

 HOME | ÍNDICE POR TÍTULO | NORMAS PUBLICACIÓN
HOME | ÍNDICE POR TÍTULO | NORMAS PUBLICACIÓN Espacios. Vol. 37 (Nº 26) Año 2016. Pág. 25
Mauricio Johnny LOOS 1; Carlos Manuel TABOADA RODRIGUEZ 2; Sérgio Murilo PETRI 3; Lucas dos Santos MATOS 4
Recibido: 24/04/16 • Aprobado: 20/05/2016
ABSTRACT: The objective of the present study is to create a mapping of publications dealing with the topic of Airport Performance Measurement, and, based on that, select a bibliographic portfolio composed of the most relevant and applicable works in the field, as per the opinion of the authors of this study. Towards these ends, a bibliometric analysis was carried out with the goal of gaining insight as to the most-recurring topics: authors, articles, journals, and keywords falling under the topic. This work is characterized as exploratory-descriptive research; beside this, it employs mixed qualitative and quantitative approaches to data analysis by way of the Knowledge Development Process – Constructivist (ProknowC) intervention instrument. Resulting from this, 26 relevant –and 661 reference- articles were selected, which went on to form the Bibliographic Portfolio. Upon completion of bibliometric analysis of the articles and references making up the Bibliographic Portfolio, the following was shown: the academic journals "Journal of Air Transport Management" and "Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review"; the scholarly articles "Analysis of the operational efficiency of major airports in the United States", "Measuring airport quality from the airlines' view point: an application of data envelopment analysis" and "Inefficiencies and scale economies of European airport operations"; the keywords "Data envelopment analysis (DEA)", "Airport(s)", "Benchmarking", "Performance evaluation", "Productivity" and "Efficiency"; and the most-cited authors Sarkis, J.; Adler, N.; Berechman, J.; Pels, E.; Nijkamp, P. and Rietveld, P. These results are deemed singular, given the limitations set by this work´s authors and the ample nature of the approach employed during research; regardless, they stand to contribute to the work of future researchers in this, or other, fields. |
RESUMO: El objetivo del presente estudio es crear un mapeo de las publicaciones que tratan el tema de Aeropuerto de Funcionamiento de la medida, y, basándose en esto, seleccione una cartera bibliográfico compuesto por las obras más relevantes y aplicables en la materia, de acuerdo con la opinión de la autores de este estudio. Para alcanzar estos fines, un análisis bibliométrico se llevó a cabo con el objetivo de obtener una visión en cuanto a los temas más recurrentes: autores, artículos, revistas, y las palabras clave que entran en el tema. Este trabajo se caracteriza por la investigación exploratoria-descriptiva; Junto a esto, se emplea enfoques cualitativos y cuantitativos mixtos de análisis de datos a través del Proceso de Desarrollo del Conocimiento - Constructivista (ProknowC) instrumento de intervención. Como resultado de esto, se seleccionaron 26 relevantes -y 661 artículos referencia-, que pasó a formar la Cartera bibliográfica. Una vez completado el análisis bibliométrico de los artículos y referencias que componen la Cartera bibliográfica, se ha representado lo siguiente: las revistas académicas "Diario de Gestión de Transporte Aéreo" y "Transporte de Investigación Parte E: Logística y Transporte de la opinión"; los artículos académicos "Análisis de la eficacia operativa de los aeropuertos en los Estados Unidos", "La medición de la calidad del aeropuerto desde el punto vista de las compañías aéreas: una aplicación del análisis envolvente de datos" y "Las ineficiencias y las economías de escala de las operaciones aeroportuarias europeas"; Las palabras clave "Análisis Envolvente de Datos (DEA)", "Aeropuerto (s)", "Evaluación del desempeño" "Benchmarking", "productividad" y "eficiencia"; y los autores más citados Sarkis, J .; Adler, N .; Berechman, J .; Pels, E .; Nijkamp, P. y Rietveld, P. Estos resultados se consideran singular, dadas las limitaciones establecidas por la presente realización trabajo autores y la amplia naturaleza del enfoque empleado durante la investigación; independientemente, se paran para contribuir a los trabajos de futuros investigadores en este u otros, campos. |
In today´s world, airports face an ever-stronger demand for efficient and high-quality services. The implementation of benchmarking tools might be useful in the development of consistent airport performance measurements, as well as in the search for potential efficiency improvements (GITTO & MANCUSO, 2012). An airport is a place where air transportation service providers (airlines) and their customers meet and conduct business. Airport operations and management are handled by administrative bodies that see both passengers and airlines as their customers. Airport operation is similar to any other company, from a corporate ethics and operational efficiency standpoint. As they carry this out, airports must incorporate a knowledge of broader concerns, such as safety and security, which are less important in other types of business (WANG et al., 2004). Currently, benchmarking in airports is receiving quite a bit of attention in both academic literature as well as in practice, but it has presented a certain difficulty as a result of the heterogeneity inherent to any reasonably sized collection of data. The majority of existing studies on the topic would treat airport production technology as a black box, or seek to separate terminal from airside activities for individual evaluation (ADLER, LIEBERT, & YAZHEMSKY, 2013). Studies on performance stand to provide answers to the following queries: are private airports more efficient than public ones? Does contracting services out (outsourcing) improve productivity and performance? What is the impact of commercial activity in airport productivity performance? Insight into these issues stands to contribute to policy decision-making, allowing for the selection of the best structure for airport system organization (OUM, YU, & FU, 2003).
The airport industry is highly diversified and heterogeneous, with a great degree of differentiation in terms of quality, ownership, regulatory structures, different combinations of services and the characteristics of related operations, as well as external restrictions, such as location and environmental factors. As such, the measurement and comparison of airport performance is a complex proposition (OUM, YU, & FU, 2003). In parallel, the airport terminal exhibits dynamic behavior in time and space and is characterized as a highly complex large-scale system, since it involves, as per Manataki & Zografos (2009):
"(i) a substantial number of entities (for example, departure / arrival / transfer passengers, well-wishers, greeters, visitors, airport operators, airlines) and types of services (for example, ticketing, check-in, boarding pass control, passport control, security screening, ancillary services, etc.);
(ii) complex interrelations between successive phases of processing of the various customer groups;
(iii) trade-offs between resources requirements and offered level of service, and
(iv) variability and stochastic events (e.g., seasonality and peaking patterns of airport demand, stochastic flight delays, randomness and stochastic variations in arrival and service operations, stochastic airport users' behavior)."
