

Vol. 38 (Nº 29) Año 2017. Pág. 22
MARINHO, Erica Z. 1; ROCHA, Renan C. 2; GALDINO, André G. de S. 3
Recibido:13/01/2017 • Aprobado: 18/02/2017
RESUMO: Este trabalho traz uma análise e perspectivas de alternativas para destinação de resíduos de rochas ornamentais através de um estudo bibliométrico. O estudo foi realizado em dezembro de 2016 e considerou artigos publicados nos últimos cinco anos na plataforma ScienceDirect (Elsevier). Os artigos foram classificados por áreas de reaproveitamento do resíduo, periódico, ano e região geográfica. Constatou-se que há tendência crescente no número de publicações e a maior área de reaproveitamento é a construção civil. |
ABSTRACT: This paper presents an analysis and perspectives of alternatives for the destination of ornamental stone residues through a bibliometric study. The study was conducted in December 2016 and considered articles published in the last five years on the platform ScienceDirect (Elsevier). Articles were classified by areas of reuse of the waste, periodical, year and geographic region. It was observed that there is an increasing trend in the number of publications and the largest reuse area is civil construction. |
As rochas ornamentais são materiais rochosos extraídos e beneficiados com finalidade de uso estrutural, de revestimento ou de decoração. Comercialmente, as rochas ornamentais são divididas principalmente em mármores e granitos (Cetem, 2013). Essas rochas são reconhecidas pela qualidade, durabilidade, variedade e beleza o que explica seu uso na maioria dos projetos arquitetônicos mundiais.
No Brasil a indústria de rochas ornamentais é expressiva. Em 2014, o país foi o quarto maior produtor mundial e o quinto maior exportador. O estado do Espírito Santo lidera o ranking nacional como maior produtor, tanto na lavra quanto no beneficiamento, e também como maior exportador (Montani, 2015). Em 2015, a produção brasileira de rochas ornamentais foi de cerca de 9,5 milhões de toneladas, aproximadamente 7% da produção mundial. As rochas ornamentais foram o quinto maior produto de base mineral exportado pelo Brasil, totalizando 2,32 milhões de toneladas, que corresponde a US$ 1,21 bilhão e gerando US$ 1,17 bilhão de saldo positivo na balança comercial brasileira (Abirochas, 2015).
Porém, essa indústria também gera degradação de áreas naturais no processo de lavra das rochas e grande quantidade de resíduos sólidos no processo de beneficiamento (Cetem, 2013). Baseado em dados da Abirochas (2015) estima-se que foram gerados cerca de 2,5 milhões de toneladas somente de resíduos finos e ultrafinos, como efluentes, em forma de lama no Brasil no ano de 2015. Esses efluentes ficam armazenados nas serrarias em lagoas abertas e são um problema para os empresários que não conseguem uma melhor destinação aos Resíduos de Rochas Ornamentais (RRO).
Temas ambientais, como os RRO têm tomado cada vez mais importância no cenário mundial devido às alterações climáticas e à poluição que se agravaram após a Revolução Industrial. A Conferência das Nações Unidas sobre o Meio Ambiente e o Desenvolvimento, em 1992, consolidou em nível mundial a necessidade de desenvolvimento sustentável.
Nesse contexto, o artigo destina-se a avaliar a dinâmica e a evolução da informação científica sobre o uso dos RRO com o objetivo de identificar as alternativas de destinação adequada desses resíduos industriais, de forma que sejam reaproveitados ao invés de descartados. Para isso, foi realizada uma análise bibliométrica com termos correlatos ao tema na plataforma ScienceDirect, da Elsevier, com auxílio do Portal de Periódicos da Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Neste estudo, os RRO são considerados resíduos finos originários do processo de beneficiamento das rochas ornamentais. Eles podem ter composição à base de silicato se provenientes de granito ou composição à base de carbonato se provenientes de mármore (Chiodi Filho, 2002).
No Brasil, o RRO é classificado de acordo com a norma regulamentadora NBR 10004:2004 como resíduo não perigoso e inerte (ABNT, 2004). Entretanto, os estudos de classificação ambiental de Braga, Buzzi, Couto & Lange (2010) e Manhães & Holanda (2008) afirmam que os RRO podem ser classificados como resíduo não perigoso e não inerte. Também o estudo de De Freitas, Raymundo, & De Jesus (2012) classifica os RRO como resíduo perigoso. Assim, esses resíduos podem prejudicar o meio ambiente se não dispostos adequadamente.
Os RRO, além de prejudicarem o meio ambiente, também causam transtorno para os empresários do setor no Brasil devido ao grande volume gerado e aos custos de transporte e aterro dos mesmos.
No processo de beneficiamento, aproximadamente 26% das rochas extraídas se transformam em resíduos finos (2-0,075 mm) e ultrafinos (<0,075 mm) na forma de efluente, que são basicamente uma mistura de pó de rocha, água e insumos de serragem e polimento, do qual aproximadamente 95% da água é recirculada no processo e os sólidos ficam dispostos nos pátios das serrarias e posteriormente são destinados a aterros (Cetem, 2013). Dessa forma, usando como base os dados da Abirochas (2015), estima-se que foram gerados aproximadamente 2,5 milhões de toneladas somente de resíduos finos e ultrafinos, como efluentes, em forma de lama no Brasil no ano de 2015.
Este estudo está classificado de acordo com Vergara (2013) como descritivo e exploratório, sendo utilizadas as estratégias de pesquisa bibiográfica e documental, com abordagem quantitativa.
Foi realizado estudo bibliométrico sobre reaproveitamento de RRO nos artigos publicados nos últimos cinco anos na plataforma ScienceDirect, da Elsevier, com o auxílio do portal de periódicos da CAPES. O levantamento ocorreu no mês de dezembro de 2016 com o uso das palavras-chave “granite”, “marble”, “ornamental stone”, “natural stone”, “ornamental rock” e “natural rock”, associadas às palavras-chave “residue”, “waste”, “powder”, “dust”, “sludge”, “slurry” e “tailings” (com suas respectivas formas no plural) através do uso do operador booleano AND.
A busca foi realizada em diversas etapas. Em cada etapa foram combinadas duas palavras-chave, por exemplo, “granite” AND “residue”, depois “granite” AND “waste”, etc. No total foram feitas 42 combinações de palavras-chave.
Após leitura e resumo dos artigos gerados pela busca, foram encontrados 108 artigos relacionados ao reaproveitamento do RRO. As informações dos 108 artigos selecionados foram exportadas para o EndNote®, e posteriormente convertidas em arquivo de texto, que foi exportado para o Microsoft Excel®, no qual foi realizada a análise dos dados e a confecção das tabelas e gráficos que compõem este estudo.
