

Vol. 38 (Nº 27) Año 2017. Pág. 30
Vladimir Ivanovich TRUHACHEV 1; Elena Ivanovna KOSTYUKOVA 2; Aleksey Nikolaevich BOBRISHEV 3
Recibido: 22/12/16 • Aprobado: 01/02/2017
ABSTRACT: The aim of the study is to identify the prospects and limitation of further development of management accounting as a science and its distribution in the practice of accounting and analytical work of Russian enterprises of the agrarian sector. As a result, stimulating and bounding factors were identified and classified. The research also identified the most popular tools, methods and forms of management accounting in the condition of Russian reality, as well as the most important competence of specialists in the field of management accounting. The expert survey results were compared with similar, previously conducted, most representative researches both in Russia and abroad. As a result, there were identified hidden reserves for wider dissemination of management accounting in practice of enterprises of agrarian sector of the Russian Federation. |
RESUMEN: El objetivo del estudio es identificar las perspectivas y la limitación de un mayor desarrollo de la contabilidad gerencial como ciencia y su distribución en la práctica de la contabilidad y el trabajo analítico de las empresas rusas del sector agrario. Como resultado, se identificaron y clasificaron factores estimulantes y delimitadores. La investigación también identificó las herramientas más populares, métodos y formas de contabilidad de gestión en la condición de la realidad rusa, así como la competencia más importante de los especialistas en el campo de la contabilidad de gestión. Los resultados de la encuesta de expertos se compararon con investigaciones similares, previamente realizadas y más representativas tanto en Rusia como en el extranjero. Como resultado, se identificaron reservas ocultas para una mayor difusión de la contabilidad de gestión en la práctica de las empresas del sector agrario de la Federación de Rusia. |
Every year management accounting increasingly ranged as an independent science, with immanent subject, object and tools oriented to the adoption of effective management decisions. The period of active formation of system of management accounting in Russia shows that today this science is considered generally recognized both in scientific environment and business environment, and efficiency in the use of individual elements of management accounting raises less doubt among researchers and practitioners. At the same time, 20 years of experience in discussions and disputes concerning interpretation of key economic categories, further prospects of use of tools for identification of objects, subjects and methods of management accounting witness about the need to summarize some further development of subtotals of management accounting, identifying different deficiencies in its methodology, search of existing limitations of its distribution. The present research performs analyses of the functional validity of the existing accounting system, which allows to identify the basic functional limitations that prevent the introduction of management accounting in the economic performance of agricultural sector in Russia, as well as uncover hidden opportunities for its further development.
The research is performed in the framework of the grant of the President of the Russian Federation for the State Support of Young Russian Scientists (MK-8806.2016.6) and is focused on the identification of regularities of development and the functional validity of the existing system of management accounting in the agricultural regions of Russia. Methodological framework of the research was formed taking into account the results obtained by Russian and foreign authors in the study of issues of formation and development of management accounting. This study is a continuation of the early works of the authors (Bobryshev, Elchaninova and Tatarinova 2015).
The study has examined various aspects of development of management accounting. In this context, it is worth noting the following work and scientific results:
Causes and consequences of accounting system changes are described in the research (Hopwood 1987), while the factors contributing to the change of accounting as well as reflecting the role of accounting were highlighted and ways of influencing the process of institutional changes in the future were mentioned. In the context of the research it is worth mentioning works, dedicated to the issues of transformation processes of accounting and analytical procurement to the management of economic entities: (Butler and Ghosh, 2015; Burns and Scapens 2000; Davison 2015; Ezzamel, Willmott and Worthington 2008; Nagar, Venky, and Gwen 2014, Schleicher and Walker 2015; Smith, Morris and Ezzamel 2005; Johnson and Kaplan 1987).
Research on a number of interconnected terms of reference have shown: increasing distribution of analytical methods of management accounting in comparison with traditional; harmonization of the methodology of management accounting in accordance with postindustrial processes in the economy; the increasing diffusion of managerial accounting, related to small and medium-sized firms; the common complication of the process of decision-making on the background of depressive economy phenomena.