The total performance of an airline company is divided into three categories (production, marketing, and management), based on the operating cycle and organizational characteristics. The division of total performance can successfully be used as a diagnostics tool, providing preliminary insight into an airline for operators (FENG & WANG, 2000). Airport decision-makers frequently face complex decision-making problems related to airport planning, layout, and operations. The airport decision-making process is even more convoluted due to the large number of interested parties, each of which defends its own interests and objectives in terms of airport performance measurement, which can, in some cases, conflict with one another. Despite the wealth of experience behind both the models and tools for analysis of airport performance, existing models and tools touch on but a portion of the airport decision-making process (ZOGRAFOS & MADAS, 2006). Air transportation companies seek to place and expand their operations in efficient airports to reduce their costs and improve the quality of their respective services. The movement towards deregulation, or liberalization, also led to a growing worldwide trend of airport commercialization and privatization. Airport managers are being faced with new challenges in an era of growing commercial pressures; given the circumstances, it is of great importance to airports that the best-possible services be provided in the most-efficient way possible. In order to do this, airports need to know the best practices over various dimensions of airport operations within the industry, and how their performance compares to the best industry practices (OUM, YU, & FU, 2003).
In light of these circumstances and within the topic of Airport Performance Measurement, this study seeks to answer the following questions: i) Which are the most relevant articles on Airport Performance Measurement? and ii) Which articles, authors, journals and their respective impact factors, and keywords stand out in that field? With the objective of providing response to the research questions, this study endeavors to compile a mapping of existing publications on the topic of Airport Performance Measurement. This task is divided into two stages: a) gather a collection of scientifically recognized articles (the Bibliographic Portfolio) that bear relevance to the authors' conception of "Airport Performance Evaluation"; and, b) carry out a bibliometric study on the literature comprising the Bibliographic Portfolio, with the goal of establishing the standout authors, journals, and keywords within the topic of interest. To achieve these objectives, the study initially establishes the methods employed during research, following by the results of the study, data derived from bibliometric analysis, a discussion on the findings and, lastly, its final considerations.
The purpose of this section is to present the framework of the present scientific work, providing a methodological structure and allowing the reader a contextualization in regards to the lens through which the research was outlined and completed. This, while reaching its objectives and generating the final results. It is divided into six subsections: a) the research objective; b) the underlying logic of the inquiry; c) the research process; d) the results of the study; e) the technical procedures employed throughout, and f) the intervention instrument to be utilized.
The analysis, description, or explanation of the procedures and approaches employed in academic research, seeking to specify the grouping of philosophical assumptions or areas of study, which in turn serve as foundation for the topics or purposes, explaining or clarifying a given study in respects to the scientific method, are termed the methodological framework (TASCA et al., 2010; ROSA et al., 2011).
Regarding the general category of its objective, the present work is described as exploratory-descriptive: exploratory, given that it aims to build knowledge, on part of the researcher, regarding its topic by way of the selection and analysis of scientific articles published in scholarly journals, fitting within the preset confines established by the authors; descriptive, in turn, as a result of its description of the articles that comprise its bibliographic portfolio by way of bibliometrics, discussing articles of scientific recognition, authors of note, the publications that most often broach the topic of interest and its respective impacts, and the keywords that appear most frequently in the works sampled (GIL, 1999).
In concerns to the classification of this work, it is categorized as a theoretical illustration as it seeks to consolidate information on performance measurement in a determined field (in this case, airports), which guided the steps and procedures carried out during research (ALAVI & CARLSON, 1992).
An inductive approach to logical reasoning was applied, given the purpose of creating new knowledge in a given area, one on which the authors did not possess existing conclusions and set out to find them (IUDÍCIBUS, 2004). Said knowledge is built by way of the selection of the bibliographic portfolio, the identification of the articles most adherent to the authors´ preconceptions and, also, the determination of that portfolio´s most prominent articles, journals, authors, and keywords.
The data collected were both primary and secondary in nature. The utilization of primary data is characterized by the particular framing established by the authors over the course of the selection of the works that compose the bibliographic portfolio. The secondary data taken into consideration were collected from within the results of analyses of those same articles making up the bibliographic portfolio and their respective bibliographies (RICHARDSON, 1999).
In terms of the approach taken to address the research problem, this work is regarded as a mixed qualitative-qualitative study. Qualitative, owing to the process of selecting articles that make up the bibliographic portfolio, contributing to the creation of knowledge on the topic on part of the researcher. Quantitative, resulting from the collection and examination of quantitative data furnished by bibliometrics (RICARDSON, 1999).
Due to the overall intention of generating knowledge for eventual application towards, and the solution of, specific problems, gathering data via planned procedures and analyzing them in accordance with structured methodologies, the outcome of this work is demonstrated as being applied results.
Since it was carried out through an analysis of scientific publications, with several distinct authors of note in the field –their respective works accessed in the Portal CAPES online databases- adding to the sample, the present research is categorized as bibliographic in terms of its technical procedures (GIL, 1999; SÁ-SILVA et al., 2009).
In order to construct a mapping of the state of the art, the Knowledge Development Process – Constructivist (ProKnow-C) research instrument was employed (CHAVES et al., 2013; ENSSLIN et al., 2010; ENSSLIN et al., 2012). The ProKnow-C process is made up for four stages: i) the formation of the bibliographic portfolio that provides for later literature review; ii) a bibliometric analysis of the bibliographic portfolio; iii) a systemic analysis of the bibliographic portfolio; and iv) the determination of the research objectives. In this investigation, use was made of the two former steps, seeking to map the topic of the research.