Para avaliar a dinâmica e a evolução da informação científica sobre o uso dos RRO e alcançar o objetivo deste estudo, que é identificar as alternativas para uma melhor destinação desses resíduos industriais, foi realizada leitura do título e resumo dos 108 artigos selecionados para serem classificados em diversas áreas de reaproveitamento. A tabela 1 apresenta o resumo dos resultados.
Tabela 1 - Resumo sobre as pesquisas atuais de reaproveitamento de RRO na plataforma ScienceDirect.
Nº |
Ano |
Título |
Aplicação |
1 |
2011 |
Characterization of eco-cement paste produced from waste sludges |
Cimento |
2 |
2011 |
Cr-doped perovskite and rutile pigments derived from industrial by-products |
Pigmento inorgânico |
3 |
2011 |
Effect of mineral admixtures on properties of self-compacting concrete |
Concreto |
4 |
2011 |
Effects of the usage of diatomite and waste marble powder as partial replacement of cement on the mechanical properties of concrete |
Concreto |
5 |
2011 |
High-strength rice husk ash concrete incorporating quarry dust as a partial substitute for sand |
Concreto |
6 |
2011 |
Performance of self-compacting concrete containing different mineral admixtures |
Concreto |
7 |
2011 |
Predicting the core compressive strength of self-compacting concrete (SCC) mixtures with mineral additives using artificial neural network |
Concreto |
8 |
2011 |
Recycled aggregate concrete produced with red granite dust as a partial cement replacement |
Concreto |
9 |
2011 |
Reuse of ornamental rock-cutting waste in aluminous porcelain |
Porcelana aluminosa |
10 |
2011 |
Reuse of sludge from the decorative quartz industry in hot bituminous mixes |
Asfalto |
11 |
2011 |
The use of solid residues derived from different industrial activities to obtain calcium silicates for use as insulating construction materials |
Tijolo |
12 |
2011 |
Use of waste marble aggregates in concrete |
Concreto |
13 |
2011 |
Utilization of muscovite granite waste in the manufacture of ceramic tiles |
Ladrilho cerâmico |
14 |
2012 |
An overview of using solid wastes for pigment industry |
Pigmento inorgânico |
15 |
2012 |
Characterization of stone powder sludge foams and their application to wastewater treatment: Role of pore connectivity |
Tratamento de água |
16 |
2012 |
Combining mineral and clay-based wastes to produce porcelain-like ceramics: An exploratory study |
Cerâmica |
17 |
2012 |
Effect of marble waste and pig slurry on the growth of native vegetation and heavy metal mobility in a mine tailing pond |
Tratamento de solo |
18 |
2012 |
Effect of natural pozzolana and marble powder on the properties of self-compacting concrete |
Concreto |
19 |
2012 |
Effectiveness of amendments on the spread and phytotoxicity of contaminants in metal–arsenic polluted soil |
Tratamento de solo |
20 |
2012 |
Estimation of compressive strength of self compacting concrete containing polypropylene fiber and mineral additives exposed to high temperature using artificial neural network |
Concreto |
21 |
2012 |
Fatigue behavior of dense asphalt mixes in dry and environmental-conditioning states |
Asfalto |
22 |
2012 |
Fresh and hardened characteristics of self compacting concretes made with combined use of marble powder, limestone filler, and fly ash |
Concreto |
23 |
2012 |
Investigation of using granite sludge as filler in bituminous hot mixtures |
Asfalto |
24 |
2012 |
Preparation and characterization of glazes from combinations of different industrial wastes |
Esmalte cerâmico |
25 |
2012 |
Probabilistic analysis of Mode II fracture of concrete with crushed granite stone fine aggregate replacing sand |
Concreto |
26 |
2012 |
Properties of concrete paving blocks made with waste marble |
Bloco de concreto |
27 |
2012 |
Properties of concrete prepared with low-grade recycled aggregates |
Concreto |
28 |
2012 |
Recycling of sawdust, spent earth from oil filtration, compost and marble residues for brick manufacturing |
Tijolo |
29 |
2012 |
Self-compacting concrete incorporating filler additives: Performance at high temperatures |
Concreto |
30 |
2012 |
The effect of fly ash content and types of aggregates on the properties of pre-fabricated concrete interlocking blocks (PCIBs) |
Bloco de concreto |
31 |
2012 |
The effect of mineral admixtures on mechanical properties, chloride ion permeability and impermeability of self-compacting concrete |
Concreto |
32 |
2012 |
Use of waste marble powder in brick industry |
Tijolo |
33 |
2013 |
An investigation on the influence of filler loading and compatibilizer on the properties of polypropylene/marble sludge composites |
Polímero |
34 |
2013 |
Carbon mineralization, microbial activity and metal dynamics in tailing ponds amended with pig slurry and marble waste |
Tratamento de solo |
35 |
2013 |
Characteristics of natural rubber hybrid composites based on marble sludge/carbon black and marble sludge/rice husk derived silica |
Compósito híbrido |
36 |
2013 |
Compressive strength of fly ash magnesium oxychloride cement containing granite wastes |
Cimento |
37 |
2013 |
Granitic quarry sludge waste in mortar: Effect on strength and durability |
Argamassa |
38 |
2013 |
Historical plasterwork techniques inspire new formulations |
Argamassa |
39 |
2013 |
Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of concrete modified with granite dust |
Concreto |
40 |
2013 |
Polyester polymer concrete: Effect of the marble particle sizes and high gamma radiation doses |
Concreto |
41 |
2013 |
Properties of bricks made using fly ash, quarry dust and billet scale |
Tijolo |
42 |
2013 |
Strength and durability properties of concrete made with granite industry waste |
Concreto |
43 |
2013 |
Sustainability perspective of marble and granite residues as concrete fillers |
Concreto |
44 |
2013 |
The effect of silica on the properties of marble sludge filled hybrid natural rubber composites |
Compósito híbrido |
45 |
2014 |
Adsorptive removal of methylene blue as organic pollutant by marble dust as eco-friendly sorbent |
Sorvente |
46 |
2014 |
Assessment of marble waste utilization as an alternative sorbent to limestone for SO2 control |
Sorvente |
47 |
2014 |
Blending of industrial waste from different sources as partial substitution of Portland cement in pastes and mortars |
Argamassa |
48 |
2014 |
Durability performance of structural concrete containing fine aggregates from waste generated by marble quarrying industry |
Concreto |
49 |
2014 |
Effects of mineral powders on hydration process and hydration products in normal strength concrete |
Concreto |
50 |
2014 |
Lead separation by sorption onto powdered marble waste |
Sorvente |
51 |
2014 |
Methodology for the mix design of self-compacting concrete using different mineral additions in binary blends of powders |
Concreto |
52 |
2014 |
Performance evaluation of cement mortars containing marble dust and glass fiber exposed to high temperature by using Taguchi method |
Argamassa |
53 |
2014 |
Portland cement systems with addition of sewage sludge ash. Application in concretes for the manufacture of blocks |
Bloco de concreto |
54 |