The research was conducted in accordance with the developed algorithm (Figure 1) using the method of expert survey.
For this purpose, highly qualified specialists in the field of management accounting have been selected and arranged into three focus groups:
1. "Accounting workers" - this focus group included employees of the accounting and analytical services enterprises of various economic activities in several regions of the Russian Federation;
2. "Scientists" - are employees of higher educational institutions and scientific establishments of the Russian Federation, with the degree of candidate and doctor of economic sciences, involved in the development of management accounting;
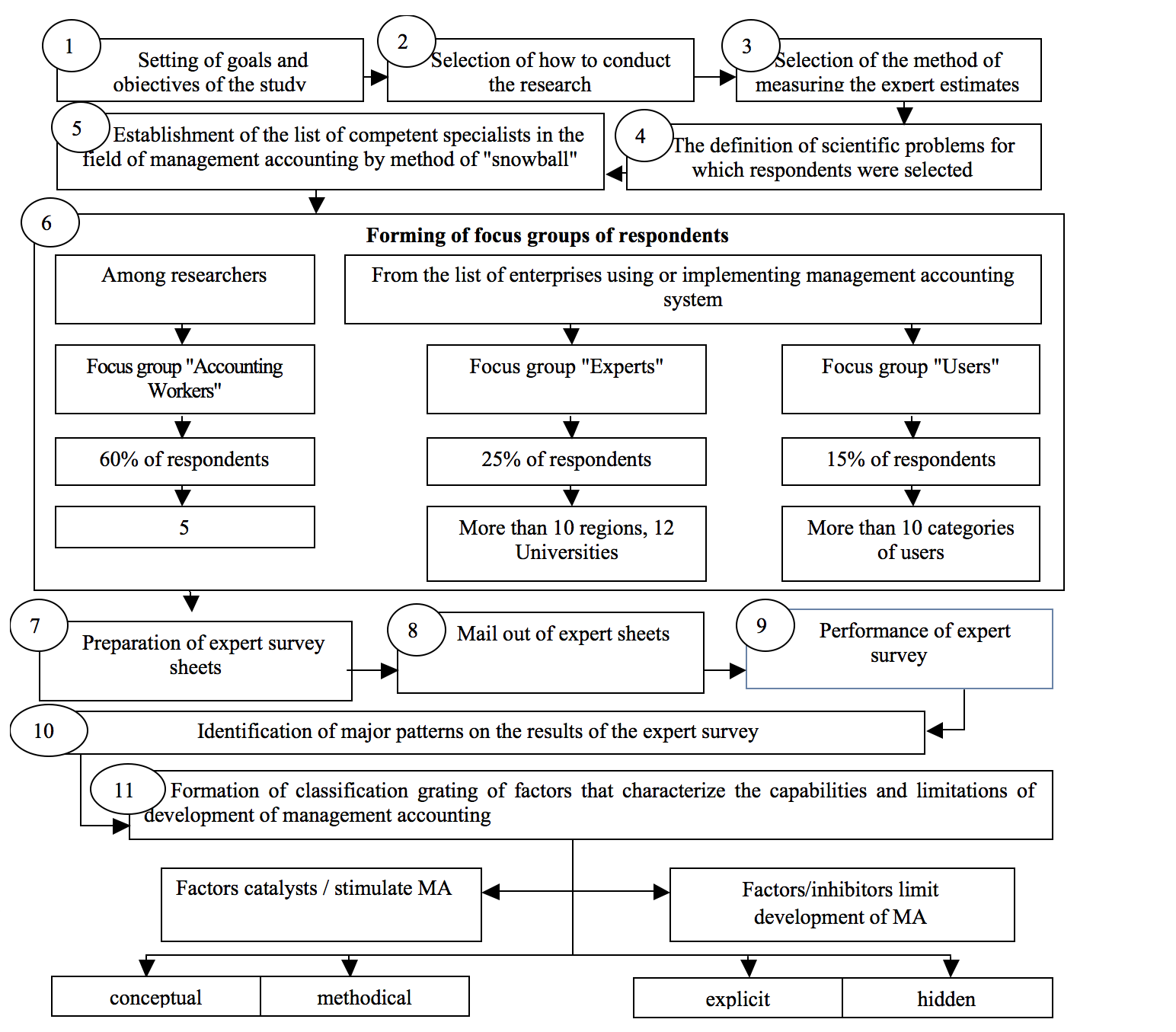
Figure 1. The algorithm of the research
3. "Users" - are individuals who use data of management accounting to make decisions based on financial and management reporting (CEOs, business owners, investors, financial and credit analysts, etc.).