The assembly of a portfolio of scholarly articles allows for the selection of a Bibliographic Portfolio (BP), itself composed of those articles considered most relevant to the field of study related to the research topic, in accordance with the authors´ estimation of such and as represented by their predetermined boundaries (ENSSLIN et al., 2013). The BP selection is carried out in two stages: a) the gathering of scholarly articles in databases, yielding the bulk collection of articles; and b) the filtering of those articles, based on their relevance to the research topic, and c) a test for representativeness, based on an analysis of the references included in the selected articles. The results of the selection of the article portfolio is the collection of articles deemed both relevant in the opinion of the researcher and associated with the research topic. This collection is then designated the bibliographic portfolio (ENSSLIN et al., 2010; AFONSO et al., 2011; BORTOLUZZI et al., 2011; LACERDA, ENSLINN, ENSLINN, 2012).
So as to compile the bulk collection of articles, the thematic axes were determined, in accordance with the judgment of the authors (TASCA et al, 2010). This work incorporates two thematic axes: a) Performance Measurement, which is the topic central to its research, and b) Airports, in terms of its applications to the first axis.
The bulk collection of articles process is composed of the following:
Upon filtering the bulk collection of articles, 324 publications were analyzed in concerns to the following criteria: a) repeated articles; b) compatibility between the articles´ titles and the research topic; c) scientifically-recognized articles; d) the congruency of each article's abstract with the research topic; and e) the research topic's inclusion or appearance in the body text of the article.
The articles gathered from the consulted databases were imported using Endnote library software. Following this step, 43 of the publications were discovered not to be scholarly articles in nature. Resulting from their exclusion, 281 articles remained. Upon subsequent examination for redundancy, 101 repeated articles were removed from the collection, leaving 180 in the bulk collection of articles.
While verifying for compatibility between the articles´ titles and the topic researched, a great many among the bulk collection were identified as being outside of the scope of this work. As such, 94 non-repeated articles with titles related to the research topic remained, which were then checked for scientific recognition in the online Google Scholar tool. For the purposes of this analysis, an article's scientific recognition is understood as the number of times it is cited, as per the results of a search in Google Scholar. At this stage, the articles were divided into two groups:
Among the first group, 21 articles were selected, to which 80% of the total number of citations corresponded, with the cutoff point being a minimum of 25 citations. These 21 articles were submitted to an analysis as to the congruency of their abstracts with the research topic. In this way, 19 non-repeated articles remained, each of them categorized by scientific recognition, and their titles and abstracts deemed relevant to the research topic. These articles went on to make up Vault A. For the next step, the authors of the articles making up Vault A will be evaluated; this group of authors comprises the Selected Authors grouping.
In relation to Vault P, itself composed of 73 articles, the same articles were resubmitted to the search tool to evaluate their potential for scientific recognition. Firstly, it was shown that the publication period (given that searches were carried out only within relatively recent publications) might deter the accumulation of the set minimum number of citations for the article to meet the criteria. In this case, only articles published as of 2012 are deemed recent, for the purposes of the study.
Among the non-recent articles, the authors of the same were picked out for comparison with those included in the Selected Authors. In the event that an author falling under the Selected Authors grouping had also a non-recent article, the latter was evaluated for the congruency of their abstract with the research topic. Analysis of Vault P found 31 articles considered recent and another 11 that are the work of a member of the Selected Authors grouping. Upon analysis of the abstracts of these 42 articles, five were selected for said congruency, which then went on to make up Vault B. Vault C was created by pooling Vaults A and B, itself composed of 24 non-repeated, scientifically-recognized articles with relevant titles and abstracts.
Successively, those 24 selected articles were analyzed, seeking to establish a relationship between their body text and the research topic. Of those same 24, just one was filtered out for lack of relevance, with the remaining 23 going on to be listed in the Primary Portfolio.
With the goal of testing the scope of the 23 works comprising the Primary Portfolio, each was subjected to a test for representation. Upon analysis of the bibliographies of each of the 23 articles, 190 articles were revealed, each of which was entered into Google Scholar so to identify each one´s number of citations; five were found to encompass 30% of the total of citations. All five were available in full-text in the Portal CAPES service, and just one was a repeat of the 23 selected previously. The four remaining works were each read in their entirety, yielding three of thematic significance, which were then added to the 23 articles composing the bibliographic portfolio, itself now in its final version.
The filtration process ultimately resulted in a bibliographic portfolio made up of 26 articles (see Appendix A).
An analysis of the characteristic of the articles that comprise the bibliographic portfolio concerning Performance Measurement within the field of Airports, in terms of the selection of the principal works, authors, journals, and keywords in that area of study, is presented here.
Bibliometric analysis consists of the application of mathematical and statistical methods to a determined collection of articles, to manage information and scientific knowledge in a research field (AFONSO et al., 2011; ENSSLIN et al., 2012). Towards these ends, bibliometric analysis was carried out on the bibliographic portfolio in the following four stages: a) evaluation of the each journal´s degree of relevance; b) verification of the scientific recognition of each article; c) estimation of each author´s respective degree of relevance; and d) determination of the keywords most frequently used. For the first three of these stages, analyses were carried out in the following order: a) bibliometric analysis of the articles comprising the bibliographic portfolio; b) bibliometric analysis of the articles contained in each one´s bibliography; and c) bibliometric analysis of the group made up of both the articles and the works that they cite (hereafter "reference articles").
It bears mentioning that, for the purposes of bibliometric analysis, the total sample of data to be analyzed breaks down thusly: 26 articles making up the bibliographic portfolio, and 661 reference articles, classified as journal articles, displayed in reference sections of each of the former.
Evaluation of each journal´s degree of relevance: the initial analysis sought to identify the journal in which the greatest number of articles included in the bibliographic portfolio was published. Thirteen different journals were found, with the Journal of Air Transport Management containing six of the works published (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Relevance of Articles Composing the Bibliographic Portfolio. Source: data provided by the authors (2014).
The ensuing analysis demonstrated which journals contain the greatest number of articles among those cited in the bibliographic portfolio's reference articles. Works that were cited in articles making up the bibliographic portfolio were published in a total 185 different journals, and of those, the Journal of Air Transport Management stands out, with 31 articles, followed by the European Journal of Operational Research, with 28 articles (Figure 2).