2014 |
Reinforcement of natural rubber hybrid composites based on marble sludge/Silica and marble sludge/rice husk derived silica |
Compósito híbrido |
55 |
2014 |
Restoration of dump deposits from quarries in a Mediterranean climate using marble industry waste |
Tratamento de solo |
56 |
2014 |
Re-use of waste marble dust in the production of cement and concrete |
Concreto |
57 |
2014 |
The effects of marble wastes on soil properties and hazelnut yield |
Tratamento de solo |
58 |
2014 |
Use of waste marble and recycled aggregates in self-compacting concrete for environmental sustainability |
Concreto |
59 |
2014 |
Using marble wastes as a soil amendment for acidic soil neutralization |
Tratamento de solo |
60 |
2015 |
A study of the laboratory polishing behavior of granite as road surfacing aggregate |
Asfalto |
61 |
2015 |
An investigation on chloroprene-compatibilized acrylonitrile butadiene rubber/high density polyethylene blends |
Polímero |
62 |
2015 |
Changes in the chemical composition of an acidic soil treated with marble quarry and marble cutting wastes |
Tratamento de solo |
63 |
2015 |
Characteristics of fired clay bricks with waste marble powder addition as building materials |
Tijolo |
64 |
2015 |
Effect of graphite and granite dust particulates as micro-fillers on tribological performance of Al 6061-T6 hybrid composites |
Compósito híbrido |
65 |
2015 |
Evaluation of industrial based adsorbents for simultaneous removal of arsenic and fluoride from drinking water |
Tratamento de água |
66 |
2015 |
Homogeneity of filler distribution within asphalt mix – A microscopic study |
Asfalto |
67 |
2015 |
Hybrid composites prepared from Industrial waste: Mechanical and swelling behavior |
Compósito híbrido |
68 |
2015 |
Incorporation of fillers from marble and tile wastes in the composition of self-compacting concretes |
Concreto |
69 |
2015 |
Mechanical activation of natural acidic igneous rocks for use in cement |
Argamassa |
70 |
2015 |
Mechanical properties and microstructural analysis of cement mortar incorporating marble powder as partial replacement of cement |
Argamassa |
71 |
2015 |
Mechanical properties of structural concrete containing very fine aggregates from marble cutting sludge |
Concreto |
72 |
2015 |
Preparation and modification of nano calcium carbonate filler from waste marble dust and commercial limestone for papermaking wet end application |
Papel |
73 |
2015 |
Properties of cold bonded quarry dust coarse aggregates and its use in concrete |
Agregado para construção civil |
74 |
2015 |
Raw and treated marble wastes reuse as low cost materials for phosphorus removal from aqueous solutions: Efficiencies and mechanisms |
Tratamento de água |
75 |
2015 |
Sustainable use of marble slurry in concrete |
Concreto |
76 |
2015 |
Using marble sludge increases the success of dump deposit restoration under Mediterranean climate |
Tratamento de solo |
77 |
2015 |
Utilization of granulated marble wastes and waste bricks as mineral admixture in cemented paste backfill of sulphide-rich tailings |
Cimento |
78 |
2015 |
Utilization of hard rock dust with red clay to produce roof tiles |
Telha |
79 |
2016 |
Addition of quartzite residues on mortars: Analysis of the alkali aggregate reaction and the mechanical behavior |
Argamassa |
80 |
2016 |
Advancements in mechanical and physical properties for marble powder–cement composites strengthened by nanostructured graphite particles |
Argamassa |
81 |
2016 |
Clay-bricks from recycled rock tailings |
Tijolo |
82 |
2016 |
Durability properties of structural concrete containing very fine aggregates of marble sludge |
Concreto |
83 |
2016 |
Effect of granite dust on mechanical and some durability properties of manufactured sand concrete |
Concreto |
84 |
2016 |
Effect of low cost fillers on cement hydration |
Concreto |
85 |
2016 |
Effects of elevated temperature and water quenching on strength and microstructure of mortars with river sand substitutes |
Argamassa |
86 |
2016 |
Effects of marble sludge incorporation on the properties of cement composites and concrete paving blocks |
Bloco de concreto |
87 |
2016 |
Enhancement of concrete properties by waste physicochemical treatment sludge of travertine processing wastewater |
Concreto |
88 |
2016 |
Experimental investigation of surface modified EOF steel slag as coarse aggregate in concrete |
Concreto |
89 |
2016 |
Laboratory validation of a gradation design concept for sustainable applications of unbound granular materials in pavement construction |
Pavimento na construção civil |
90 |
2016 |
Lightweight aggregates from mixtures of granite wastes with clay |
Agregado para construção civil |
91 |
2016 |
Lightweight aggregates from waste materials: Reappraisal of expansion behavior and prediction schemes for bloating |
Agregado para construção civil |
92 |
2016 |
Metakaolin as a precursor of materials for applications in Cultural Heritage: Geopolymer-based mortars with ornamental stone aggregates |
Argamassa |
93 |
2016 |
Microbial growth and community structure in acid mine soils after addition of different amendments for soil reclamation |
Tratamento de solo |
94 |
2016 |
Performance of granite cutting waste concrete under adverse exposure conditions |
Concreto |
95 |
2016 |
Performance of sustainable concrete containing granite cutting waste |
Concreto |
96 |
2016 |
Potential of using granite waste as raw material for geopolymer synthesis |
Polímero |
97 |
2016 |
Preparation of calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cement from marble sludge waste |
Cimento |
98 |
2016 |
Production of price-competitive bricks using a high volume of stone powder sludge waste and blast furnace slag through cementless CaO activation |
Tijolo |
99 |
2016 |
Properties of NaOH activated geopolymer with marble, travertine and volcanic tuff wastes |
Polímero |
100 |
2016 |
Reinforcing concrete: comparison of filler effects |
Concreto |
101 |
2016 |
Removal of Cr(III) from chrome tanning wastewater by adsorption using two natural carbonaceous materials: Eggshell and powdered marble |
Tratamento de água |
102 |
2016 |
Reusing of marble and granite powders in self-compacting concrete for sustainable development |
Concreto |
103 |
2016 |
Rheological and mechanical properties of concrete containing crushed granite fine aggregate |
Concreto |
104 |
2016 |
Study of natural hydraulic lime-based mortars prepared with masonry waste powder as aggregate and diatomite/fly ash as mineral admixtures |
Argamassa |
105 |
2016 |
Sustainable utilization of granite cutting waste in high strength concrete |
Concreto |
106 |
2016 |
Crystallization behavior and properties of CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 glass-ceramics synthesized from granite wastes |
Vidro-cerâmica |
107 |
2016 |
Mineralogical study of granite waste in a pozzolan/Ca(OH)2 system: Influence of the activation process |
Cimento |
108 |
2016 |
Using marble sludge and phytoextraction to remediate metal(loid) polluted soils |
Tratamento de solo |
Fonte: Elaborado pelos autores (2016).