Unlike the mass survey, the expert one forms a limited number of members of expert groups, whilst a choice of specialists for focus groups is one of the most important stages that define the terminal effectiveness of the research and relevance of information received in order to identify the relevant determinants and patterns.
To conduct the expert survey, the best specialists in the field of setting and implementation of management accounting in agricultural organizations with more than 10 years of practical work were selected. In the focus group "Scientists" Doctors of Science with the highest rates of citation (Russian Science Citation Index) scientific works in the field of management accounting were selected.
The conclusion of the research is that it is currently impossible to speak of widespread management accounting in Russian regions with agricultural specialization. 53.8% of the interviewed representatives of enterprises, only partially and arbitrarily use its separate elements, and 7.7% of the respondents do not see the need to implement it. But on the other hand, the positive practice and the possibility for further distribution exist.
Most often functions of conducting of management accounting were connected with accountants, it was mentioned by 40.3% of all respondents replied; 12.9% of respondents reported that such functions were connected with accountant-analyst, within the scope of activity of which is exclusively conducting of management accounting.
From the position of different categories of users of management accounting targets are treated differently, this explains isolation and at the same time, a wide variety of methods and tools. Architectonics of management accounting in this connection has a unique structure within various economic entities, but at the same time, there are basic objectives of management accounting and corresponding methods of formulating the relevant information to make effective decisions, as demonstrated by this research, such objectives should include, primarily: "Accounting, control, and minimization of expenses; "Assessing the effectiveness of the Organization; "Planning and budgeting.
As a result of dynamic assessment of the importance of challenges facing accountants engaged in management accounting, which intended to express the views on how different aims have varied over time, there were revealed the following pattern: in all focus groups, respondents indicated their substantial transformation. This confirms latent evolutionary processes in the methodology of accounting science that is changing under the influence of postindustrial processes in economy. For example, the most important current objective of management accounting is planning and budgeting, but in the future, according to respondents from all the focus groups, the significance of this trend for accountants will drop significantly, the new objectives which have not previously been the subject of managerial accounting will come, they are, first of all, the implementation of business strategies, development of optimal business model (Figure 2).