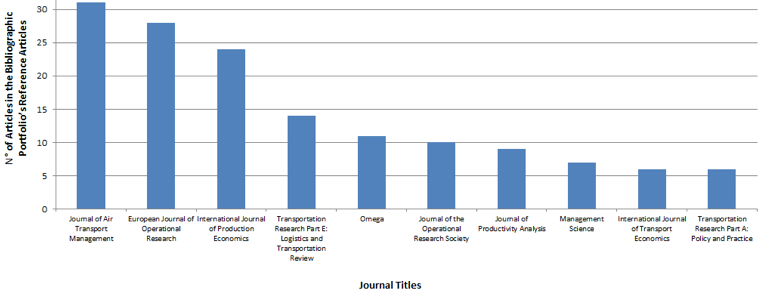
Figure 2. : Relevance of Journals included in the Bibliographic Portfolio Reference Articles. Source: data provided by the authors (2014).
The third analysis compares the relevance of the journals containing the articles that make up the bibliographic portfolio with that of the journals in which its reference articles are published, highlighting that: a) the Journal of Air Transport Management stands out in both the portfolio and the reference articles; b) the International Journal of Production Economics stands out in the references of the bibliographic portfolio; c) Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review stands out in the Bibliographic Portfolio; and d) among the journals which appeared in both the portfolio and reference articles, the following stand out: Omega and Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice.
The noted Journal of Air Transport Management (JATM) sets out to address, through high quality research articles and authoritative commentary, the major economic, management, and policy issues facing the air transport industry today. It offers practitioners and academics an international and dynamic forum for analysis and discussion of these issues, linking research and practice and stimulating interaction between the two. The refereed papers in the journal cover all the major sectors of the industry (airlines, airports, air traffic management) as well as related areas such as tourism management and logistics. Papers are blind reviewed, normally by two referees, chosen for their specialist knowledge. The journal provides independent, original and rigorous analysis in the areas of: Policy, regulation and law; Strategy; Operations, Marketing; Economics and finance, and Sustainability. Papers are welcomed covering key industry developments and trends, such as changes in government thinking towards air transport; evolving competitive environments and new industry structures; emerging and maturing markets and changing customer needs; sustainability and security challenges; and industry innovation and technological developments (Journal of Air Transport Management, 2014).
Determination of each article´s degree of scientific recognition: the Google Scholar search tool allows for the determination of the exact number of times the articles comprising the bibliographic portfolio are cited in other works, as well as their references, shedding light on their scientific recognition.
In the first analysis, upon rating the scientific recognition of the articles comprising the bibliographic portfolio, these articles were noted: "Analysis of the operational efficiency of major airports in the United States", by Sarkis, J., with 236 citations; "Measuring airport quality from the airlines' viewpoint: An application of data envelopment analysis", by Adler & Berechman; and "Inefficiencies and scale economies of Europe an airport operations", by Pels, Nijkamp & Rietveld, each with 190 citations.
The second analysis sought to identify the scientific recognition of the articles included in the bibliographic portfolio by way of the references cited in each of them. At this point, "Benchmarking airports from a managerial perspective" by Adler, Liebert e Yazhemsky, with 12 citations in the BP, and "Analysis of the operational efficiency of major airports in the United States" by Sarkis, J., with 11 citations in the BP, stood out.
The third analysis compares the number of citations of each of the articles comprising the bibliographic portfolio with the number of citations of the most-cited author within the portfolio´s reference articles, as per Google Scholar. It was shown that: a) one article in the bibliographic portfolio stands out, by the authors Feng & Wang (2000); and b) four of the articles that stand out in the bibliographic portfolio are the work of authors of note in the reference articles, being: Sarkis (2000); Pels, Nijkamp & Rietveld (2003); Adler & Berechman (2001) and, Pels, Nijkamp & Rietveld (2001).; and, c) the studies Sarkis & Talluri (2004); Barros & Dieke (2007); Francis, Humphreys & Fry (2002); Humphreys & Francis (2002) and Adler, Liebert & Yazhemsky (2013) are the work of authors of note in the reference articles.
Determining each authors´ degree of relevance: the first analysis was carried out so as to highlight the authors of greatest relevance among the 49 whose works are included in the bibliographic portfolio. The authors Lozano, S. and Gutiérrez, E. stand out with three articles each included in the Bibliographic Portfolio.
The second analysis seeks to identify which authors of the 512 listed in the bibliographic portfolio reference articles are of most relevance. As such, Cooper, W. W. met that criteria, with 27 published articles (Figure 3).

Figure 3. Prevalent Authors in the Bibliographic Portfolio's References. Source: prepared by the authors (2014)
The third analysis presents the authors of greatest prevalence in the portfolio and its references. From this, the following was shown: a) two authors stand out (Lozano, S. and Gutiérrez, E.) with three articles contained in the Bibliographic Portfolio each, followed by Feng, C. M.; Rietveld, P.; Sarkis, J.; Adler, N.; Nijkamp, P.; Pels, E.; Wang, R. T.; Francis, G.; Humphreys, I. and Zografos, K. G., each with two articles in the same; and b) among these, Sarkis, J. (author of 22 articles contained in the reference articles), followed by Nijkamp, P.; Rietveld, P.; Humphreys, I. and Pels, E., each with 20 articles in the same.
The fourth analysis compares the numbers of articles written by each of the authors who appear in the bibliographic portfolio with that of each of the authors whose works are cited in its reference articles. The following was determined, as shown below in Figure 4: a) Lozano, S. and Gutiérrez, E. are the standout authors in the Bibliographic Portfolio; b) there are no authors that stand out in both the Bibliographic Portfolio and the reference articles; and c) Sarkis, J.; Rietveld, P.; Adler, N. and Barros, C. P. are the authors that stand out in the reference articles.

Figure 4: Authors of Note in the Bibliographic Portfolio. Source: prepared by the authors (2014).