A tabela 2 traz a quantidade e a porcentagem de artigos publicados por periódico, com seu respectivo fator de impacto JCR, que é um dos indicadores mais usados para classificar os periódicos acadêmicos.
Tabela 2 – Artigos publicados por periódico.
Periódico |
Quantidade de Artigos |
Porcentagem |
Fator de Impacto (JCR) |
Construction and Building Materials |
50 |
46,3% |
2,883 |
Journal of Cleaner Production |
15 |
14,0% |
5,315 |
Ceramics International |
5 |
4,7% |
2,661 |
Applied Clay Science |
3 |
2,8% |
3,065 |
Chemosphere |
3 |
2,8% |
4,068 |
Journal of Advanced Research |
3 |
2,8% |
- |
Journal of Environmental Management |
3 |
2,8% |
4,049 |
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry |
3 |
2,8% |
3,458 |
Cement and Concrete Composites |
2 |
1,9% |
3,982 |
Ecological Engineering |
2 |
1,9% |
3,223 |
Journal of Geochemical Exploration |
2 |
1,9% |
2,749 |
Fonte: Elaborado pelos autores (2016).
Nota-se tendência da área de aplicação na construção civil, sendo o periódico Construction and Building Materials o que possui o maior número de publicações, totalizando 50 artigos. Também se destaca o periódico Journal of Cleaner Production, com 15 publicações, o que confirma a tendência das pesquisas atuais em destinar corretamente esses resíduos.
A figura 1 ilustra o número de publicações por ano, com sua linha de tendência. Nota-se aumento no número de publicações na área. O aumento do número de publicações sugere que há a preocupação das pesquisas atuais em destinar corretamente esses resíduos.
Figura 1 - Quantidade de artigos publicados por ano.
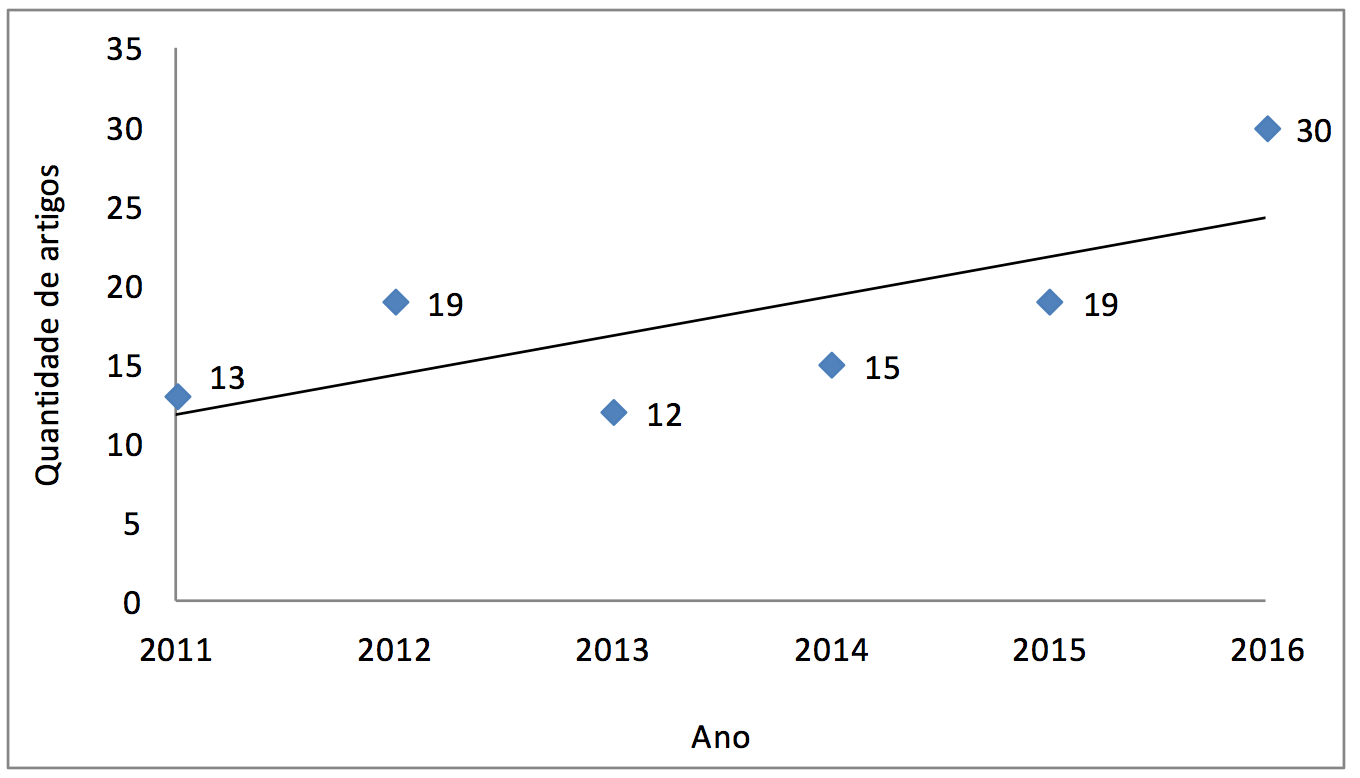
Fonte: Elaborado pelos autores (2016).
A figura 2 traz a quantidade de artigos publicados por área de aplicação. O gráfico evidencia um grande número de possibilidades distintas para o uso do RRO.
Figura 2 – Quantidade de artigos publicados por área de aplicação.

Fonte: Elaborado pelos autores (2016).
Nota-se que a maior quantidade de aplicações estudada envolve o uso do RRO no desenvolvimento de produtos sustentáveis para a área de construção civil (concreto, argamassa, cimento, bloco, agregado e pavimento) totalizando 61 artigos, e para a área de materiais cerâmicos (tijolo, cerâmica, esmalte, ladrilho, vidro-cerâmica, telha e porcelana) totalizando 13 artigos. A área de tratamento de solo também se destaca com 10 artigos. As áreas menos pesquisadas são a que envolvem seu uso para fabricação de sorvente químico, pigmento inorgânico e papel, respectivamente.
A figura 3 traz o número de publicações por país, sendo que 12 países possuem apenas uma publicação, e não foram considerados no gráfico.
Figura 3 – Quantidade de artigos publicados por região.

Fonte: Elaborado pelos autores (2016).
Nota-se que a maior quantidade de publicações foi realizada na Turquia, Índia e Espanha,
Evidenciando uma forte relação entre estudos sobre RRO com os grandes produtores mundiais de rochas ornamentais, visto que os países citados são o 3º, 2º e 7º maiores produtores mundiais de rochas ornamentais. (Montani, 2014).