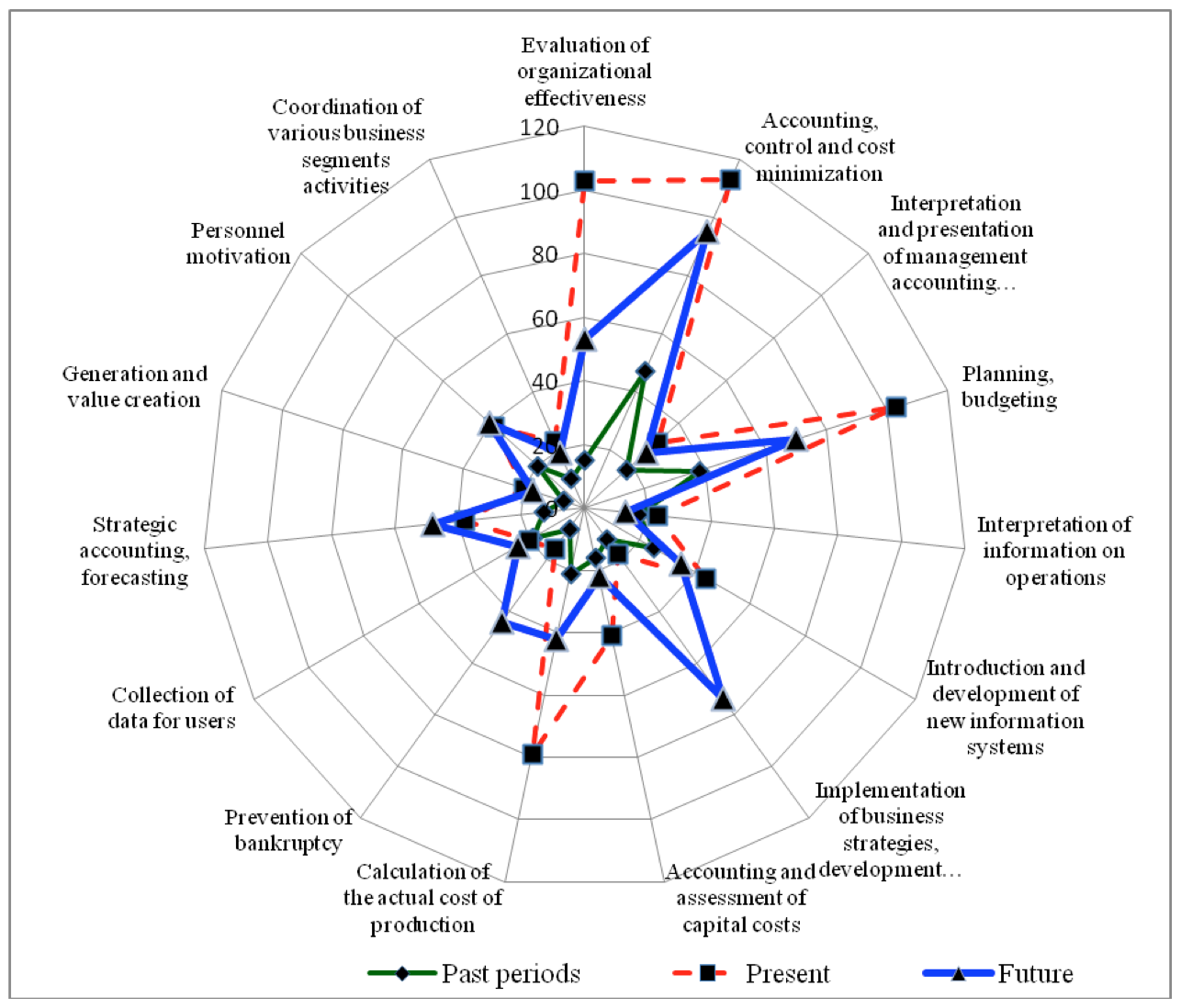
Figure 2. Comparison of the goals facing accountants engaged in management
accounting in different historical stages of development (points for all respondents)
As the most important competencies in the field of management accounting, respondents have indicated: 1. Skills in the methods the accounting of expenses and calculation of the cost of production (15.9% of the total number of points); 2. The ability to form an effective system of planning (budgeting) (14.6%); 3. Collection and analysis of data for decision making (14.2%).
The results confirm that the role of an accountant is currently and significantly being changed, accountant is increasingly involved in the process of developing business strategy, and management accounting system acquires strategic direction. Whilst, management accounting functions and objects are becoming wider, that requires improvements in its methods and tools.
The largest number of respondents (24.2%) as the primary limiter for distribution management accounting sees the size of the Organization, believing that "management accounting is introduced mostly in a large corporations and agricultural holdings". An important factor is the availability of qualified staff, capable to apply effectively management accounting tools for the formulation of relevant information. Ranked third as a factor encouraging the greatest management accounting, according to respondents, is the presence of claims by shareholders and owners (14.2%).
In the next stage, the respondents were asked to rate the directions of further development of management accounting in Russia. As the most significant factor contributing to the dissemination of management accounting, were mentioned "creation of specialized software", the importance of this factor was 21.1%, followed by the higher "qualifications of staff" which is 20.9%.