Note: a) Lozano, S.; b) Gutiérrez, E.; c) Sarkis, J.; c) Humphreys, I.; d) Rietveld, P.; d) Nijkamp, P.; d) Pels, E.; e) Adler, N.; f) Francis, G.; g) Zografos, K. G.; h) Feng, C. M.; h) Wang, R. T.; i) Barros, C. P.; j) Yu, M. M.; k) Fernandes, E.; k) Pacheco, R. R.; k) Oum, T. H.; l) Yu, C.; m) Berechman, J.; n) Vasigh, B.; n) Talluri, S.; o) Fry, J.; o) Dieke, P. U. C.; p) Yeh, C. H.; q) Dresner, M.; r) Fu, X.; s) Lin, L. C.; t) Windle, R. J.; t) Hong, C. H.; t) Haghani, A.; t) Pathomsiri, S.; t) Kuo, Y. L.; u) Yazhemsky, E.; u) Mancuso, P.; u) Gitto, S.; v) Moreno, P.; v) Hartmann, E.; v) Jahns, C.; v) Manataki, I. E.; v) Schmidberger, S.; v) Gorjidooz, J.; v) Low, J. M. W.; v) Tang, L. C.; v) Madas, M. A.; v) Bals, L; x) Lam, S. W.; x) Ho, C. T.; x) Liebert, V.; x) Yang, Y. K.
Analysis of the Impact Factor of the Journals Contained in the Bibliographic Portfolio: The Journal Impact Factor, as presented by Journal Citation Reports (JCR), is a measurement that reflects the average number of citations of scientific articles published in a determined journal (Web of Knowledge, 2012). Also, Scientific Journal Rankings (SJR), developed by SCImago Journal and Country Rank, presents a measure of scientific publications' visibility (data available as of 1996), which is to say, it gauges the average "scientific influence" of articles published in a given journal (SCImago, 2007).
As such, the first analysis sought to determine the relevance of the research topic within the 13 journals comprising the bibliographic portfolio. The following were shown as having the greatest impact factor: the "Journal of Operations Management" with a JCR of 4.400; and the "International Journal of Production Economics" for its corresponding JCR of 2.081.
The aim of the second analysis was to determine the SJR indicator of the articles composing the bibliographic portfolio, or, rather, to rank the scientific influence of the research topic. The "Journal of Operations Management" stands out for having the greatest impact factor (SJR: 4.997), followed by the journals "Omega" with an SJR of 3.162 and "Computers & Operations Research", with an SJR of 3.136.
Determination of the most-used keywords: the goal of this analysis is to determine the keywords that are most apparent and prevalent in the bibliographic portfolio. The study identified 66 keywords utilized a total of 99 times in the bibliographic portfolio. Of that total, nine were used two or more times, showing the most-used among them to being "Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA)", appearing in the Bibliographic Portfolio in 13 instances, and the keyword "Airport(s)", with ten. At this stage, the comparison of the keywords employed towards the research topic to those found in the Bibliographic Portfolio was carried out.

Figure 5. Keywords Most Prevalent in the Bibliographic Portfolio. Source: prepared by the authors (2014).
In Figure 5, the keywords that were employed in the research topic, and which later appeared in the bibliographic portfolio, are indicated within the dotted lines. Of the six keywords employed in the research topic, three appeared two or more times in the bibliographic portfolio.
Bibliometrics is a quantitative and statistical technique that allows for the measurement of the production and dissemination of knowledge, acting alongside the development of various scientific fields, as well as the standards and practices concerning authorship, publication, and the utilization of results from research (OKUBO, 1997; ARAÚJO, 2006). An evaluation of a scientific publication, given its chief importance vis-à-vis the national and international scientific community´s recognition of researchers, is done by way of the application of diverse bibliometric indicators (SANCHO, 2002).
Though it was initially applied for the purposes of evaluating books (number of editions and copies in print, word counts, shelf space occupied in libraries by a given book, book industry statistics), it was soon employed in the study of other formats, such as journal articles and other types of documents, and later in concerns to individual authors´ production as well as citation analysis (ARAÚJO, 2006).
In light of this, the results generated concerning the mapping of the state of the art of the research topic (Airport Performance Measurement) allowed the conditions necessary the execution of a bibliometric analysis. The coupled use of the two theoretical axes, Performance Measurement and Airports, provided the foundation for the research -characterized as exploratory-, given its goal of constructing new knowledge in this field.
By way of the comprehensive analysis of the articles considered in the study, and to tie the results of the study to the research topic, the authors put forth the following considerations:
The rapid growth of international air passenger traffic across the globe has resulted in international airports that employ management practices steered toward the customer. To measure the management in place in an airport and improve passenger satisfaction, a mechanism that evaluates the quality of service in relation to other airports is necessary. Along these lines, to gain an understanding of passenger needs, the level of quality of airport services must take into account the perceptions and opinions of the user, in terms of specific attributes and characteristics (YEH & KUO, 2003). The implementation of a given operational concept may bring on efficiency gains in one facility, while proving detrimental to another, thusly damaging the overall performance of the airport system (MANATAKI & ZOGRAFOS, 2009). Normally, inputs, in this context, include all of the factors dealing with production (labor and capital), or airport physical infrastructure, while outputs are the volume of aircraft operations, whether they be passenger or cargo in nature. Efficient airports are those that maximize their results with the supplies provided to them. The pursuit of efficiency, however, strives to increase the number of flights, as well as the number of passengers and cargo contained in these. In other words, as per the majority of studies on efficiency in the related literature, these results are pushed as much as possible within the possibilities of production as shown in existing data (LOZANO & GUTIÉRREZ, 2011).
Airport efficiency has been a central concern in the realm of cost control for reasons including the following: the monopoly power enjoyed by many airports; shifts in ownership structures; higher competition between airlines and airports; the goal, of certain governments, of growing a hub of air travel in their nation and by extension logistical center. It is believed that by way of reducing costs and prices through increasing labor and productivity, a given airport might be able to achieve greater operating efficiency and its competitiveness on an international level. The precise evaluation of production efficiency has been, as such, one of the most pertinent questions in the unending search for global competitiveness in the international aviation industry (LAM LOW & TANG, 2009). In their study, the authors of Wang et al. (2004) state that airports are evaluated in terms of their labor force (number of employees), terminals (floor area of the terminal building, number of boarding gates, and number of check-in counters), and aviation facilities (apron size, number of parking spaces, and traffic volume) and revenues (total revenue and non-aviation income). The airlines cover transport-based outputs (takeoffs and landings, tons of cargo, peak-hour takeoffs and landings, number of routes) while passenger-related considerations include the total number of people served (passengers) and the number served during peak hours. Aviation and fire services deal with police and firefighters (number of firefighters stationed at the facility), and the control of aviation activities (number of air traffic controllers). Complex and dynamic organizations such as international airports pose a challenge in developing an adequate performance measurement system. The constant interaction of airport-related parties, such as passengers, airlines, baggage handling and ground transportation companies, as well as the interests of the regional and national economy, make the development of performance measurement systems a complicated matter. Performance measurement is a critical managerial activity, whether it be at the operational or system-wide level of airport administration (HUMPHREYS & FRANCIS, 2002).