Constatou-se que há tendência de aumento no número de publicações envolvendo o reaproveitamento dos resíduos de rochas ornamentais nos últimos anos. Destaca-se a diversidade de destinação dos RRO apresentada nos artigos, com destaque para as aplicações envolvendo o desenvolvimento de produtos sustentáveis para a área de construção civil e materiais cerâmicos. Em relação aos periódicos nos quais esses artigos estão sendo publicados, nota-se a mesma tendência da área de construção civil, sendo o periódico Construction and Building Materials o que possui o maior número de publicações. Observou-se ainda que maior quantidade de publicações têm origem na Turquia.
Abd Elmoaty, M. (2013). Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of concrete modified with granite dust. Construction and Building Materials, 47, 743-752.
Abukersh, S. A.; & Fairfield, C. A. (2011). Recycled aggregate concrete produced with red granite dust as a partial cement replacement. Construction and Building Materials, 25(10), 4088-4094.
Ahmed, K.; Nizami, S. S.; & Raza, N. Z. (2013). Characteristics of natural rubber hybrid composites based on marble sludge/carbon black and marble sludge/rice husk derived silica. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 19(4), 1169-1176.
Ahmed, K.; Nizami, S. S.; Raza, N. Z.; & Habib, F. (2013). The effect of silica on the properties of marble sludge filled hybrid natural rubber composites. Journal of King Saud University - Science, 25(4), 331-339.
Ahmed, K.; Raza, N. Z.; Habib, F.; Aijaz, M.; & Afridi, M. H. (2013). An investigation on the influence of filler loading and compatibilizer on the properties of polypropylene/marble sludge composites. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 19(6), 1805-1810.
Ahmed, K.; Nizami, S. S.; & Raza, N. Z. (2014). Reinforcement of natural rubber hybrid composites based on marble sludge/Silica and marble sludge/rice husk derived silica. Journal of Advanced Research, 5(2), 165-173.
Ahmed, K. (2015). Hybrid composites prepared from Industrial waste: Mechanical and swelling behavior. Journal of Advanced Research, 6(2), 225-232.
Ahmed, K. (2015). An investigation on chloroprene-compatibilized acrylonitrile butadiene rubber/high density polyethylene blends. Journal of Advanced Research, 6(6), 811-817.
Akbulut, H.; Gürer, C.; Çetin, S.; & Elmacı, A. (2012). Investigation of using granite sludge as filler in bituminous hot mixtures. Construction and Building Materials, 36, 430-436.
Aliabdo, A. A.; Abd Elmoaty, M.; & Auda, E. M. (2014). Re-use of waste marble dust in the production of cement and concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 50, 28-41.
Altun, N. E. (2014). Assessment of marble waste utilization as an alternative sorbent to limestone for SO2 control. Fuel Processing Technology, 128, 461-470.
Associação Brasileira da Indústria de Rochas Ornamentais [Abirochas]. (2015). Balanço da produção, exportações, importações e consumo interno brasileiro de rochas ornamentais em 2015. Recuperado de https://issuu.com/abirochas/docs/abirochas_noticia_4
Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas [ABNT]. (2004). NBR 10004:2004. Resíduos sólidos − classificação. Rio de Janeiro: ABNT.
Bacarji, E.; Toledo Filho, R. D.; Koenders, E. A. B.; Figueiredo, E. P.; & Lopes, J. L. M. P. (2013). Sustainability perspective of marble and granite residues as concrete fillers. Construction and Building Materials, 45, 1-10.
Baeza-Brotons, F.; Payá, J.; Galao, O.; Saval, J. M.; & Garcés, P. (2014). Blending of industrial waste from different sources as partial substitution of Portland cement in pastes and mortars. Construction and Building Materials, 66, 645-653.
Baeza-Brotons, F.; Garcés, P.; Payá, J.; & Saval, J. M. (2014). Portland cement systems with addition of sewage sludge ash. Application in concretes for the manufacture of blocks. Journal of Cleaner Production, 82, 112-124.
Balaji Rao, K.; Bhaskar Desai, V.; & Jagan Mohan, D. (2012). Probabilistic analysis of Mode II fracture of concrete with crushed granite stone fine aggregate replacing sand. Construction and Building Materials, 27(1), 319-330.
Barra, B.; Momm, L.; Guerrero, Y.; & Bernucci, L. (2012). Fatigue behavior of dense asphalt mixes in dry and environmental-conditioning states. Construction and Building Materials, 29, 128-134.
Barros, S. V. A.; Marciano, J. E. A.; Ferreira, H. C.; Menezes, R. R.; & Neves, G. A. (2016). Addition of quartzite residues on mortars: Analysis of the alkali aggregate reaction and the mechanical behavior. Construction and Building Materials, 118, 344-351.
Belaidi, A. S. E.; Azzouz, L.; Kadri, E.; & Kenai, S. (2012). Effect of natural pozzolana and marble powder on the properties of self-compacting concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 31, 251-257.
Bibi, S.; Farooqi, A.; Hussain, K.; & Haider, N. (2015). Evaluation of industrial based adsorbents for simultaneous removal of arsenic and fluoride from drinking water. Journal of Cleaner Production, 87, 882-896.
Bilgin, N.; Yeprem, H. A.; Arslan, S.; Bilgin, A.; Günay, E.; & Marşoglu, M. (2012). Use of waste marble powder in brick industry. Construction and Building Materials, 29, 449-457.
Braga, F. S.; Buzzi, D. C.; Couto, M. C. L.; & Lange, L. C. (2010). Caracterização ambiental de lamas de beneficiamento de rochas ornamentais. Engenharia Sanitária Ambiental, 15(3), 237-244.
Brostow, W.; Chetuya, N.; Hnatchuk, N.; & Uygunoglu, T. (2016). Reinforcing concrete: comparison of filler effects. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112 (Part 4), 2243-2248.
Centro de Tecnologia Mineral [Cetem]. (2013). Tecnologia de rochas ornamentais: pesquisa, lavra e beneficiamento. Rio de Janeiro: CETEM/MCTI.
Chiodi Filho, C. (2002). Aspectos de interesse sobre rochas ornamentais e de revestimento: identificação, especificação e utilização. Recuperado de https://issuu.com/abirochas/docs/aspectos_interesse
Choudhary, A.; Shah, V.; & Bishnoi, S. (2016). Effect of low cost fillers on cement hydration. Construction and Building Materials, 124, 533-543.
Clausi, M.; Tarantino, S. C.; Magnani, L. L.; Riccardi, M. P.; Tedeschi, C.; & Zema, M. (2016). Metakaolin as a precursor of materials for applications in Cultural Heritage: Geopolymer-based mortars with ornamental stone aggregates. Applied Clay Science, 132–133, 589-599.