Let us mention that only 3% of the amount of distributed points were relegated in favor of the opinion that "the data produced in management accounting system is sufficient for the adoption of effective management decisions" that was explained by us as the complete lack of prospects for further dissemination of managerial accounting.
Further the trends of development of management accounting in Russia in historical retrospect have been analyzed, as a result, it has been mentioned that, at present, the staff is the most important factor in the development of management accounting; although in the future this will become less meaningful and the factor "creation of specialized soft ware" will be the most important (see Figure 3).
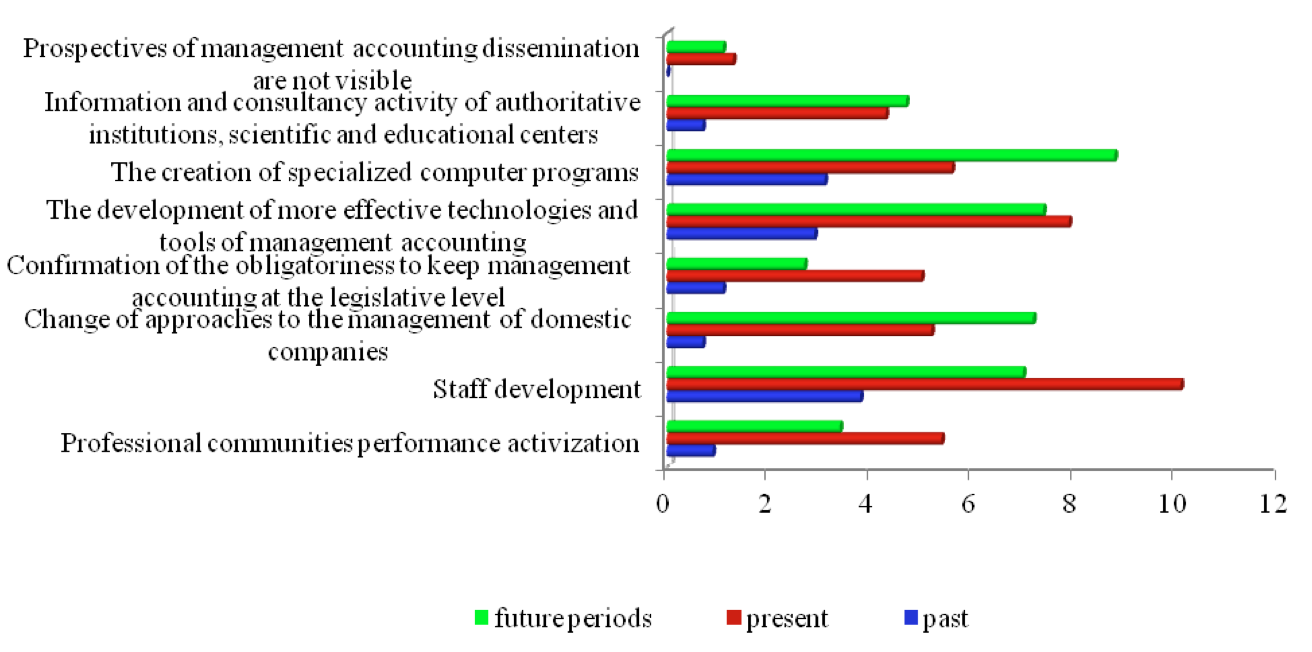
Figure 3. Distribution of the significance directions of development of management
accounting in the past, present and future (% of the total amount distributed points)
A large variety of management accounting tools and technologies, which are often used in conjunction with a promising technology in the management system, extend the range of activities of employees accounting, analytical, planning and economic services. The evolutionary process in this field makes the individual tools and technologies more or less popular. According to the results of expert survey we have estimated the importance and the information value of the most common tools of management accounting. To do this, respondents were asked to select the most important, from their point of view, technologies and evaluate them on the basis of given proportion of grades for each symbol, in the total amount of grades, we have assigned ranks to each technology (Table 1).