The majority of airport managers set goals to maximize aircraft movement, flow of passengers and quantity of cargo transported. However, each of these three outputs are fundamentally related to airport capacity. As these outputs rise to a certain level, congestion may take place, resulting in delays. It is beneficial to the administration to either reduce or maintain these at an acceptable level, as this, by extension, preserves a certain quality of service. As a result, delays are not considered an undesirable output of airport operations (PATHOMSIRI et al., 2008). The raw productivity-related numbers are affected by a great many factors, some of which are beyond the control of airport administration; the true level of efficiency achieved is not always reflected in the raw data. As such, this type of data should not be used to gauge performance nor compare efficiency between two or more airports. Along these lines, in their study, Oum, Yu, and Fu (2003) computed "residual" indexes, removing uncontrollable factors for the purpose of comparing real productive efficiency between airports. These uncontrollable factors were considered even in terms of the ownership structure, airport size, average size of aircraft using the airport, and percentage of international passenger traffic (OUM, YU & FU, 2003).
Studies on the measurement and improvement of airport operations performance bear important implications for a variety of parties interested in airports. Said practice aids air transportation companies in the identification and selection of more-efficient airports at which they might base their operations. At the same time, local governments benefit from efficient airports as they attract businesses as customers. The federal government is also assisted in its decision-making process regarding the optimal allocation of resources in airport-improvement programs, as well as in the evaluation of said programs' efficiency, for comparison is a path that managers must follow to guarantee competitiveness (SARKIS & TALLURI, 2004). According to Zografos & Madas (2006), "the decision-making and implementation process for dealing with the challenges of contemporary airport planning necessitates the development and deployment of decision support tools."
Based off the research completed throughout the development of this paper, it can be stated that the work reached its primary objective, which was to prepare a mapping of publications on the topic of Airport Performance Measurement, and, based on this, compile a bibliographic portfolio of the most relevant and applicable works, as per the opinion of the authors of the current study.
On the one hand is Performance Measurement, which seeks to support decision-making and build knowledge in relation to management methods in effect within a given field. Along with that, besides striving for improvements (should they be necessary), comparisons can be made to other parties participating in an organizational process, allowing for criteria on which future actions might be based. On the other, the growing need for airports to remain competitive is becoming more and more apparent, while they, at the same time, aim to maintain positive and satisfactory results. This, given that they are faced with emerging competitors and other factors in their operating environment. One of the ways to know if that result is being reached is performance measurement, which includes, for example, passenger satisfaction as a key indicator of performance within airport operation. The process of evaluating airport services demands continuous monitoring to maintain high levels of service quality. In considering the two axes that steered the current work, there exists the overlying challenge facing managers and professionals working in this large field: incorporating the two concepts while working towards delivering results, which requires a positive measurement of performance and, more and more, an effort for continuous improvements to the airport system on the whole. This philosophy stands to benefit not only users of that system, but also stockholders and facility supervisors.
The results obtained in this bibliometric study, alongside the larger goal of contributing to scientific progress, can guide readers interested in the field of Airport Performance Measurement through its identification of databases, keywords, journals, and authors of note and relevance to the topic examined. Chief among the findings are the following: the academic journals "Journal of Air Transport Management" and "Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review"; the scholarly articles "Analysis of the operational efficiency of major airports in the United States", "Measuring airport quality from the airlines' view point: an application of data envelopment analysis" and "Inefficiencies and scale economies of European airport operations"; the keywords "Data envelopment analysis (DEA)", "Airport(s)", "Benchmarking", "Performance evaluation", "Productivity" and "Efficiency"; and the most-cited authors Sarkis, J.; Adler, N.; Berechman, J.; Pels, E.; Nijkamp, P. and Rietveld, P.
To better define the scope of the current work, the limitations set by the authors bear mentioning as they, in truth, helped to shape the results obtained: a) the sources of data were restricted to the Portal CAPES database; b) only works published between January 2000 and May 2014 were analyzed; c) only articles that are theoretical-empirical in nature were considered; d) the determination of the relevance and applicability of the content of each article to the topic Airport Performance Measurement was made by the authors.
As a suggestion for further research, use of the ProKnow-C instrument is recommended for effective organization of information and subsequent development of advanced contextualization and analysis constructs.
Gratitude goes to the authors of Ensslin et al. (2010) and Ensslin et al. (2012), who proposed the research instrument "Knowledge Development Process – Constructivist (ProknowC)", which went on to contribute to the systematization of bibliometric analyses, as well as other types of academic investigation.
ADLER, Nicole; LIEBERT, Vanessa; YAZHEMSKY, Ekaterina. Benchmarking airports from a managerial perspective. Omega, v. 41, n. 2, p. 442-458, 2013.
AFONSO, M. H. F.; SOUZA, J. V.; ENSSLIN, S. R.; ENSSLIN, L. Como Construir Conhecimento Sobre o Tema de Pesquisa? Aplicação do Processo ProKnow-C na Busca de Literatura Sobre Avaliação do Desenvolvimento Sustentável. Revista de Gestão Social e Ambiental, v. 5, n. 2, p. 47-62, May/Aug, 2011.
ALAVI, M.; CARLSON, P. A Review of MIS Research and Disciplinary Development. Journal of Management Information Systems, v. 8, n. 4, p. 45-62, 1992.
ARAÚJO, Carlos Alberto – Bibliometria: evolução histórica e questões atuais. Em Questão. Porto Alegre. [Em linha]. Vol.12, nº 1 (2006), p.11-32. Available online: www: <http://revistas.univerciencia.org/index.php/revistaemquestao/article/viewFile/3707/3495>. Cited: May 11, 2014.