Cordeiro, G. C.; de Alvarenga, L. M. S. C.; & Rocha, C. A. A. (2016). Rheological and mechanical properties of concrete containing crushed granite fine aggregate. Construction and Building Materials, 111, 766-773.
Da Silva, R. C.; Pianaro, S. A.; & Tebcherani, S. M. (2012). Preparation and characterization of glazes from combinations of different industrial wastes. Ceramics International, 38(4), 2725-2731.
De Freitas, J. J. G.; Raymundo, V.; & De Jesus, H. C. (2012). Características químicas dos resíduos de serragem segregados de rochas ornamentais no Estado do Espírito Santo. Revista Brasileira de Geociências, 42(3), 615-624.
Dondi, M.; Cappelletti, P.; D’Amore, M.; de Gennaro, R.; Graziano, S. F.; Langella, A.; Raimondo, M.; & Zanelli, C. (2016). Lightweight aggregates from waste materials: Reappraisal of expansion behavior and prediction schemes for bloating. Construction and Building Materials, 127, 394-409.
Elabbas, S.; Mandi, L.; Berrekhis, F.; Pons, M. N.; Leclerc, J. P.; & Ouazzani, N. (2016). Removal of Cr(III) from chrome tanning wastewater by adsorption using two natural carbonaceous materials: Eggshell and powdered marble. Journal of Environmental Management, 166, 589-595.
El-Alfi, E. A.; & Gado, R. A. (2016). Preparation of calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cement from marble sludge waste. Construction and Building Materials, 113, 764-772.
Eliche-Quesada, D.; Corpas-Iglesias, F. A.; Pérez-Villarejo, L.; & Iglesias-Godino, F. J. (2012). Recycling of sawdust, spent earth from oil filtration, compost and marble residues for brick manufacturing. Construction and Building Materials, 34, 275-284.
El-Sherbiny, S.; El-Sheikh, S. M.; & Barhoum, A. (2015). Preparation and modification of nano calcium carbonate filler from waste marble dust and commercial limestone for papermaking wet end application. Powder Technology, 279, 290-300.
Ercikdi, B.; Külekci, G.; & Yılmaz, T. (2015). Utilization of granulated marble wastes and waste bricks as mineral admixture in cemented paste backfill of sulphide-rich tailings. Construction and Building Materials, 93, 573-583.
Ergün, A. (2011). Effects of the usage of diatomite and waste marble powder as partial replacement of cement on the mechanical properties of concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 25(2), 806-812.
Felipe-Sesé, M.; Eliche-Quesada, D.; & Corpas-Iglesias, F. A. (2011). The use of solid residues derived from different industrial activities to obtain calcium silicates for use as insulating construction materials. Ceramics International, 37(8), 3019-3028.
Gameiro, F.; de Brito, J.; & Correia da Silva, D. (2014). Durability performance of structural concrete containing fine aggregates from waste generated by marble quarrying industry. Engineering Structures, 59, 654-662.
Gencel, O.; Ozel, C.; Koksal, F.; Erdogmus, E.; Martínez-Barrera, G.; & Brostow, W. (2012). Properties of concrete paving blocks made with waste marble. Journal of Cleaner Production, 21(1), 62-70.
Gesoğlu, M.; Güneyisi, E.; Kocabağ, M. E.; Bayram, V.; & Mermerdaş, K. (2012). Fresh and hardened characteristics of self compacting concretes made with combined use of marble powder, limestone filler, and fly ash. Construction and Building Materials, 37, 160-170.
Ghazy, S. E.; & Gad, A. H. M. (2014). Lead separation by sorption onto powdered marble waste. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 7(3), 277-286.
Gómez Mercado, F.; de Haro Lozano, S.; Delgado Fernández, I. C.; & Simón-Torres, M. (2015). Using marble sludge increases the success of dump deposit restoration under Mediterranean climate. Ecological Engineering, 84, 305-310.
González, V.; García, I.; Del Moral, F.; & Simón, M. (2012). Effectiveness of amendments on the spread and phytotoxicity of contaminants in metal–arsenic polluted soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 205–206, 72-80.
González, V.; Salinas, J.; García, I.; del Moral, F.; & Simón, M. (2016). Using marble sludge and phytoextraction to remediate metal(loid) polluted soils. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 174, 29-34.
Haddad, K.; Jellali, S.; Jaouadi, S.; Benltifa, M.; Mlayah, A.; & Hamzaoui, A. H. (2015). Raw and treated marble wastes reuse as low cost materials for phosphorus removal from aqueous solutions: Efficiencies and mechanisms. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 18(1), 75-87.
Hajjaji, W.; Zanelli, C.; Seabra, M. P.; Dondi, M.; & Labrincha, J. A. (2011). Cr-doped perovskite and rutile pigments derived from industrial by-products. Chemical Engineering Journal, 171(3), 1178-1184.
Hajjaji, W.; Costa, G.; Zanelli, C.; Ribeiro, M. J.; Seabra, M. P.; Dondi, M.; & Labrincha, J. A. (2012). An overview of using solid wastes for pigment industry. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 32(4), 753-764.
Hamed, M. M.; Ahmed, I. M.; & Metwally, S. S. (2014). Adsorptive removal of methylene blue as organic pollutant by marble dust as eco-friendly sorbent. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20(4), 2370-2377.
Han, Y.; Kim, H.; & Tong, M. (2012). Characterization of stone powder sludge foams and their application to wastewater treatment: Role of pore connectivity. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 134(1), 26-30.
Hebhoub, H.; Aoun, H.; Belachia, M.; Houari, H.; & Ghorbel, E. (2011). Use of waste marble aggregates in concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 25(3), 1167-1171.
Hojamberdiev, M.; Eminov, A.; & Xu, Y. (2011). Utilization of muscovite granite waste in the manufacture of ceramic tiles. Ceramics International, 37(3), 871-876.
Jeyaprabha, B.; Elangovan, G.; & Prakash, P. (2016). Effects of elevated temperature and water quenching on strength and microstructure of mortars with river sand substitutes. Construction and Building Materials, 114, 688-698.
Junkes, J. A.; Prates, P. B.; Hotza, D.; & Segadães, A. M. (2012). Combining mineral and clay-based wastes to produce porcelain-like ceramics: An exploratory study. Applied Clay Science, 69, 50-57.
Kabas, S.; Faz, A.; Acosta, J. A.; Zornoza, R.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Carmona, D. M.; & Bech, J. (2012). Effect of marble waste and pig slurry on the growth of native vegetation and heavy metal mobility in a mine tailing pond. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 123, 69-76.
Kang, J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Yuan, J.; Hou, Y.; & Qian, S. (2017). Crystallization behavior and properties of CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 glass-ceramics synthesized from granite wastes. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 457, 111-115.
Keleştemur, O.; Arıcı, E.; Yıldız, S.; & Gökçer, B. (2014). Performance evaluation of cement mortars containing marble dust and glass fiber exposed to high temperature by using Taguchi method. Construction and Building Materials, 60, 17-24.