Table 1. The results of the assessment of the views of respondents
on the importance and value of information technology on management accounting
Parameters of the survey |
In the aggregate for all respondents, % |
Rank |
Budgeting |
11.2 |
1 |
Forecasting |
10.4 |
2 |
Strategic management accounting |
5.4 |
7 |
Standard cost method (normative method of expenses accounting) |
3.7 |
15 |
Direct costing method |
4.8 |
10 |
Total quality management (TQM) |
5.0 |
9 |
Calculation of value added |
4.0 |
13 |
Economic value added |
2.4 |
18 |
System of balanced indicators |
4.6 |
11 |
Expenses accounting by activity (AB-costing "ABC" method, activity-based costing) |
6.2 |
5 |
Management of responsibility centers |
5.1 |
8 |
Management reporting |
9.0 |
3 |
Managerial analysis |
8.1 |
4 |
KPI-technology |
3.1 |
16 |
CVP analysis (break-even analysis) |
4.3 |
12 |
Management accounting of business model of the enterprise |
2.9 |
17 |
Cost accounting and calculation of the cost of production |
6.1 |
6 |
Calculation of the last operation ("just in time" JIT) |
3.8 |
14 |
Total |
100.0 |
x |
The most popular tools in practice of enterprises of agrarian sector of Russia are: budgeting, which is used in practice of 82.4% of the survey respondents. 74.5% of all respondents used forecasting in the practice, 64.7% are actively using management reporting.
According to respondents, the most popular technologies in the future, according to respondents, will remain: 9.7%"forecasting"; 9.3%"budgeting"; 9.3% "management accounting" (Table 2).
Table 2. The results of the evaluation of the importance of technology of management accounting
(in% of total points assigned in the corresponding time interval, for all respondents)
Technology of management accounting |
Historicalperiod |
Current time |
Future |
Budgeting |
13.4 |
12.3 |
9.3 |
Forecasting |
7.6 |
10.0 |
9.7 |
Strategic management accounting |
3.7 |
4.1 |
6.8 |
Standard cost method (normative method of expenses accounting) |
8.5 |
3.1 |
2.3 |
Direct costing method |
3.4 |
5.1 |
2.7 |
Total quality management (TQM) |
5.2 |
5.5 |
5.6 |
Calculation of value added |
3.0 |
3.7 |
3.7 |
Economic value added |
2.7 |
2.1 |
4.1 |
System of balanced indicators |
3.4 |
4.9 |
5.8 |
Expenses accounting by activity (AB-costing "ABC" method, activity-based costing) |
3.4 |
6.0 |
5.6 |
Management of responsibility centers |
4.9 |
6.4 |
7.2 |
Management reporting |
6.7 |
9.5 |
9.3 |
Managerial analysis |
6.1 |
7.4 |
7.6 |
KPI-technology |
4.6 |
3.4 |
3.9 |
CVP analysis (break-even analysis) |
7.0 |
4.7 |
5.6 |
Management accounting of business model of the enterprise |
2.1 |
2.6 |
4.5 |
Cost accounting and calculation of the cost of production |
11.0 |
5.5 |
3.1 |
Calculation of the last operation ("just in time" JIT) |
3.4 |
3.8 |
3.3 |
Total |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
Dissemination of new methods of management accounting depends on a variety of internal and external factors. Among the most significant respondents has mentioned: information technology (13% of all respondents assigned points); crisis processes in the economy (11.6%); the emergence of new accounting software (10.5%).
It should be noted that information technology, which in addition to specialized computer programs can include cloud, neural networks, digital data exchange tools and other tools for efficient processing of sorting, storing and retrieving data, to facilitate the implementation of the process of human interaction and computer science, focus-group "scientists" recognized as the most significant (Figure 4).