BORTOLUZZI, S. C.; ENSSLIN, S. R.; ENSSLIN, L.; VALMORBIDA, S. M. I. Avaliação de Desempenho em Redes de Pequenas e Médias Empresas: Estado da arte para as delimitações postas pelo pesquisador. Revista Eletrônica de Estratégia & Negócios, v. 4, n. 2, p-202, 2011.
CHAVES, L. C.; ENSSLIN, L.; ENSSLIN, S. R.; VALMORBIDA, S. M.; ROSA, F. S. Sistemas de apoio à decisão: mapeamento e análise de conteúdo. Revista Eletrônica de Ciência Administrativa, v. 12, n. 1, 2013.
ENSSLIN, L.; GIFFHORN, E.; ENSSLIN, S. R.; PETRI, S. M.; VIANNA, W. B. Avaliação do desempenho de empresas terceirizadas com o uso da metodologia multicritério de apoio à decisão-construtivista. Pesquisa Operacional, v.30, n.1, 125-152, 2010.
ENSSLIN, Leonardo; ENSSLIN, Sandra Rolim; PACHECO, Giovanni Cardoso. Um estudo sobre segurança em estádios de futebol baseado na análise bibliométrica da literatura internacional. Perspectivas em Ciência da Informação, v. 17, n. 2, p. 71-91, 2012.
ENSSLIN, S. R.; ENSSLIN, L.; LACERDA, R. T. O.; MATOS, L. S. Evidenciação do estado da arte do tema avaliação do desempenho na regulação de serviços públicos segundo a percepção dos pesquisadores. Gestão Pública: Práticas e Desafios, v. 4, n. 7, 2013.
FENG, Cheng-Min; WANG, Rong-Tsu. Performance evaluation for airlines including the consideration of financial ratios. Journal of Air Transport Management, v. 6, n. 3, p. 133-142, 2000.
GIL, A. C. Métodos e Técnicas de Pesquisa Social. São Paulo: Atlas, 1999.
GITTO, Simone; MANCUSO, Paolo. Bootstrapping the Malmquist indexes for Italian airports. International Journal of Production Economics, v. 135, n. 1, p. 403-411, 2012.
HUMPHREYS, Ian; FRANCIS, Graham. Performance measurement: a review of airports. International Journal of Transport Management, v. 1, n. 2, p. 79-85, 2002.
IUDICIBUS, S. Teoria da contabilidade. São Paulo: Atlas, 2004.
JATM - Journal of Air Transport Management. Available online: www: <http://www.journals.elsevier.com/journal-of-air-transport-management>. Cited: June 09, 2014.
LACERDA, R. T. O.; ENSSLIN, L.; ENSSLIN, S. R. Uma análise bibliométrica da literatura sobre estratégia e avaliação de desempenho. Gestão&Produção, v 19, n.1, 2012.
LAM, Shao Wei; LOW, Joyce MW; TANG, Loon Ching. Operational efficiencies across Asia Pacific airports. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, v. 45, n. 4, p. 654-665, 2009.
LOZANO, Sebastián; GUTIÉRREZ, Ester. Slacks-based measure of efficiency of airports with airplanes delays as undesirable outputs. Computers & Operations Research, v. 38, n. 1, p. 131-139, 2011.
MANATAKI, Ioanna E.; ZOGRAFOS, Konstantinos G. A generic system dynamics based tool for airport terminal performance analysis. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, v. 17, n. 4, p. 428-443, 2009.
OKUBO, Yoshiko – Bibliometric indicators and analysis of research systems: methods and examples. OECD Science, Technology and Industry Working Papers. [Emlinha].Nº 1 (1997). Available online: <www: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/208277770603>/ Cited: May 11, 2014.
OUM, Tae Hoon; YU, Chunyan; FU, Xiaowen. A comparative analysis of productivity performance of the world's major airports: summary report of the ATRS global airport benchmarking research report - 2002. Journal of Air Transport Management, v. 9, n. 5, p. 285-297, 2003.
PATHOMSIRI, S.; HAGHANI, A.; DRESNER, M.; WINDLE, R. J. Impact of undesirable outputs on the productivity of US airports. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, v. 44, n. 2, p. 235-259, 2008.
ROSA, F. S., ENSSLIN, S. R., ENSSLIN, L., LUNKES, R. J. Gestão da Evidenciação Ambiental: Um Estudo Sobre as Potencialidades e Oportunidades do Tema. Engenharia Sanitária e Ambiental, v. 16, n. 2, p. 157-166, Apr./Jun, 2011.
RICHARDSON, R. J. Pesquisa Social: Métodos e Técnicas. São Paulo: Atlas, 1999.
SÁ-SILVA, J. R.; ALMEIDA, C. D.; GUINDANI, J. F. Pesquisa Documental: Pistas Teóricas e Metodológicas. Revista Brasileira de História & Ciências Sociais, n. 1, 2009.
SANCHO, Rosa – Indicadores bibliométricos utilizados enlaevaluación de laciencia y la tecnologia: revisión bibliográfica. In Inteligencia competitiva: documentos de lecture. [Online]. Barcelona: Fundación per a la Universitat Oberta de Catalunya, 2002, p.77-106. Available: <www:http://www.tramasoft.com/documentos/I+D+i/UND2/L ecturas%20complementarias/79059.Inteligencia%2520Competitiva.Lecturas.pdf#page=77>. Accessed: May 11, 2014.
SARKIS, Joseph; TALLURI, Srinivas. Performance based clustering for benchmarking of US airports. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, v. 38, n. 5, p. 329-346, 2004.
SCIMAGO. SJR: Scimago journal & country rank. 2007. Available online: <http://www.scimagojr.com/>. Accessed: May 11, 2014.
TASCA, J. E.; ENSSLIN, L.; ENSSLIN, S. R.; ALVES; M. B. M. An Approach for Selecting a Theoretical Framework For The Evaluation Of Training Programs. Journal of European Industrial Training, v. 34, n. 7, p. 631-655, 2010.
WANG, Rong-Tsu et al. A comparative analysis of the operational performance of Taiwan's major airports. Journal of Air Transport Management, v. 10, n. 5, p. 353-360, 2004.