Kirgiz, M. S. (2016). Advancements in mechanical and physical properties for marble powder–cement composites strengthened by nanostructured graphite particles. Mechanics of Materials, 92, 223-234.
Kou, S.; Poon, C.; & Wan, H. (2012). Properties of concrete prepared with low-grade recycled aggregates. Construction and Building Materials, 36, 881-889.
Kuity, A.; & Das, A. (2015). Homogeneity of filler distribution within asphalt mix – A microscopic study. Construction and Building Materials, 95, 497-505.
Li, H.; Huang, F.; Cheng, G.; Xie, Y.; Tan, Y.; Li, L.; & Yi, Z. (2016). Effect of granite dust on mechanical and some durability properties of manufactured sand concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 109, 41-46.
Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Zheng, L.; Wen, J.; Wu, C.; & Tan, Y. (2013). Compressive strength of fly ash magnesium oxychloride cement containing granite wastes. Construction and Building Materials, 38, 1-7.
Manhães, J. P. V. T.; & Holanda, J. N. F. (2008). Caracterização e classificação de resíduo sólido “pó de rocha granítica” gerado na indústria de rochas ornamentais. Química Nova, 31(6), 1301-1304.
Martínez-Barrera, G.; Menchaca-Campos, C.; & Gencel, O. (2013). Polyester polymer concrete: Effect of the marble particle sizes and high gamma radiation doses. Construction and Building Materials, 41, 204-208.
Mashaly, A. O.; El-Kaliouby, B. A.; Shalaby, B. N.; El – Gohary, A. M.; & Rashwan, M. A. (2016). Effects of marble sludge incorporation on the properties of cement composites and concrete paving blocks. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112(Part 1), 731-741.
Medina, G.; Sáez del Bosque, I. F.; Frías, M.; Sánchez de Rojas, M. I.; & Medina, C. (2017). Mineralogical study of granite waste in a pozzolan/Ca(OH)2 system: Influence of the activation process. Applied Clay Science, 135, 362-371.
Mohamed Soltan, A. M.; Pöhler, K.; Fuchs, F.; El-Raoof, F. A.; El-Kaliouby, B. A.; Koenig, A.; & Pöllmann, H. (2016). Clay-bricks from recycled rock tailings. Ceramics International, 42(15), 16685-16696.
Montani, C. (2014). XXV Report marble and stones in the world 2014. Recuperado de https://issuu.com/abirochas/docs/rapporto2014
Montani, C. (2015). Dossiê Brasil 2015. Recuperado de https://issuu.com/abirochas/docs/dossierbrasile2015
Moreno, F.; Rubio, M. C.; & Martinez-Echevarria, M. J. (2011). Reuse of sludge from the decorative quartz industry in hot bituminous mixes. Construction and Building Materials, 25(5), 2465-2471.
Nepomuceno, M. C. S.; Pereira-de-Oliveira, L. A.; & Lopes, S. M. R. (2014). Methodology for the mix design of self-compacting concrete using different mineral additions in binary blends of powders. Construction and Building Materials, 64, 82-94.
Pai, A.; Sharma, S. S.; D’Silva, R. E.; & Nikhil, R. G. (2015). Effect of graphite and granite dust particulates as micro-fillers on tribological performance of Al 6061-T6 hybrid composites. Tribology International, 92, 462-471.
Park, H.; Jeong, Y.; Jun, Y.; & Oh, J. E. (2016). Production of price-competitive bricks using a high volume of stone powder sludge waste and blast furnace slag through cementless CaO activation. Construction and Building Materials, 122, 343-353.
Pourghahramani, P.; & Azami, M. A. (2015). Mechanical activation of natural acidic igneous rocks for use in cement. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 13, 482-88.
Raman, S. N.; Ngo, T.; Mendis, P.; & Mahmud, H. B. (2011). High-strength rice husk ash concrete incorporating quarry dust as a partial substitute for sand. Construction and Building Materials, 25(7), 3123-3130.
Ramos, T.; Matos, A. M.; Schmidt, B.; Rio, J.; & Sousa-Coutinho, J. (2013). Granitic quarry sludge waste in mortar: Effect on strength and durability. Construction and Building Materials, 47, 1001-1009.
Rana, A.; Kalla, P.; & Csetenyi, L. J. (2015). Sustainable use of marble slurry in concrete. Journal of Cleaner Production, 94, 304-311.
Rodrigues, R.; de Brito, J.; & Sardinha, M. (2015). Mechanical properties of structural concrete containing very fine aggregates from marble cutting sludge. Construction and Building Materials, 77, 349-356.
Sabapathy, Y. K.; Balasubramanian, V. B.; Shiva Shankari, N.; Yeshwant Kumar, A.; & Ravichandar, D. (2016). Experimental investigation of surface modified EOF steel slag as coarse aggregate in concrete. Journal of King Saud University - Engineering Sciences.
Sadek, D. M.; El-Attar, M. M.; & Ali, H. A. (2016). Reusing of marble and granite powders in self-compacting concrete for sustainable development. Journal of Cleaner Production, 121, 19-32.
Salavessa, E.; Jalali, S.; Sousa, L. M. O.; Fernandes, L.; & Duarte, A. M. (2013). Historical plasterwork techniques inspire new formulations. Construction and Building Materials, 48, 858-867.
Sardinha, M.; de Brito, J.; & Rodrigues, R. (2016). Durability properties of structural concrete containing very fine aggregates of marble sludge. Construction and Building Materials, 119, 45-52.
Shakir, A. A.; Naganathan, S.; & Mustapha, K. N. (2013). Properties of bricks made using fly ash, quarry dust and billet scale. Construction and Building Materials, 41, 131-138.
Silva, M. A.; Paes Jr, H. R.; & Holanda, J. N. F. (2011). Reuse of ornamental rock-cutting waste in aluminous porcelain. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(3), 936-940.
Simón-Torres, M.; del Moral-Torres, F.; de Haro-Lozano, S.; & Gómez-Mercado, F. (2014). Restoration of dump deposits from quarries in a Mediterranean climate using marble industry waste. Ecological Engineering, 71, 94-100.
Singh, S.; Nagar, R.; & Agrawal, V. (2016). Performance of granite cutting waste concrete under adverse exposure conditions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 127, 172-182.
Singh, S.; Khan, S.; Khandelwal, R.; Chugh, A.; & Nagar, R. (2016). Performance of sustainable concrete containing granite cutting waste. Journal of Cleaner Production, 119, 86-98.
Singh, S.; Nagar, R.; Agrawal, V.; Rana, A.; & Tiwari, A. (2016). Sustainable utilization of granite cutting waste in high strength concrete. Journal of Cleaner Production, 116, 223-235.