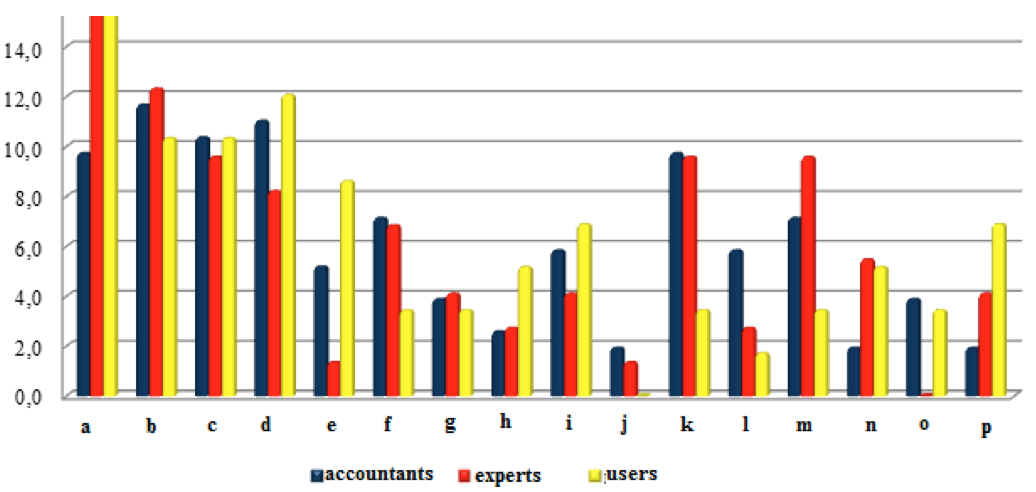
Figure 4. Distribution of factors importance, the most influencing on management accounting technologies: a) Information technology; b) Crisis processes in the economy; c) Changes in approaches to business management; d)The emergence of new accounting of computer programs; e) Tactic of consumer orientation; f) New management style (new demands of owners, shareholders, founders); g) New external reporting requirements; h) Globalization, the expansion of foreign trade and export-import operations; i) Tactics targeting quality; j) Advice of external consultants) (activities of professional communities); k) Introduction of new technologies in manufacture; l) The emergence of new economic activities; m) Complexity of business structure; n) The emergence of new objects; o) Increased attention to the environmental dimension of the activities of the enterprise and socially responsible behaviour; p) Arrival of foreign owners to the company(partners, consultants)
Scientists also appreciated the importance of factors such as: crisis processes in the economy-12.3%; changes in ways of enterprise management - 9.6%; the introduction of new technologies in production-9.6%; the increasing complexity of business structure-9.6%.
General discussion results in scientific-expert community of methodical aspects of management accounting development and their correlation with the results of the research in this area of study confirms the authors view that traditional technologies such as cost accounting, calculation and budgeting remain dominant in management accounting system while one of the most distinct restrictions of further development of management accounting is limitation and conservative views on the objective of management accounting recording. Management accounting is often equated with the term "cost accounting", which severely restricts its tools, goals and ways of information production. Furthermore, the current system of management accounting in Russia should be more adapted to the diagnosis of macroeconomic factors and external environment of an economic entity, in this context it requires theoretical underpinning and methodological formation of special models (subsystem) of management accounting for usage in conditions of crisis processes in the economy (Bobryshev 2015; Bobryshev, Uryadova, Lyubenkova,Yakovenko and Alekseeva 2014).
The study does not contradict the fundamental works of Russian authors in accounting (Shigaev 2010; Sidorova 2012; Vahrushina 2014; Kostukova, Elchaninova and Manzhosova 2009; Shyrobokov, Kosteva and Barekova 2007) and others.
The results of the study allowed to conclude that opportunities and limiters of management accounting methodological development are largely supported by the interpretation of the autonomy of this scientific direction that many scientists both in Russia and in the international practice (Horngren, Datar and Foster 2003; Sokolov 2000) identified with the term "cost accounting", finding it difficult to draw a clear line between them. This largely limits its toolkit, objectives and ways to develop information. There is another point of view, according to which management accounting is more voluminous, includes "processes for the collection, preparation and analytical processing of different information of accounting and not accounting nature, providing the necessary data for business management system" (Boyns and Edwards 2013; Satubaldin 1980; Bulgakov 2006; Rozhnova 2015, and others).