WEB OF KNOWLEDGE. Journal citation reports: information for new users. 2012. Available online: <http://admin-apps. webofknowledge.com/JCR/help/h_info.htm#information>. Accessed: May 11, 2014.
YEH, Chung-Hsing; KUO, Yu-Liang. Evaluating passenger services of Asia-Pacific international airports. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, v. 39, n. 1, p. 35-48, 2003.
ZOGRAFOS, Konstantinos G.; MADAS, Michael A. Development and demonstration of an integrated decision support system for airport performance analysis. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, v. 14, n. 1, p. 1-17, 2006.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC PORTFOLIO USED IN RESEARCH |
ADLER, Nicole; BERECHMAN, Joseph. Measuring airport quality from the airlines' viewpoint: an application of data envelopment analysis. Transport Policy, v. 8, n. 3, p. 171-181, 2001. |
ADLER, Nicole; LIEBERT, Vanessa; YAZHEMSKY, Ekaterina. Benchmarking airports from a managerial perspective. Omega, v. 41, n. 2, p. 442-458, 2013. |
FENG, Cheng-Min; WANG, Rong-Tsu. Performance evaluation for airlines including the consideration of financial ratios. Journal of Air Transport Management, v. 6, n. 3, p. 133-142, 2000. |
FERNANDES, Elton; PACHECO, R. R. Efficient use of airport capacity. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, v. 36, n. 3, p. 225-238, 2002. |
FRANCIS, Graham; HUMPHREYS, Ian; FRY, Jackie. The benchmarking of airport performance. Journal of Air Transport Management, v. 8, n. 4, p. 239-247, 2002. |
GITTO, Simone; MANCUSO, Paolo. Bootstrapping the Malmquist indexes for Italian airports. International Journal of Production Economics, v. 135, n. 1, p. 403-411, 2012. |
HUMPHREYS, Ian; FRANCIS, Graham. Performance measurement: a review of airports. International Journal of Transport Management, v. 1, n. 2, p. 79-85, 2002. |
LAM, Shao Wei; LOW, Joyce MW; TANG, Loon Ching. Operational efficiencies across Asia Pacific airports. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, v. 45, n. 4, p. 654-665, 2009. |
LIN, L. C.; HONG, C. H. Operational performance evaluation of international major airports: An application of data envelopment analysis. Journal of Air Transport Management, v. 12, n. 6, p. 342-351, 2006. |
LOZANO, Sebastián; GUTIÉRREZ, Ester. Efficiency analysis and target setting of Spanish airports. Networks and Spatial Economics, v. 11, n. 1, p. 139-157, 2011. |
LOZANO, Sebastián; GUTIÉRREZ, Ester. Slacks-based measure of efficiency of airports with airplanes delays as undesirable outputs. Computers& Operations Research, v. 38, n. 1, p. 131-139, 2011. |
LOZANO, Sebastián; GUTIÉRREZ, Ester; MORENO, Plácido. Network DEA approach to airports performance assessment considering undesirable outputs. Applied Mathematical Modelling, v. 37, n. 4, p. 1665-1676, 2013. |
MANATAKI, Ioanna E.; ZOGRAFOS, Konstantinos G. A generic system dynamics based tool for airport terminal performance analysis. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, v. 17, n. 4, p. 428-443, 2009. |
OUM, Tae Hoon; YU, Chunyan; FU, Xiaowen. A comparative analysis of productivity performance of the world's major airports: summary report of the ATRS global airport benchmarking research report—2002. Journal of Air Transport Management, v. 9, n. 5, p. 285-297, 2003. |
PATHOMSIRI, Somchai et al. Impact of undesirable outputs on the productivity of US airports. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, v. 44, n. 2, p. 235-259, 2008. |
PELS, Eric; NIJKAMP, Peter; RIETVELD, Piet. Relative efficiency of European airports. Transport Policy, v. 8, n. 3, p. 183-192, 2001. |
PELS, Eric; NIJKAMP, Peter; RIETVELD, Piet. Inefficiencies and scale economies of European airport operations. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, v. 39, n. 5, p. 341-361, 2003. |
PESTANA BARROS, Carlos; DIEKE, Peter UC. Performance evaluation of Italian airports: a data envelopment analysis. Journal of Air Transport Management, v. 13, n. 4, p. 184-191, 2007. |
SARKIS, Joseph. An analysis of the operational efficiency of major airports in the United States. Journal of Operations Management, v. 18, n. 3, p. 335-351, 2000. |
SARKIS, Joseph; TALLURI, Srinivas. Performance based clustering for benchmarking of US airports. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, v. 38, n. 5, p. 329-346, 2004. |
SCHMIDBERGER, Stephan et al. Ground handling services at European hub airports: development of a performance measurement system for benchmarking. International Journal of Production Economics, v. 117, n. 1, p. 104-116, 2009. |
VASIGH, Bijan; GORJIDOOZ, Javad. PRODUCTIVITY ANALYSIS OF PUBLIC AND PRIVATE AIRPORTS: A CAUSAL INVESTIGATION. Journal of Air Transportation, v. 11, n. 3, 2006. |
YEH, Chung-Hsing; KUO, Yu-Liang. Evaluating passenger services of Asia-Pacific international airports. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, v. 39, n. 1, p. 35-48, 2003. |
YU, Ming-Miin. Assessment of airport performance using the SBM-NDEA model. Omega, v. 38, n. 6, p. 440-452, 2010. |
ZOGRAFOS, Konstantinos G.; MADAS, Michael A. Development and demonstration of an integrated decision support system for airport performance analysis. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, v. 14, n. 1, p. 1-17, 2006. |
WANG, Rong-Tsu et al. A comparative analysis of the operational performance of Taiwan's major airports. Journal of Air Transport Management, v. 10, n. 5, p. 353-360, 2004. |
1. Doctorate Candidate in Production Engineering – Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC) (email: mauricioloos@hotmail.com).
2. PhD – Technical University of Madrid (UPM), and Professor at the Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC). (email: taboada@deps.ufsc.br).
3. Doctor in Production Engineering – Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC), and Professor at the Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC). (email: smpetri@gmail.com).
4. Master Student in Accounting – Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC). (email: l.matos@ufsc.br).