Sogancioglu, M.; Yel, E.; Aksoy, S.; & Unal, V. Ec. (2016). Enhancement of concrete properties by waste physicochemical treatment sludge of travertine processing wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112(Part 1), 575-580.
Soltan, A. M. M.; Kahl, W.; Abd El-Raoof, F.; Abdel-Hamid El-Kaliouby, B.; Abdel-Kader Serry, M.; & Abdel-Kader, N. A. (2016). Lightweight aggregates from mixtures of granite wastes with clay. Journal of Cleaner Production, 117, 139-149.
Sultana, M. S.; Ahmed, A. N.; Zaman, M. N.; Rahman, M. A.; Biswas, P. K.; & Nandy, P. K. (2015). Utilization of hard rock dust with red clay to produce roof tiles. Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 3(1), 22-26.
Sutcu, M.; Alptekin, H.; Erdogmus, E.; Er, Y.; & Gencel, O. (2015). Characteristics of fired clay bricks with waste marble powder addition as building materials. Construction and Building Materials, 82, 1-8.
Tchadjié, L. N.; Djobo, J. N. Y.; Ranjbar, N.; Tchakouté, H. K.; Kenne, B. B. D.; Elimbi, A.; & Njopwouo, D. (2016). Potential of using granite waste as raw material for geopolymer synthesis. Ceramics International, 42(2, Part B), 3046-3055.
Tekin, I. (2016). Properties of NaOH activated geopolymer with marble, travertine and volcanic tuff wastes. Construction and Building Materials, 127, 607-617.
Tennich, M.; Kallel, A.; & Ben Ouezdou, M. (2015). Incorporation of fillers from marble and tile wastes in the composition of self-compacting concretes. Construction and Building Materials, 91, 65-70.
Thomas, Job; & Harilal, B. (2015). Properties of cold bonded quarry dust coarse aggregates and its use in concrete. Cement and Concrete Composites, 62, 67-75.
Tikkanen, J.; Cwirzen, A.; & Penttala, V. (2014). Effects of mineral powders on hydration process and hydration products in normal strength concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 72, 7-14.
Tozsin, G.; Oztas, T.; Arol, A. I.; Kalkan, E.; & Duyar, O. (2014). The effects of marble wastes on soil properties and hazelnut yield. Journal of Cleaner Production, 81, 146-149.
Tozsin, G.; Arol, A. I.; Oztas, T.; & Kalkan, E. (2014). Using marble wastes as a soil amendment for acidic soil neutralization. Journal of Environmental Management, 133, 374-377.
Tozsin, G.; Oztas, T.; Arol, Ali I.; & Kalkan, E. (2015). Changes in the chemical composition of an acidic soil treated with marble quarry and marble cutting wastes. Chemosphere, 138, 664-667.
Uygunoğlu, T.; Topcu, I. B.; Gencel, O.; & Brostow, W. (2012). The effect of fly ash content and types of aggregates on the properties of pre-fabricated concrete interlocking blocks (PCIBs). Construction and Building Materials, 30, 180-187.
Uygunoğlu, T.; Topçu, İ. B.; & Çelik, A. G. (2014). Use of waste marble and recycled aggregates in self-compacting concrete for environmental sustainability. Journal of Cleaner Production, 84, 691-700.
Uysal, M.; & Yilmaz, K. (2011). Effect of mineral admixtures on properties of self-compacting concrete. Cement and Concrete Composites, 33(7), 771-776.
Uysal, M.; & Sumer, M. (2011). Performance of self-compacting concrete containing different mineral admixtures. Construction and Building Materials, 25(11), 4112-4120.
Uysal, M.; & Tanyildizi, H. (2011). Predicting the core compressive strength of self-compacting concrete (SCC) mixtures with mineral additives using artificial neural network. Construction and Building Materials, 25(11), 4105-4111.
Uysal, M.; Yilmaz, K.; & Ipek, M. (2012). The effect of mineral admixtures on mechanical properties, chloride ion permeability and impermeability of self-compacting concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 27(1), 263-270.
Uysal, M.; & Tanyildizi, H. (2012). Estimation of compressive strength of self compacting concrete containing polypropylene fiber and mineral additives exposed to high temperature using artificial neural network. Construction and Building Materials, 27(1), 404-414.
Uysal, M. (2012). Self-compacting concrete incorporating filler additives: Performance at high temperatures. Construction and Building Materials, 26(1), 701-706.
Vardhan, K.; Goyal, S.; Siddique, R.; & Singh, M. (2015). Mechanical properties and microstructural analysis of cement mortar incorporating marble powder as partial replacement of cement. Construction and Building Materials, 96, 615-621.
Vergara, S. C. (2013). Projetos e relatórios de pesquisa em administração 14a ed. São Paulo: Atlas.
Vijayalakshmi, M.; Sekar, A. S. S.; & Ganesh prabhu, G. (2013). Strength and durability properties of concrete made with granite industry waste. Construction and Building Materials, 46, 1-7.
Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Xie, X.; Stanjek, H.; Oeser, M.; & Steinauer, B. (2015). A study of the laboratory polishing behavior of granite as road surfacing aggregate. Construction and Building Materials, 89, 25-35.
Xiao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lyu, D.; Tutumluer, E.; & Zhang, J. (2016). Laboratory validation of a gradation design concept for sustainable applications of unbound granular materials in pavement construction. Construction and Building Materials, 129, 125-139.
Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; & Zhang, S. (2016). Study of natural hydraulic lime-based mortars prepared with masonry waste powder as aggregate and diatomite/fly ash as mineral admixtures. Journal of Cleaner Production, 119, 118-127.
Yen, C.; Tseng, D.; & Lin, T. (2011). Characterization of eco-cement paste produced from waste sludges. Chemosphere, 84(2), 220-226.
Zornoza, R.; Faz, Á.; Carmona, D. M.; Acosta, J. A.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; & de Vreng, A. (2013). Carbon mineralization, microbial activity and metal dynamics in tailing ponds amended with pig slurry and marble waste. Chemosphere, 90(10), 2606-2613.
Zornoza, R.; Acosta, J. A.; Faz, A.; & Bååth, E. (2016). Microbial growth and community structure in acid mine soils after addition of different amendments for soil reclamation. Geoderma, 272, 64-72.
1. Graduanda em Engenharia de Produção. Instituto Federal do Espírito Santo, Campus Cariacica. ericazmarinho@gmail.com
2. Mestre em Engenharia Metalúrgica e Materiais. Coordenadoria de Manutenção de Sistemas Metroferroviários. Instituto Federal do Espírito Santo, Campus Cariacica. renancarreiro@ifes.edu.br
3. Engenheiro de Materiais, Doutor em Engenharia Mecânica. Coordenadoria de Mecânica. Instituto Federal do Espírito Santo, Campus Vitória. andregsg@ifes.edu.br