Part 2). International Journal of Economic Research, 13(8), 3427-3339
Borsch L., Burkaltseva D., Vorobyov Yu., Vorobyeva E., Chepurko V. (2016) The dichotomy of opposites and the unity of the market and capitalism: the forecast and plan (Part 1). International Journal of Economic Research, 13(8), 3413-3425
Breidinger, C. (2006). Modeling Infrastructure Investments, Growth and Poverty Impact. New York.
Brown, A.C., Stern, J., Tenenbaum, B., & Gencer, G. (2006). Handbook for Evaluating Infrastructure Regulatory Systems. Washington: World Bank.
Burkaltseva, D.D. (2012). Іnstitutsіonal'ne zabezpechennya ekonomіchnoї bezpeki Ukraїni [Institutional economic security of Ukraine]. Kiev: Znannya.
Burkaltseva, D.D., Vorobyov, Yu.N., Borsch, L.M., Gerasimova, S.V., & Chepurko, V.V. (2016). Structural Modelling the System of Ensuring the Economic Security of the Complex Territorial Socio-Economic System of the EuraSec. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research, 14(9), 5683-5704.
Burkaltseva, D.D., Blazhevich, O.G., & Cherednichenko, M.S. (2016). Otsenka finansovoi ustoichivosti biznesa: teoreticheskie aspekty [Business Valuation of Financial Stability: The Theoretical Aspects]. Science Time, 5(29),96-102.
D’Agostino, D. (2008). Defense Critical Infrastructure: Risk Analysis of Critical Infrastructure Omits Highly Sensitive Assets. Washington: US Gout Accountability Office.
Dudin, M.N., Prokof'ev, M.N., Fedorova, I.J., & Frygin, A.V. (2014). The World Experience of Transformation of Innovative Approaches to Assurance of Financial Stability of Social Economic Systems. Life Science Journal, 11(9), 370-373.
Dudin, M.N., Frolova, E.E., Artemieva, Ju.A., Ivanovskaya, N.V., & Sitkareva, E.V. (2016). Transfer of Innovation Technologies as a Factor of the World Nuclear Power Industry Development. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research, 14(9), 5723-5736. Retrieved September 5, 2016, from http://serialsjournals.com/serialjournalmanager/pdf/1473070039.pdf.
Dudin, M.N., Kucuri, G.N., Fedorova, I.Ju., Dzusova, S.S., & Namitulina, A.Z. (2015). The Innovative Business Model Canvas in the System of Effective Budgeting. Asian Social Science, 11(7), 290-296.
Friesz, T.L. (Ed.). (2007). Network Science, Nonlinear Science and Infrastructure Systems. New York: Springer.
Goryacheva, K.S. (2006). Mekhanіzm upravlіnnya fіnansovoyu bezpekoyu pіdpriєmstva [Mechanism of Financial Security Company (Ph.D. Thesis Abstract)]. Kiev: Ukraine Institute of Economics and Forecasting of NAS.
Gukova, A.V., & Anikin, I.D. (2006). Rol' finansovoi bezopasnosti predpriyatiya v sisteme ego bezopasnosti [The Role of Financial Security of the Company in its Security System]. Obrazovanie i obshchestvo, 3, 98-102.
Kosten, D. (2016). Bitcoin Manifesto Or Crypto-Socialism as Next Phase of Socio-Economic Relations. Retrieved May 20, 2016, from https://ideas.repec.org/p/pra/mprapa/73601.html.
Kunitsyn, A.V. (1998). Vostok-Zapad: import tekhnologii i ekonomicheskaya bezopasnost' [East-West: technology import and economic security]. Moscow.
Mikhalkin, V.A. (1990). Ekonomicheskaya bezopasnost' SSSR [The Economic Security of the USSR]. Moscow.
Murray, A., & Grybeste, T. (2007). Critical Infrastructure: Reliability Vulnerability. Berlin.
Oleynikov, E.A. (2005). Ekonomicheskaya i natsional'naya bezopasnost' [Economic and National Security]. Moscow: Ekzamen.
Oleynikov, E.A., Filin, S.A., Vidyapin, V.I. et al. (2005). Ekonomicheskaya i natsional'naya bezopasnost' [Economic and National Security]. Moscow: Ekzamen.
Osnovnye sostavlyayushchie i napravleniya obespecheniya ekonomicheskoi bezopasnosti predpriyatiya [The Main Components and the Direction of Ensuring the Economic Security of the Enterprise]. (2016). Retrieved January 27, 2016, from http://www.itspecial.ru/osnovnye_sostavljyushie_i_napravlenij_obespechenij.html
Papekhin, R.S. (2007). Indikatory finansovoi bezopasnosti predpriyatiya [Indicators of Financial Security of the Enterprise]. Wolgograd: Volgogradskoe nauchnoe izdatel'stvo.
Pogosova, M., & Lebedev, V. (2014). Analіz metodichnogo zabezpechennya otsіnyuvannya fіnansovoї bezpeki pіdpriєmstva [Analysis of Methodological Support Assessment of the Financial Safety of an Enterprise]”. Ekonomіchnі nauki, 3.
Romadina, L.N. (2008). Ekonomicheskaya bezopasnost': razvitie nauchnykh predstavlenii [Economic Security: The Development of Scientific Concepts]. Vestnik Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta. Seriya 5. Ekonomika, 5(4), 161-164.
Sutnata, D., & Byrd, D.M. (2007). Computational Models of Risks to Infrastructure, Amsterdam.
Sullivaut, S. (2007). Strategies for Protecting National Critical Infrastructure Assets: A Focus on Problem Solving. Hoboken: Wiley.
United Nations. Economic Commission for Europe. (2003). A Set of Guidelines for Socio-Economic Cost Benefit Analysis of Transport Infrastructure Project Appraisal. New York: United Nations.
Vechkanov, G.S. (2007). Ekonomicheskaya bezopasnost' [Economic security]. Saint Petersburg: Piter.
Vivchenko, E.M. (2013). Modelirovanie ekonomicheskoi bezopasnosti predpriyatiya na primere OAO "Rovnegaz" [Simulation of Economic Security of the Enterprise on an Example of "Rovnegaz"]. Retrieved May 20, 2016, from http://naub.oa.edu.ua/2013/modelyuvannya-ekonomichnoji-bezpeky-pidpryjemstva-na-prykladi-pat-rivnehaz.
Yakunin, V.I., Bagdasaryan, V.E., & Sulakshin, S.S. (2008). Ideologiya ekonomicheskoi politiki [The ideology of economic policy]. Moscow: Nauchnyi ekspert.
1. V.I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University, 295007, Russia, Simferopol, Republic of Crimea, Vernadskogo Avenue, 4. Email: di_a@mail.ru
2. V.I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University, 295007, Russia, Simferopol, Republic of Crimea, Vernadskogo Avenue, 4
3. V.I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University, 295007, Russia, Simferopol, Republic of Crimea, Vernadskogo Avenue, 4
4. Peoples Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), 117198, Russian Federation, Moscow, Miklouho-Maclay Str., 6
5. Far Eastern Federal University, 690950, Russian Federation, Vladivostok, Suhanova Str., 8