Discovered patterns are comparable with the results of the development prospects of evaluation of management accounting in developing countries (Hopper, Tsamenyi, Uddin and Wickramasinghe 2009; Anderson and Lanen 1999).
On the basis of the expert survey, we have formulated a number of conclusions, patterns and determinants:
1. While studying the enterprises functioning practice, where management accounting system is implemented and successfully used, we have found that they are basically large enterprises, employing more than 1000 people (33.3%), representing the holding structure type (in the second place there are enterprises with employees number from 100 to 200 people (20%), small business patterns (with less than 100 people) represent the smallest share of those enterprises that use or introduce a system of management accounting (7.1%); 40% of them are limited liability companies, 53.3% are joint-stock companies, 6.7% are other organizational-legal forms. Industry classification of establishment of enterprises is very diverse: 39.8% are from agrarian sector of the economy, 21.7% are from trade, 16.3% are from construction. The number of accounting department employees for such enterprises in 47% of cases is up to 10 people, in 26% of companies the number of employees successfully using the system of management accounting varies from 10 to 30 people, in 13% of enterprises it ranges from 50 to 100 employees.
2. Availability of functioning system of management accounting in an enterprise is often justified by experts only by the size of organization, suggesting that it may be introduced only in large economic entities, while in world practice this system is quite widespread not only in middle-sized, but also in small business patterns, as well as in non-profit organizations. Currently in our country only the first studies on the formation of management accounting system in budgetary institutions are appearing (Vahrushina and Malinovskaya 2014; Tsapulina, Romanova and Ilyina 2015; Vahrushina 2016; Vahrushina 2015), we also consider this direction to be promising and establishing new methodological peculiarities of accounting science.
3. Contrary to established practices in management accounting at the international level, in Russia such a goal as "interpreting and reporting the results of activities of management accounting" is not considered to be significant. Underestimation of such an important factor in our view leads to the problem that such competence is either not formed or acquired after some period of time among specialists. Fragmentary usage of similar skills, in our opinion, does not allow management personnel to fully look at advantages of information, which is formed in the framework of management accounting and consequently hinders its development and distribution.
4. Managerial accounting should not be limited to the collection and analysis of data needed for decision-making, in accordance with the tendencies of post-industrial economic development the need for making recommendations for the development of an economic entity becomes more and more popular as well as the description of its business model and the macroeconomic environment in which it functions, development of recommendations and alternatives for operational and strategic nature concerning the directions of further development.
5. Many technologies that were effective in the past, according to respondents, will become considerably less popular in the future. Among the technologies that will become significantly more important in the long term, respondents identified: strategic management accounting, management accounting of business model of the enterprise, the concept of the balanced scorecard, concept of economic value added.
6. During the expert poll it was revealed that a pattern according to which if the organization is larger in size, and in the number of accounting employees, the greater the amount of management accounting tools it uses effectively. This fact creates the preconditions for practical improvement of management accounting systems in relation to the characteristics of operation of small and medium-sized businesses. These issues are discussed in particular in the works: (Perren and Grant 2000; Amat, Carmona and Roberts 1994).
7. The effectiveness of technology in terms of materiality generated information for decision-making, according to respondents, dominates, that is more important in its implementation than the laboriousness of this technology or the costs associated with its acquisition and subsequent use.
Chenhall, R. and Langfield-Smith, K. (1998). Factors influencing the role of management accounting in the development of performance measures within organizational change programs. Management Accounting Research, 9 (4): 361-386.
Johansson, T. and Siverbo, S. (2009). Why is research on management accounting change not explicitly evolutionary? Taking the next step in the conceptualisation of management accounting change. Management Accounting Research, 20 (2): 146-162.
1. Stavropol state agrarian University, Russian Federation. Email: truh.vl.asu@bk.ru
2. Stavropol state agrarian University, Russian Federation
3. Stavropol state agrarian University, Russian Federation